In oil circuit breakers, some insulating oil (e.g., transformer oil) is used as an arc quenching medium.
Working Principle of Oil Circuit Breaker
When the contacts of the oil circuit breaker are opened under oil and an arc is struck between them. The heat of the arc evaporates the surrounding oil and dissociates it into a substantial volume of gaseous hydrogen at high pressure.
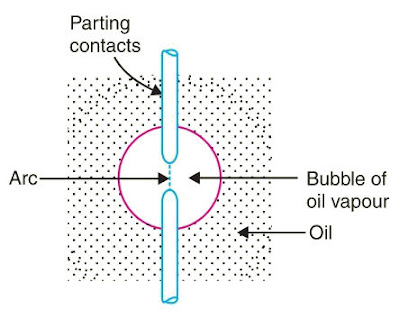 The hydrogen gas occupies a volume about one thousand times that of the oil decomposed. The oil is, therefore, pushed away from the arc and an expanding hydrogen gas bubble surrounds the arc region and adjacent portions of the contacts (See Figure).
The hydrogen gas occupies a volume about one thousand times that of the oil decomposed. The oil is, therefore, pushed away from the arc and an expanding hydrogen gas bubble surrounds the arc region and adjacent portions of the contacts (See Figure).
The arc extinction is facilitated mainly by two processes.
- Firstly, the hydrogen gas has high heat conductivity and cools the arc, thus aiding the de-ionization of the medium between the contacts.
- Secondly, the gas sets up turbulence in the oil and forces it into the space between contacts, thus eliminating the arcing products from the arc path.
The result is that arc is extinguished and circuit current interrupted.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Oil CB
|
Advantages
|
Disadvantages
|
|
1. It absorbs the arc energy to decompose the oil into gases which have excellent cooling properties.
2. It acts as an insulator and permits smaller clearance between live conductors and earthed components.
3. The surrounding oil presents the cooling surface in close proximity to the arc.
|
1. It is inflammable and there is a risk of a fire.
2. It may form an explosive mixture with air
3. The arcing products (e.g., carbon) remain in the oil and its quality deteriorates with successive operations. This necessitates periodic checking and replacement of oil.
|
Types of Oil Circuit Breaker
The oil circuit breakers find extensive use in the power system. These can be classified into the following types :
- Bulk oil circuit breakers
- Plain break oil circuit breakers
- Arc control oil circuit breakers
- Low oil circuit breakers
In Bulk oil CB oil has to serve two purposes.
- it extinguishes the arc during the opening of contacts
- it insulates the current-conducting parts from one another and from the earthed tank.
Plain Break Oil Circuit Breakers
A plain-break oil circuit breaker is a bulk oil circuit breaker which involves the simple process of separating the contacts under the whole of the oil in the tank. There is no special system for arc control other than the increase in length caused by the separation of contacts. The arc extinction occurs when a certain critical gap between the contacts is reached.
The plain-break oil circuit breaker is the earliest type from which all other circuit breakers have developed.
Arc Control Oil Circuit Breakers
However, it is necessary and desirable that final arc extinction should occur while the contact gap is still short. For this purpose, some arc control is incorporated and the breakers are then called arc control circuit breakers.
There are two types of such breakers, namely :
- Self-blast oil circuit breakers— in which arc control is provided by internal means i.e. the arc itself is employed for its own extinction efficiently.
- Forced-blast oil circuit breakers— in which arc control is provided by mechanical means external to the circuit breaker.
Low Oil Circuit Breakers
In the bulk oil circuit breakers discussed so far, the oil has to perform two functions. Firstly, it acts as an arc quenching medium and secondly, it insulates the live parts from the earth. It has been found that only a small percentage of oil is actually used for arc extinction while the major part is utilized for insulation purposes.

For this reason, the quantity of oil in bulk oil circuit breakers reaches a very high figure as the system voltage increases. This not only increases the expenses, tank size and weight of the breaker but it also increases the fire risk and maintenance problems.





Comments are closed.