An Electrical Fuse is a vital component of any equipment. It is used as an indicator of a defect in the system. It protects the equipment from overcurrent or overloading.
Its essential component is a metal wire or strip (fuse wire) that melts when too much current flows through it.

Just like a fuse, a circuit breaker is another protective switchgear device that operates to provide overcurrent protection of an electrical circuit.
Working of an Electrical Fuse?
Fuses work on the principle of heating effect of current. It consists of a piece of wire called fuse wire made of a metal or an alloy of low melting point. As the current increases beyond a limit, the wire in the electric fuse melts and breaks off. The fuse is then said to have blown off.
Let’s assume a real-life example. We all connect different types of machines to an electric circuit. Sometimes current drawn by a machine or appliance connected in that circuit gets exceeded from the rated (predetermined) value. This happens due to any one of the following reasons.
- Increase in load condition (Overload)
- Short circuit
- Leakage from the mains
The damages due to this overcurrent can be limited by a short length of wire known as an electrical fuse.
An electrical fuse automatically melts due to this excessive current, and thus the circuit is broken. This is how the wiring or any appliance is protected. Otherwise, the wiring and the appliance will be damaged due to the excessive flow of the current in the circuit.
Shortly, it can be stated that the fuse is a device used to prevent overheating due to excessive current. This in turn protects the insulation of the wire, machine, or appliances from overheating and damage.
Desirable Characteristics of Fuse Element
- The function of a fuse is to carry the normal current without overheating but when the current exceeds its rated or normal value, it rapidly heats up to melting point and disconnects the circuit to be protected by it. In order that it may perform this function satisfactorily, the fuse element should have the following desirable characteristics:
Characteristics:
- Low melting point (e.g. tin, lead)
- High conductivity (e.g. silver, copper)
- Free from deterioration due to oxidation (e.g. silver)
- Low cost (e.g. lead, tin, copper).
Since no material posesses all the above mentioned desirable characteristics, a compromise is made in the selection of the material for a fuse.
The table below lists the important fuse materials and their melting point.
| Metal | Specific Resistance (micro ohm-cm) | Melting Point (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Tin | 11.2 | 231 |
| Lead | 21.6 | 327 |
| Zinc | 6.2 | 419 |
| Silver | 1.65 | 960 |
| Copper | 1.72 | 1085 |
Specification of Electrical Fuse
Following points should be noted before installing an electrical fuse in an electric circuit.
- The fuse is to be put in the live wire (+ve phase) in the mainboard and at the sub-branches.
- The size of the fuse wire should be based on the value of current and not on the melting current value.
- If the fuse of proper rating is not provided in the circuit and any fault develops due to overload or short circuit, the flow of heavy current will heat up the wires and fire may take place.
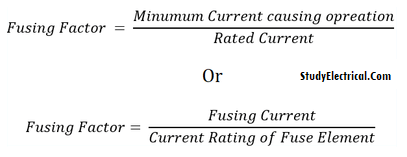
Rated Current of Fuse:
By rated current, we mean the current that can be carried safely for an indefinite period without undue heating and melting the fuse wire. This rated value also depends upon types of the fuse holder, temperature, and fuse contacts.
Fusing Current of Fuse:
It means the value of current at which the fusing wire melts when current passes through it even for a fraction of second. The rated current is approximately half of the fusing current.
Fusing factor = Minimum fusing current / Rated current of the fusing element
Properties & Applications
An Electrical Fuse unit should have following properties:
- Easy isolation or separation from terminals.
- Box/case, which holds the fuse wire, should be an insulating material such as porcelain.
- Ease of replacement.
The fuse basically consists of a current-carrying element (fusing wire), which melts when heated to temperatures above 170 F. The melting action opens the circuit thereby removing the source of voltage from the circuit.
The fuse will heat and remain intact provided the applied current does not produce heat that exceeds the melting point of the metal.

It is therefore important that the material used as a fusing element is engineered to accurate thickness, lengths, and widths to carry specific voltage and current loads.
Obviously, the basic laws of electricity are applied for the selection of fuse ratings for a specific circuit taking into consideration the current required to maintain the normal circuit operation, total energy dissipation, and voltage requirements.
Selection / Replacing an Electrical Fuse
A short circuit in the equipment will melt a circuit fuse instantaneously. When a fuse needs to be replaced the exact replacement of a fuse with both proper voltage and current ratings must be used.

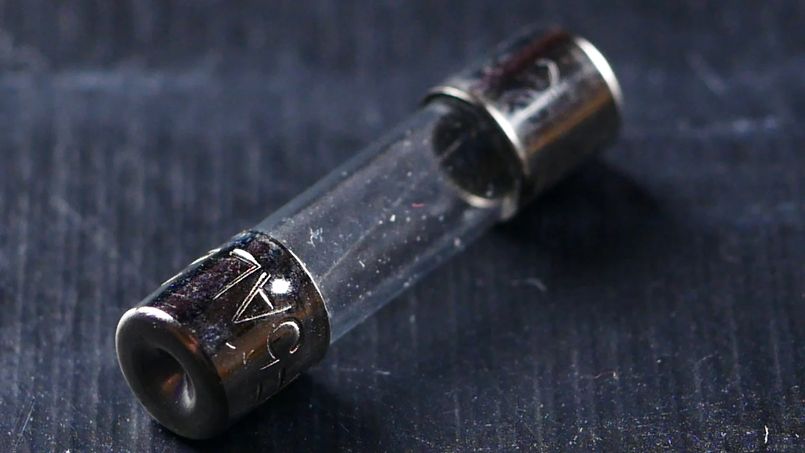
The blown-up fuse can indicate the type of service problem in non-functional electronic equipment. Usually, if the glass case of the fuse appears clear and there are broken pieces of the center conductor, the problem has been caused by a slow, gradual overload on the power supply.
If the glass cover of the fuse is discolored and the center conductor is almost missing, it shows that the fault was caused due to a short circuit. It also indicates that there may be other problems that produced a lot of currents to flow very quickly and destroying the fuse violently with the production of a lot of heat.
Fuse is a vital component of equipment. It is used as an indicator of a defect in the system. It protects the equipment from the overcurrent/ overloading.
An Electrical Fuse unit should have the following features:
- Easy isolation or separation from terminals.
- Box/case which holds the fuse wire should be made of an insulating material such as porcelain.
- Ease of replacement.
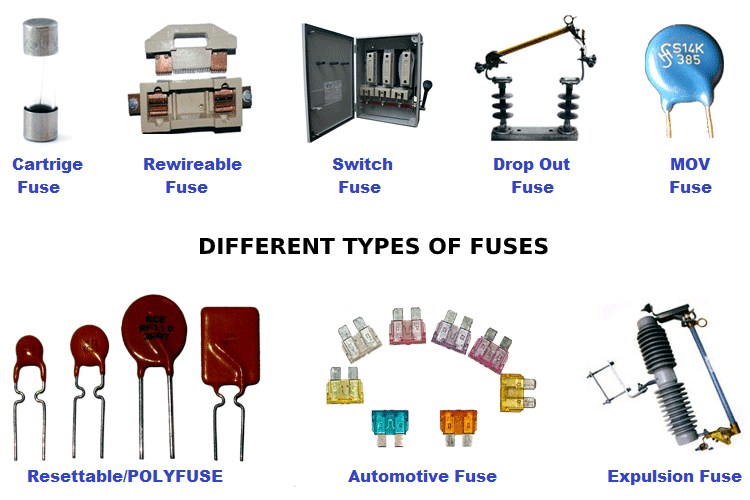
Types of Fuses
Fuses are the simplest current interrupting devices for protection against excessive current. They are available in the market in different names and different types.
In general, all electrical fuses may be classified into two groups:
(1) High Voltage Fuses (> 1000 V):
- Cartridge Type High Rupturing Capacity (HRC) Fuses: These fuses feature a helix-shaped fuse element to mitigate the corona effect at higher voltages. They are suitable for use up to 33 kV.
- Liquid Type High Voltage (HV) HRC Fuse: This type of fuse is filled with carbon tetrachloride and sealed at both ends. When a fault occurs and the current exceeds permissible limits, the fuse element is blown out. It can be utilized for voltages up to 132 kV.
(2) Low Voltage Fuses (< 1000 V):
- Rewireable/Kit-Kat Type Fuses: These fuses offer the advantage of easy removal of the fuse carrier without risk of electrical shock or injury. They find applications in domestic wiring and small industries, typically used for voltages up to 240 V.
- Striker Type Fuses: Striker type fuses are designed for circuit closing and tripping. They possess sufficient force and displacement.
- Drop Out Fuses: This type of fuse is engineered so that when the fuse element melts, it causes the element to drop under gravity from its lower support. Drop-out fuses are primarily used for the protection of outdoor transformers.
Some other important types of electrical fuses are listed below.
- Round type fuse unit (cut out) (Rewirable)
- Kit-kat type fuse unit (Rewirable)
- Cartridge type fuse unit.
- HRC type Fuses
- Automatic Cut Out
- Plug type
- Expulsion fuse
- Liquid fuse
- Drop out fuse.
- Mini Circuit Breaker
The first four in this list are discussed in the below section.
Round Type (Cut Out) Fuse
Round Type (cut out) fuse looks similar to a ceiling rose. It is made up of Bakelite or porcelain material. Its base is fixed on a wooden board with a screw. This type of fuse is not used as a common fuse.
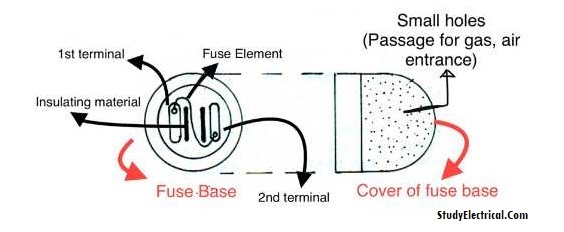
There are two terminals on the base in which the fuse element is fitted. Threads are provided on the box as well as on the cover for placing and replacing purposes.
Small holes are provided on the cover, for air entrance. The holes also provide a passage for gases formed due to melting (burning) of the fuse element.
Following are disadvantages of this type of fuse.
- One of the terminals is always energized with live (+ve) wire of the supply.
- Due to the above reason, it is difficult to replace the fuse element with mains on. The main switch must be open.
- When the fuse blows off there is too much arcing and the unit may be damaged.
Kit-Kat type Fuse Unit
Kit-Kat type is a semi-closed type electrical fuse unit. Neither it is kept in free air nor it is completely enclosed.
These are used for household or laboratory purposes mostly. This type of fuse unit can be rewired; even the cut out terminals are energized without taking any safety precautions.
This can be fitted on wooden blocks or boards or also used in iron-boxes. (In Iron-clad switch.)
Following terms are used in connections with this type of fuse units.
- Fuse links: This part consists of a fuse element.
- Fuse carrier: This carries a fuse link.
- Fuse base: It is a fixed part carrying fixed contact terminals.
Fuse base carriers are made of porcelain, whereas contacts and terminals are of hard bronze materials.
Fuse carrier on which the fuse link is kept can be taken out very easily and safely (even with the switch in ON position). Fix contacts are fitted to the base.
Both terminals and wires are fitted to the top terminal. No fuse element is kept in the neutral wire. For this purpose, Neutral Link (copper or bronze) is provided in D.P.I.C. switches.
When fuse bridge with fuse element is inserted and the switch is made ‘on’ then only the circuit is completed. These fuse units are rated as 5.15, 30 up to 300 Amps.
These types of fuse units are very simple in operation and very cheap and easy for replacement.
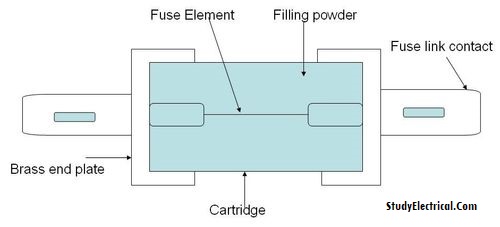
Cartridge Type fuse unit
Cartridge types of fuse units are completely enclosed.
The fuse element is kept in a peculiar shape just like a bucket known as the cartridge. This container is filled with the materials ’quartz’.

The container is heat resistant; good insulating material and it is sealed completely. If the fuse goes off the complete unit is to be replaced. Therefore it is costly.
It cannot be rewired (in some types, rewiring is possible).
There is an index circle on the container, which under normal condition is clear, but when the fuse blows off it becomes dark. These fuses are fixed in fuse carriers just like a kit-kat fuse in the D.P.I.C. unit.
HRC Tube Fuse Unit
HRC fuse unit means a high rupturing capacity fuse unit. These are similar in construction to cartridge types with the exception that the fuse wire can carry heavy current for a known short time period.
This heavy current can be much more than the normal rated current. During this time if the fault is removed, its use does not blow off otherwise it blows off and breaks the continuity of the circuit. Thus these fuses are sometimes also called Slow Blow Fuses.
The cartridge of HRC type is either made of glass or some other chemical compound and has airtight construction to avoid the effect of atmospheric air on the fuse material (results in lowering its rated capacity due to continuous slow oxidization of the wire material).
These fuses are available in 2A to 800 Amps. Capacity ranges. The fuse element used here is silver. The most popularly used fuses in electronic circuits are 2 amp to 5 amp.
Conclusion
The fuse basically consists of a current-carrying element, which melts when heated to temperatures above 170°F. The melting action opens the circuit thereby removing the source of voltage from the circuit.
The fuse normally heats up and remains intact provided the applied current does not produce heat that exceeds the melting point of the fuse metal wire. It is therefore important, that the material used as a fusing element is engineered to accurate thickness, lengths and widths to carry specific voltage and current loads.
For this the basic laws of electricity are applied for selection of fuse ratings for a specific circuit, taking into consideration the current required to maintain the normal circuit operation, total energy dissipation and voltage requirements.
A short circuit in the equipment will melt the circuit fuse instantaneously. When a fuse needs to be replaced the exact replacement of a fuse with respect to both proper voltage and current ratings must be used.
The blown up fuse can indicate the type of service problem in non-functional electronic equipment. Usually if the glass case of the fuse appears clear and there are broken pieces of the center conductor, the problem has been caused by a slow, gradual overload on the power supply.
If the glass cover of the fuse is discolored and the center conductor is almost missing, it shows that the fault was caused due to a short circuit or other problem that produced a lot of currents to flow very quickly and destroying the fuse violently with the production of lot of heat.
Fuse is a vital component of any equipment. It is used as an indicator of a defect in the system. It protects the equipment from over current or overloading.



Comments are closed.