A basic understanding of the fundamental concepts of current and voltage requires a degree of familiarity with the atom and structure of atom.
The matter has mass and takes up space. Atoms are basic building blocks of matter, and cannot be chemically subdivided by ordinary means.
The word atom is derived from the Greek word atom which means indivisible. The Greeks concluded that matter could be broken down into particles to small to be seen. These particles were called atoms.
Structure of Atom
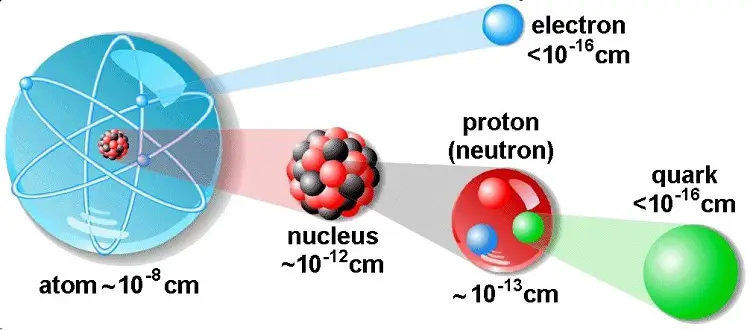
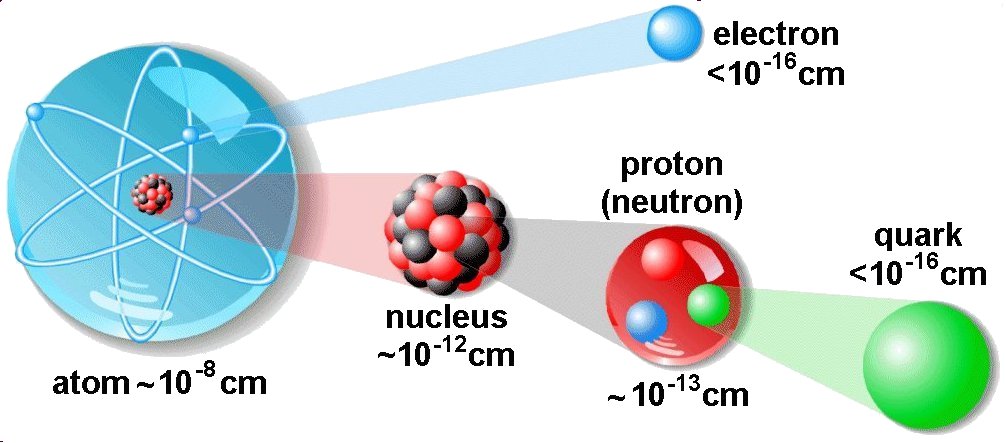
Atoms are composed of three types of particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Protons and neutrons are responsible for most of the atomic mass. E.g in a 150 person 149 lbs, 15 oz is protons and neutrons while only 1 oz. is electrons. The mass of an electron is very small (9.108 X 10^-28 grams).
The central part of the atom is called the nucleus and contains protons and neutrons. A proton is a positively charged particle and neutron has no charge. The protons and neutrons are very closely held together with tremendous forces.
The nucleus is surrounded by a number of tiny particles called electrons. The electrons are spinning around themselves and also are revolving around the nucleus in ‘orbits’ or shells. The electrons cam the smallest negative charge and have a negligible mass.
Under ordinary conditions, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons in an atom. Therefore, an atom is electrically neutral as a whole. Electrons have negative charge exactly equal in magnitude to the positive charge of the protons.
Energy Levels and Shells
The electrons are kept in the structure of atom by the attraction exerted on them by the positive nucleus. In fact, the electrons can be regarded as arranged and revolving in successive orbits or levels around the nucleus.
The electrons in each orbit or levels are associated with a definite amount of energy. Thus the orbits are referred to as energy levels. The energy levels are denoted by the letters K, L, M, N, O, P etc, The K level is nearest to the nucleus.
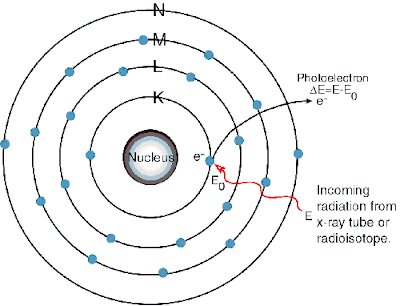
To remove the electron from its orbit, some definite amount of energy is required.
To remove the electrons from the first orbit, the energy required is maximum and to remove the electrons from the outer most orbit the energy required is minimum.
The electrons in the outermost orbit are called the valence electrons.
The valence electrons are comparatively loosely bound to the rest of the atom, and they may be removed by various means e.g., by applying electrical voltage to the material.
Hydrogen and Silicon Atom
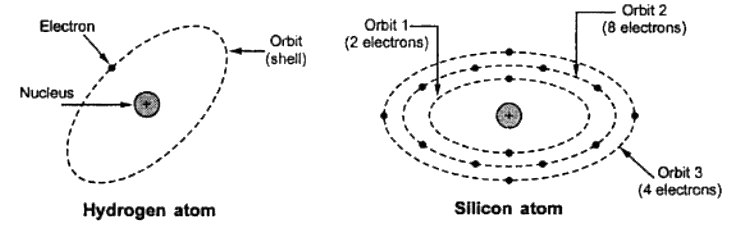
The above figure shows a hydrogen atom and a silicon atom.
The hydrogen atom consists of one proton and one electron revolving around the nucleus. It is the simplest atom.
Silicon atom consists of 14 electrons. These electrons revolve around the nucleus in three orbits. The first orbit has 2 electrons, the second orbit has 8 electrons and the third orbit has the remaining 4 electrons.
The 4 electrons located in the farthest shell of silicon atom are loosely held by the nucleus and generally available as free electrons.
If by any means some of the electrons are removed, the negative charge of that atom decreases while positively charged protons remain the same. The resultant charge on the atom remains more positive in nature and such an element is called positively charged.
While if by any means the electrons are added, then the total negative charge increases than positive and such elements are called negatively charged.




Comments are closed.