An analog instrument is one in which the output or display is a continuous function of time and bears a constant relation to its input. The analog instruments find extensive use in present-day applications although digital instruments are increasing in number and applications.
The areas of application which are common to both analog and digital instruments are fairly limited at present. Hence, it can safely be predicted that the analog instruments will remain in extensive use for a number of years and are not likely to be completely replaced by digital instruments for certain applications.
In this article you will learn different types of analog instruments and their classification based on different criteria.
Types of Analog Instruments
Different types of analog instruments (and digital instruments, for that matter) can be broadly categorized based on the quantity they measure.
For example, an instrument meant for measurement of current is classified as an ammeter while an instrument that measures voltage is classified as a voltmeter. In addition we have wattmeters, power factor meters, frequency meters, etc…
Types of Analog Instruments Based on Current Measured
Electrical instruments may also be classified according to the kind of current that can be measured by them. Electrical instruments may be classified as instruments for:
- Direct Current (DC)
- Alternating Current (AC)
- Direct and Alternating Current (DC/AC)
Instruments depend for their operation on one of the many effects produced by current and voltage and thus can be classified according to which of the effects is used for their working.
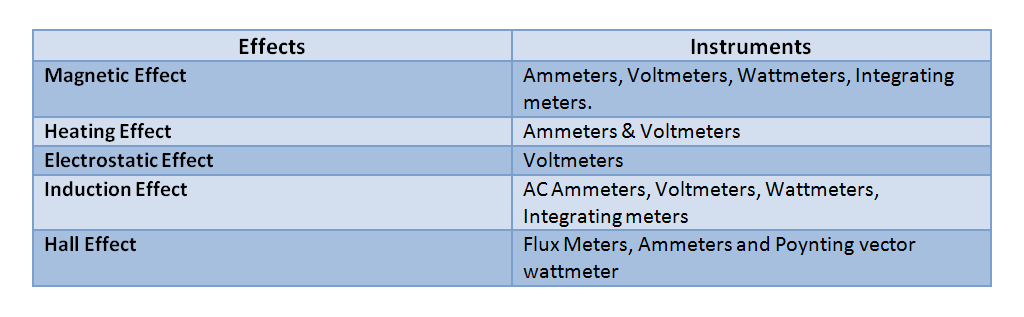
Types of Analog Instruments based on Function and Purpose
The analog instruments are also classified based on their function and purpose as :
- Indicating instruments
- Recording instruments
- Integrating instruments
1. Indicating Instruments
Indicating instruments are those instruments that indicate the magnitude of a quantity being measured. They generally make use of a dial and a pointer for this purpose. Ordinary voltmeters, ammeters, and wattmeters belong to this category.

The analog indicating instruments may be divided into two groups :
- Electromechanical instruments
- Electronic instruments
Electronic instruments are constructed by the addition of electronic circuits to electromagnetic indicators in order to increase the sensitivity and input impedance.
2. Recording Instruments
Recording Instruments give a continuous record of the quantity being measured over a specified period. In principle, these are indicating instruments but so arranged that a permanent continuous record of the indication is made on a chart or dial.
The variations of the quantity being measured are recorded by a pen (attached to the moving system of the instrument ; the moving system is operated by the quantity being measured) on a sheet of paper carried by it rotating drum.
For example, we may have a recording voltmeter in a substation which keeps record of the variations of supply voltage during the day.
Example: X-Y plotter, A potentiometric type of recorder used for monitoring temperature records the instantaneous temperatures on a strip chart recorder.
3. Integrating Instruments
Integrating Instruments totalize events over a specified period of time. The summation, which they give is the product of time and an electrical quantity.
Ampere hour meter and watt hour meters are examples of integrating instruments.

The integration (summation value) is generally given by a register consisting of a set of at pointers and dials.
Types of Analog Instruments Based on Measurement Method
The analog instruments may also be classified on the basis of method used for comparing the unknown quantity (measurand) with the unit of measurement. The two categories of instruments based upon this classification are:
- Direct Measuring Instruments
- Comparison Instruments
1. Direct Measuring Instruments
Direct measuring instruments convert the energy of the measurand directly into energy that actuates the instrument and the value of the unknown quantity is measured or displayed or recorded directly.
The examples of this class of instruments are ammeters, voltmeters, wattmeter and energy meters.
2. Comparison Instruments
Comparison instruments measure the unknown quantity by comparison with a standard.
Direct measuring instruments are the most commonly used in engineering practice because they are the most simple and inexpensive. Also their use makes the measurement possible in the shortest time
The examples of comparison type instruments are DC and AC bridges.
Comparison instruments are used in cases where a higher accuracy of measurement is required.
Note
Electrical instruments can be classified based on their accuracy class. The limits of intrinsic error in the measured quantity for instruments for various classes of accuracy are:
| Accuracy class | Limit of error (percent) |
|---|---|
| 02 | +0.2 |
| 05 | +0.5 |
| 10 | +1.0 |
| 15 | +1.5 |
| 2.5 | +2.5 |
| 5 | +5.0 |







Comments are closed.