Air blast circuit breaker employs a high-pressure air blast as an arc quenching medium. The construction and working of different types of air blast circuit breakers are explained in this article.
This type of circuit breaker has been used earlier for open terminal HV application, for system voltages of 245 kV, and 400 kV up to 765 kV, especially where faster breaker operation was required. Comparing to the SF6 circuit breaker and vacuum circuit breaker, air blast circuit breaker are seldom used nowadays.
Air blast circuit breakers are using compressed air or gas as the circuit breaking or interrupting medium. Gases such as nitrogen, carbon dioxide, hydrogen or Freon can be used as arc interrupting medium.
But compressed air is the most accepted arc interrupting medium. The reasons are, nitrogen has circuit breaking properties similar to compressed air and there is no advantage of using it. Carbon dioxide has a drawback as it is difficult to control owing to freezing at valves and other restricted passages. Hydrogen has increased breaking capacity but it’s costlier.
Fast operations, suitability for repeated operation, auto reclosure, unit type multi-break constructions, simple assembly, modest maintenance are some of the main features of air blast circuit breakers. A compressors plant necessary to maintain high air pressure in the air receiver.
The air blast circuit breakers are especially suitable for railways and arc furnaces, where the breaker operates repeatedly. Air blast circuit breakers are used for interconnected lines and important lines where a rapid operation is desired.
Construction of Air Blast Circuit Breaker
The figure shows the construction of a typical air blast interrupter. Each interrupter consists of a porcelain insulator, mounted on the air inlet manifold, with the exhaust chamber fixed at the opposite end of the porcelain.
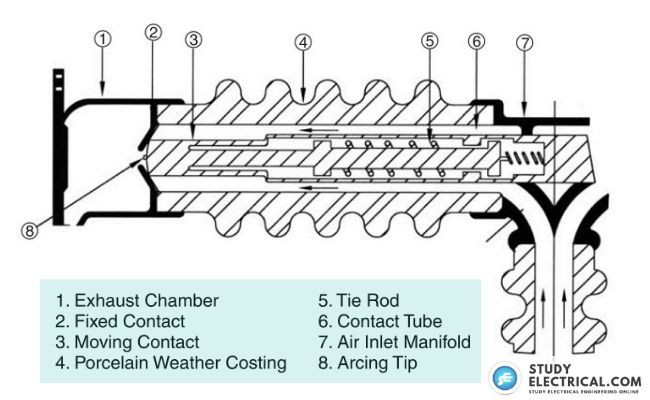
The exhaust chamber consists of casting with a curved hood for weather protection and slots on the underside for the directional exhaust of the compressed air to the atmosphere.
The moving contact assembly consists of a chromium-copper contact coupled to two pistons by means of an insulated tie rod that moves inside the contact tube. The main current in the moving contact is transferred to the contact tube by means of transfer contact fingers.
An arcing tip is provided at the end of the moving contact. The moving contact is maintained in a normally closed position with the fixed contact by springs. The details of construction of the interrupter head vary with its interruption rating.
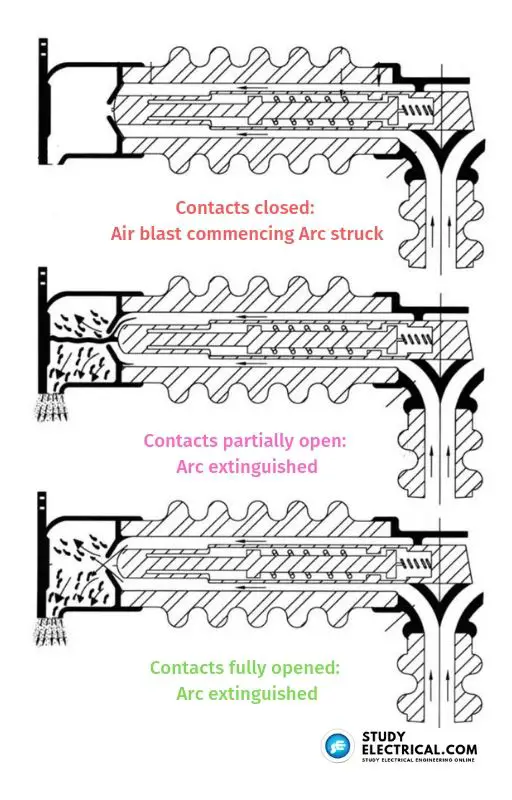
Figure 1 shows the closed position of the interrupter. Figure 2 shows contacts in a partially open position with arcing between fixed and moving contact. Figure 3 shows contacts in a fully open position with arc extinguished.
The interrupting capability of the air blast circuit switchgear is usually increased by increasing the normal pressure range. Normally the pressure level is around 30 to 35 bars. In order to maintain the insulation level and reliability of operation, it is also necessary for the condition of the air to be very dry.
Currently, however, SF6 circuit breakers have practically eliminated the use of this technology.
Working of Air Blast Circuit Breaker
Under normal condition, the contacts of air blast circuit breaker are closed.
When a fault occurs, the contacts are opened and an arc is struck between them. The opening of contacts is done by a flow of air blast established by the opening of the blast valve (located between air reservoir and arcing chamber ).
The air blast cools the arc and sweeps away the arching products into the atmosphere.
Thus the dielectric strength of the medium is increased, prevents from re-establishing the arc. The arc gets extinguished and the flow of current is interrupted.
The air blast circuit breaker requires an auxiliary compressed air system which supplies air to the breaker air receiver.
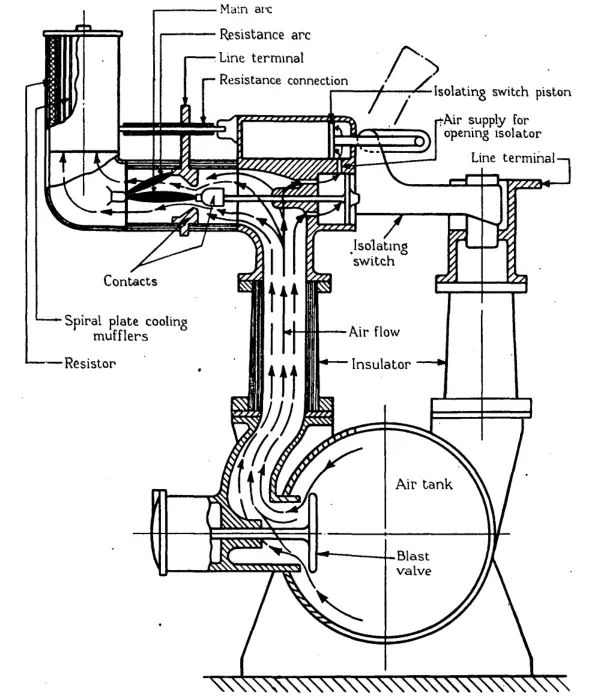
When the opening is required compressed air is admitted to the arc extinction chamber. It pushes away the moving contacts. In doing so the contacts are separated and the air blast takes away the ionized gases along with it and assists arc extinction.
Read: Air Circuit Breaker
Types of Air Blast Circuit Breakers
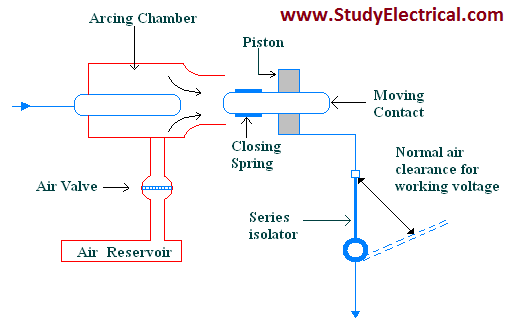
Axial Blast Circuit Breaker
Let’s look into the working of an axial blast circuit breaker under normal condition and faulty condition.
Under Normal Condition
Under Faulty Condition
When a fault occurs a tripping impulse is produced which causes the opening of the air valve.
Since the air valve connects the air reservoir and the arcing chamber, a high-pressure air enters the arcing chamber. This air pushes away the moving contact against the spring pressure.
The moving contact is separated and an arc is struck. At the same time, high-pressure air blast flows along the arc and takes away the ionized gases along with it. Consequently, the arc is extinguished and the current flow is interrupted.
Note:
- The contact separation required for arc extinction is very small generally (1.75 or so ).
- This small gap may sometimes inadequate clearance for the normal service voltage. Therefore an isolating switch is included as a part of this Circuit Breaker.
- This switch opens immediately after the fault interruption to provide the necessary clearance for insulation.
Cross Blast Circuit Breaker
The figure shows the essential components of a typical cross-blast air circuit breaker.
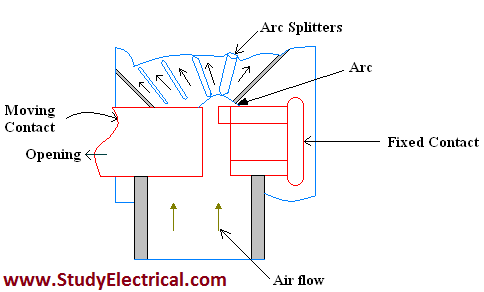
When the moving contact is withdrawn, an arc is struck between the fixed and moving contacts.
The high-pressure cross-blast forces the arc into a chute consisting of arc splitters and baffles. The splitters serve to increase the length of the arc and baffles give improved cooling.
The result is that arc is extinguished and the flow of current is interrupted. Since blast pressure is the same for all currents, the inefficiency at low currents is eliminated.
The final gap for interruption is great enough to give normal insulation clearance so that a series isolating switch is not necessary.
Advantages of Air Blast Circuit Breaker
The following are some of the advantages of Air Blast Circuit Breakers.
- Elimination of fire hazard in the substation, because of the absence of oil the risk of fire is eliminated.
- The arcing products are completely removed by the blast whereas the oil deteriorates with successive operations, the expense of regular oil is a replacement is avoided.
- Due to lesser arc energy, air blast circuit breakers are very suitable for conditions where frequent operation is required.
- The energy supplied for arc extinction is obtained from high-pressure air and is independent of the current to be interrupted.
Disadvantages of Air Blast Circuit Breaker
Some of the Disadvantages of Air Blast Circuit Breaker are:
- Air has relatively inferior arc extinguishing properties.
- Air blast circuit breakers are very sensitive to the variations in the rate of re-striking voltage.
- Considerable maintenance is required for the compressor plant which supplies the air blast.
Reference: Air-blast circuit-breakers – IET Journals & Magazine – IEEE Xplore






Comments are closed.