Before learning about different switchgear components, let us understand what is switchgear.
Read more on What is Switchgear and its features.
Important Switchgear Components
The following are some of the important components common to most of the circuit breakers:
- Bushings
- Circuit Breaker Contacts
- Instrument Transformers
- Bus-bars and conductors
Bushings of Switchgear
When a high voltage conductor passes through a metal sheet or frame which is at earth potential, the necessary insulation is provided in the form of the electrical bushing. It is one of the major switchgear components.
Function of Bushings
The use of bushing for a plain-break oil circuit breaker is shown in the figure. The high voltage conductor passes through the bushing made of some insulating material (e.g., porcelain, steatite).
Although there are several types of bushing (e.g., condenser type, oil-filled etc.), they perform the same function of insulating the conductor from the earthed tank.
Failure of Bushing
The failure of the bushing can occur in two ways.
- Firstly, the breakdown may be caused by puncture i.e., dielectric failure of the insulating material of the bushing.
- Secondly, the breakdown may occur in the form of a flash-over between the exposed conductor at either end of the bushing and the earthed metal.
Fig (ii) above illustrates these two possibilities. The bushings are so designed that flash-over takes place before they get punctured. It is because the puncture generally renders the bushing insulation unserviceable and incapable of withstanding the normal voltage.
On the other hand, a flash-over may result in comparatively harmless burning of the surface of the bushing which can then continue to give adequate service pending replacement.
Read full details of Bushings here : Electrical Bushings – Types, Purpose and Construction
Circuit Breaker Contacts
The circuit breaker contacts are another switchgear component which are required to carry normal as well as short-circuit current.
In carrying the normal current, it is desirable that the temperature should not rise above the specified limits and that there should be a low voltage drop at the point of contact.
In carrying breaking and making short-circuit currents, the chief effects to be dealt with are melting and vaporization by the heat of the arc and those due to electromagnetic forces.
Therefore, the design of contacts is of considerable importance for the satisfactory operation of the circuit breakers.
There are three types of circuit breaker contacts viz.
- Tulip type contacts
- Finger and wedge contacts
- Butt contacts
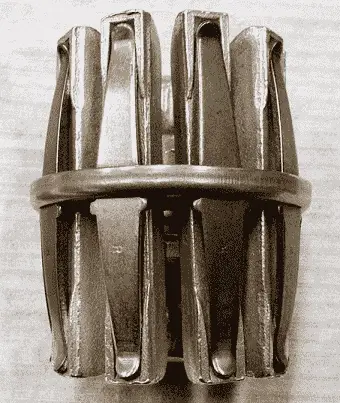
1) Tulip type contacts
It consists of moving contact which moves inside the fixed contacts. At contact separation, the arc is generally established between the tips of the fixed contacts and the tip of the moving contact.
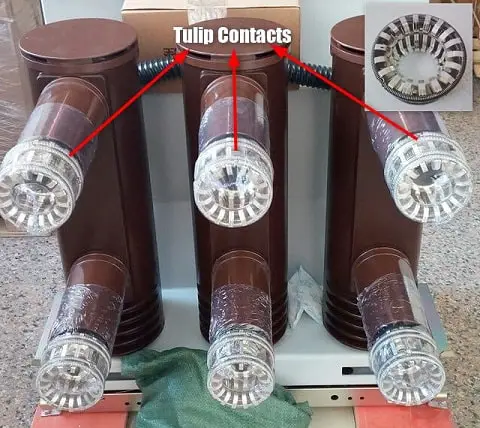
The advantage of this type of contact is that arcing is confined to the regions which are not in contact in the fully engaged position.
2) Finger and wedge contacts
3) Butt contacts
The butt type contact and is formed by the springs. It possesses two advantages.
- Firstly, the spring pressure is available to assist contact separation. This is useful in single-break oil circuit breakers and air-blast circuit breakers where relatively small “loop” forces are available to assist in opening.
- Secondly, there is no gripping force so that this type of contact is especially suitable for higher short circuit rating.
In modern vacuum interrupters, three contact designs dominate. The first is the butt contact, the second is the transverse magnetic field (TMF) contact, and the third is the axial magnetic field (AMF) contact.
Instrument Transformers
In a modern power system, the circuits operate at very high voltages and carry current of thousands of amperes. The measuring instruments and protective devices cannot work satisfactorily if mounted directly on the power lines. This difficulty is overcome by installing instrument transformers on the power lines.
The function of these instrument transformers is to transform voltages or currents in the power lines to values which are convenient for the operation of measuring instruments and relays.
There are two types of instrument transformers viz.
- Current transformer (C.T.)
- Potential transformer (P.T.)
Similarly, a potential transformer is connected with its primary in the power line. The secondary provides for the instruments and relays a voltage which is a known fraction of the line voltage.
Advantages of Instrument Transformers
- They isolate the measuring instruments and relays from high-voltage power circuits.
- The leads in the secondary circuits carry relatively small voltages and currents. This permits to use wires of smaller size with minimum insulation.
Bus-Bars and Conductors
The current-carrying members in a circuit breaker consist of fixed and moving contacts and the conductors connecting these to the points external to the breaker.
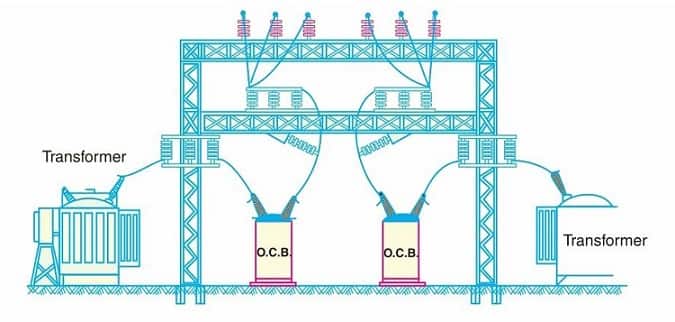
If the switchgear is of the outdoor type, these connections are connected directly to the overhead lines. In case of indoor switchgear, the incoming conductors to the circuit breaker are connected to the busbars.





