What is an RCD?
A Residual Current Device (RCCB, ELCB, RCBO, GFCI etc.) is a device that is designed to provide protection against electrocution or electrical fires by cutting off the flow of electric automatically when it senses a ‘leakage’ of electric current from a circuit.
Residual Current Devices have the following Specifications
- Sensitivity – milliAmperes (mA)
- Current Rating – Amperes (A)
- Short Circuit Rating – Kilo Amperes (kA)
- Poles – 2 Pole or 4 Pole
Difference between RCD, RCCB & RCBO
- RCD is the generic term for all types of residual current protective device.
- RCCBs are residual current operated circuit-breakers without integral overcurrent protection known in Germany as Fehlerstrom-Schutzschalter (FI-Schutzschalter).
- RCBOs are devices which feature an integrated overcurrent protection unit for overload and short-circuit protection in addition to protection against residual currents.
Read GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) – Working, Types, Installing and Troubleshooting
Operating Principle of a Residual Current Device
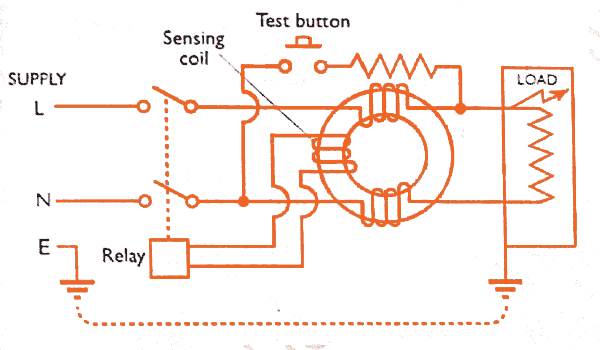
The basic operating principle of a residual current device (RCCB, ELCB, RCBO etc.) is given in the figure below.
 |
| Operating principle of Residual Current Circuit Breaker |
When the load is connected to the supply through the Residual Current Device (RCD), the line and neutral conductors are connected through primary windings on a toroidal transformer.
In this arrangement, the secondary winding is used as a sensing coil and is electrically connected to a sensitive relay or solid state switching device, the operation of which triggers the tripping mechanism.
When the line and neutral currents are balanced, as in a healthy circuit, they produce equal and opposite magnetic fluxes in the transformer core with the result that there is no current generated in the sensing coil. (For this reason, the transformer is also known as a ‘core balance transformer‘).
When the line and neutral currents are not balanced they create an out-of-balance flux. This will induce a current in the secondary winding which is used to operate the tripping mechanism. It is important to note that both the line and neutral conductors pass through the toroid.
A common cause of unwanted tripping is the failure to connect the neutral through the RCD, RCDs work equally well on single phase, three phase or three phase and neutral circuits, but when the neutral is distributed it is essential that it passes through the toroid.
Test Circuit in RCD
A test circuit is always incorporated in the RCD. Typically the operation of the test
button connects a resistive load between the line conductor on the load-side of the RCD and the supply neutral.
The test circuit is designed to pass current in excess of the tripping current of the RCD to simulate an out-of-balance condition. Operation of the test button verifies that the RCD is operational. It is important to note, therefore, that the test circuit does not check the circuit protective conductor or the condition of the earth electrode.
On all RCDs a label instructs the user to check the function of the RCD at regular intervals and to observe that the RCD trips instantly.
Types of Residual Current Device
1. RCCB
It is not designed to give protection against overloads and/or short-circuits and must always be used in conjunction with an overcurrent protective device such as a fuse or circuit-breaker.
2. RCBO
RCBO is a Residual Current Operated Circuit-Breaker with Integral Overcurrent Protection.
A mechanical switching device designed to make, carry and break currents under normal service conditions and to cause the opening of the contacts when the residual current attains a given value under specified conditions.
In addition, it is designed to give protection against overloads and/or short-circuits and can be used independently of any other overcurrent protective device within its rated short-circuit capacity.
Working of a Residual Current Device
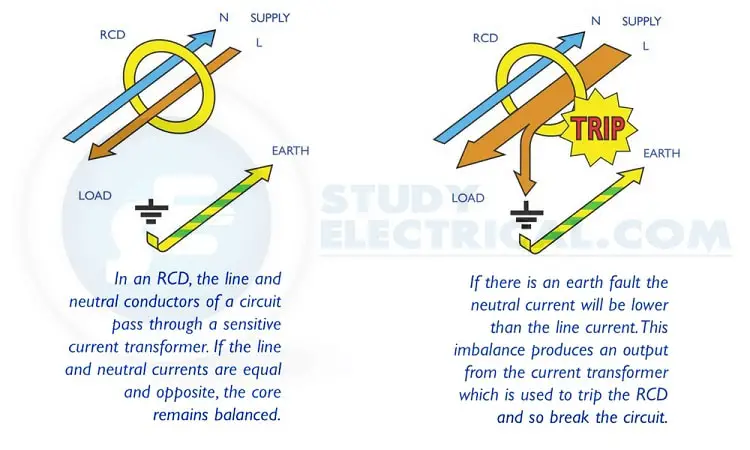
In an RCD, the line and neutral conductors of a circuit pass through a sensitive current transformer. If the line and neutral currents are equal and opposite, the core remains balanced (Figure A).
If there is an earth fault the neutral current will be lower than the line current. This imbalance produces an output from the current transformer which is used to trip the RCD and so break the circuit (Figure B).
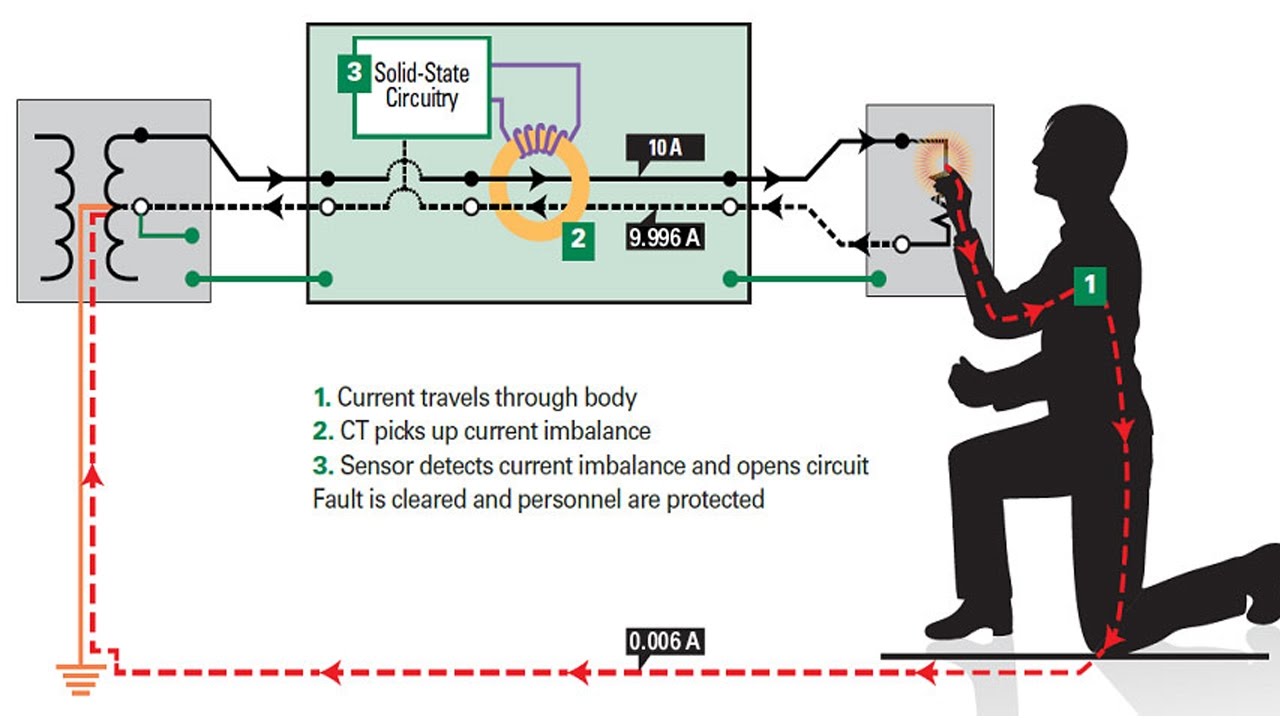
In practice, the main Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) for the premises will probably trip, or the service fuse so the situation is unlikely to lead to catastrophe, but it may be inconvenient. RCDs normally don’t offer protection against current overloads: RCDs detect an imbalance between the live and neutral currents. A current overload, however large, cannot be detected. If a line neutral fault occurs (a short circuit, or an overload), the RCD won’t trip, and may get damaged.
Standard ratings available are 25A, 40A, 63A and 100A
Standard Sensitivities available are 30mA. 100mA, 300mA and optionally 10mA is also available. Electromechanical RCCBs are designed to operate on normal supply waveforms and cannot be guaranteed to operate where none standard waveforms are generated by loads. The most common is the half-wave rectified waveform sometimes called pulsating dc generated by Computers, Speed control devices (VFD) and even dimmers.



Comments are closed.