Low voltage switchgear, according to IEC 60947, refers to switchgears with rated voltages up to 1000 V AC and 1500 V DC.
The term ‘switchgear’ is a generic term encompassing a wide range of products like circuit breakers, switches, low voltage fuses, switch fuse units, off-load isolators, HRC fuses, contactors, earth leakage circuit breakers (ELCBS), miniature circuit breakers (MCBS), and moulded case circuit breakers (MCCBS), among others.
A commonly followed network combination in LV distribution boards in shown in the figure below. It is a combination of power control centers and motor control centers or load distribution boards including lighting distribution boards.
The incomer/sub-incomer/ distribution network generally depends on the capacity of the source and the distribution of load centers.
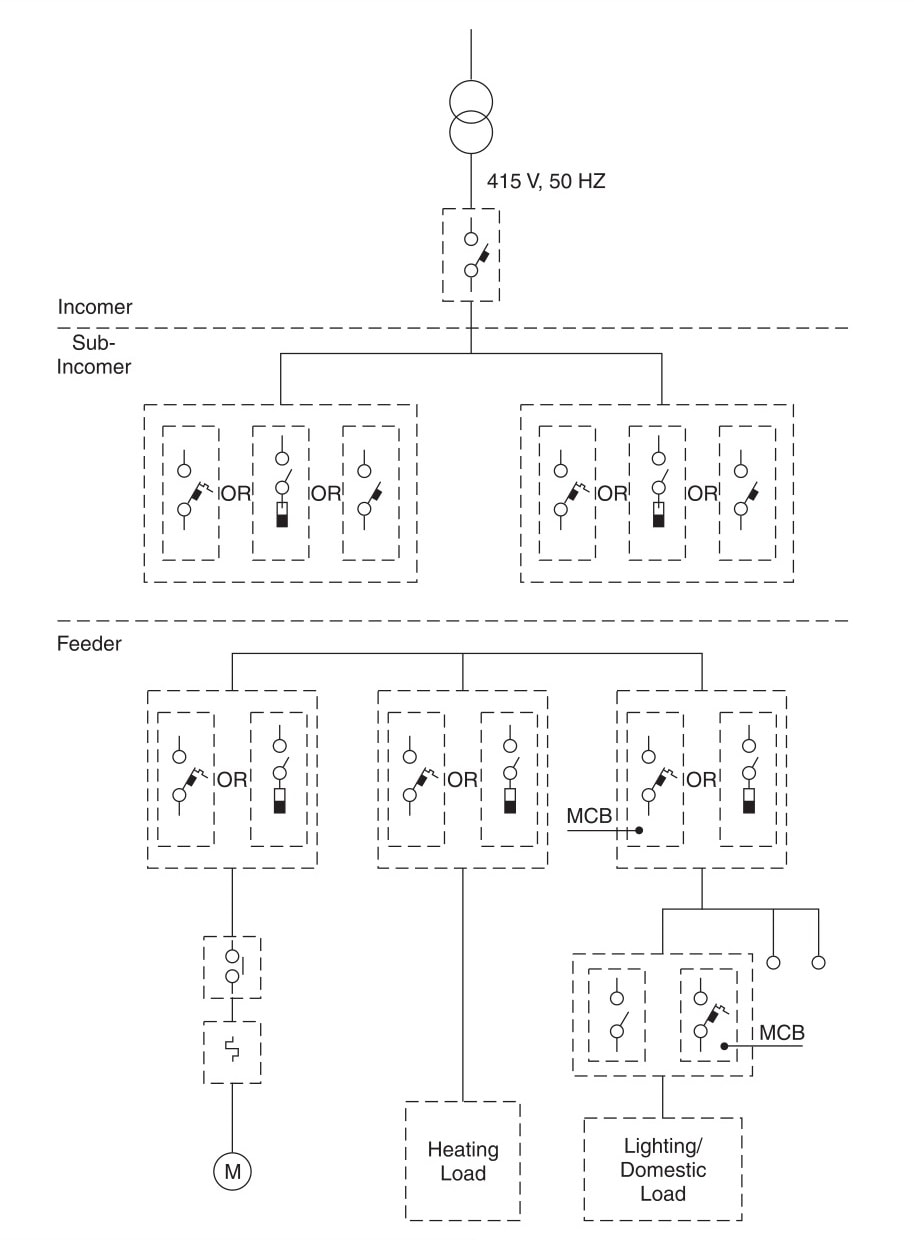 |
| Conventional Low Voltage Distribution Network |
The characteristics and feature of load controlling and protecting devices vary on the basis of the locations. The system being most commonly followed currently is detailed below.
Conventional Incomer
The devices used in the incomer should be capable of:
- Switching and carrying normal currents (generally above 1200 A);
- Withstanding abnormal currents for a short duration in order to allow downstream devices to operate;
- Interrupting the maximum value of the fault current generated in the system;
- Ensuring the safety to the operating personnel;
- Inter-locking with downstream equipment; and
- Facilitating easy maintenance.
ln the past, oil circuit breakers (OCBS), re-wireable fused isolators and air circuit breakers (ACBs) were the commonly used devices.
However, ACB has been acknowledged as an idea device for incomer in terms of the safety, reliability and maintenance needs of the system.
This is mainly due to its various characteristics like quick-make, quick-break stored energy type reliable mechanism, safety interlocks/ indications, ease of maintenance and its ability to withstand fault currents for a specified duration (1-3 secs) thereby allowing the feeder device to isolate the faulty branch of the network and ensuring reliable supply to healthy areas.
Conventional Sub-Incomer
The devices installed as parts of a sub-incomer should have the following characteristics
- Ability to achieve economy without sacrificing protection and safety
- Capability to withstand abnormal currents; and
- Need for relatively less number of inter-locking indicating accessories since it covers a limited area of network.
ACB’s and switch fuse units (SFUS) are, to a large extent, being used as sub-incomers along with modern devices like moulded case circuit breakers (MCCBs).
Conventional Feeder Protection
Feeder protection covers all load centres like motor control centres, lighting switchboards and industrial load centres.
The choice of feeder protection device based on the different conventional feeder load centres are discussed below.
1. Motor Control
The motor feeder needs to be protected against the following eventualities in addition to normal switching control:
- Short-circuit;
- Over-currents up to locked rotor condition; and
- Single-phasing.
Requirements for Motor Control
| Characteristics | Devices |
|---|---|
| Switching normal currents | Contactors |
| Single-phasing sensing | Bi-metallic Relay |
| Over—current (up to locked rotor condition) sensing | Bi-metallic Relay |
| Switching over-currents including single-phasing current as above | Contactors |
| Short-circuit current | MCCB/SFU |
| Logic | Timers/Auxiliary ; Contactors and other Accessories |
2. Other Industrial Load Control
Loads like oven, pre-treatment and electroplating baths fall under this category and the feeders need to be protected against faulty over-currents.
Presently MCCBs (https://studyelectrical.com/2015/01/moulded-case-circuit-breakers-mccb.html) and SFUs are being commonly used for this purpose.
3. Lighting/Domestic Load Control
The requirements of domestic load control are similar to those listed in other industrial load control with the addition of earth leakage current protection in order to reduce any damages to life and property that could be caused by harmful leakages of electric current and fire.
In a low voltage power distribution system, electrical appliances are protected against damages from over-loads or short-circuits by fuses or circuit breakers.
However, the human operator is not adequately protected when a fault occurs within the appliance itself. Hence the need for fast acting ELCBs operating on low leakage currents arises.
The device, which detects leakage current as low as 100 mA and is capable of disconnecting equipment in less than 100 msec is called an earth leakage circuit breaker (ELCB) (https://studyelectrical.com/2015/05/residual-current-circuit-breakers-elcb-rccb-rcbo-working-principle.html) .
The following two types of ELCBs are used depending upon the parameters to be detected:
- Voltage-operated ELCB; and
- Current-operated ELCB.