A circuit breaker is required to perform the following three major duties.
- It must be capable of opening the faulty circuit and breaking the fault current. This is described as breaking capacity of a circuit breaker
- It must be capable of being closed on to a fault. This refers to making capacity of a circuit breaker
- It must be capable of carrying fault current for a short time while another circuit breaker is clearing the fault. This refers to short time capacity of the circuit breaker.
- Rated voltage: the rated maximum voltage of a circuit breaker is the highest rms voltage, above nominal system voltage ,for which circuit breaker is designed and is the upper limit for operation. The rated voltage is expressed in kV rms and refer phase to phase voltage for three phase circuit.
- Rated current: the rated normal current of a circuit breaker is the rms value of the current which the circuit breaker shall be able to carry at rated frequency and at the rated voltage continuously, under specified condition.
- Rated frequency: the rated frequency of a circuit breaker is the frequency at which it is designed to operate.
- Operating Duty: the operating duty of a circuit breaker consist of the prescribed number of unit operations at stated intervals.
Breaking capacity:
Breaking current is the RMS value of current that a circuit breaker is required to break at the instant of contact separation. The symmetrical breaking current is the RMS value of its symmetrical component. If however, at the instant of contact separation, the wave is still asymmetrical it is known as the asymmetrical breaking current.
Making capacity:
Making capacity = 1.8 × √2 × Symmetrical breaking capacity.
Short time rating:
This happens in case of momentary fault like bird age on the transmission lines and the fault is automatically cleared and persists only for 1 or 2 seconds. For this reason the circuit breakers are short time rated and they trip only when the fault persists for a duration longer than the specified time limit.
Other Factors
Generally the fault current at various voltage levels expected are standardised while manufacturing a circuit breaker, considering the hike in fault currents in future due to adding of different sources. The voltage level and expected fault current are given below.
110kV 31.5kA
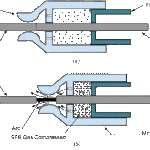
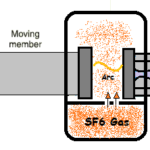
The various types of circuit breakers are Bulk oil circuit breakers (BOCB), Minimum oil circuit breakers (MOCB), Air blast circuit breakers (ABCB), Vacuum circuit breakers (VCB), SF6 gas circuit breakers etc.
SF6 CBs and VCBs are superior in performance compared with other types and hence selected for this particular sub station design for 220 & 110 KV side and 11 KV side respectively.





Comments are closed.