What is Short Circuit?
If a fuse is in the supply circuit, it will do its job and blow out, opening the circuit and stopping the current flow. An MCB is also used for protection from short circuit.
A short circuit may be in a direct-current or alternating-current (DC or AC) circuit. If it is a battery that is shorted, the battery will be discharged very quickly and will heat up due to the high current flow.
Watch a 110kV power line short circuit video below.
What is Short Circuit Current?
This is explained with the figure attached here. The figure shows a single phase generator of voltage V and internal impedance Zi is supplying to a load Z.
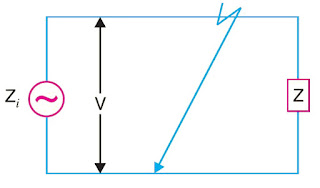
Under normal conditions, the current in the circuit is limited by load impedance Z.
However, if the load terminals get shorted due to any reason, the circuit impedance is reduced to a very low value; being Zi in this case. As Zi is very small, therefore, a large current flows through the circuit. This is called short circuit current.
Short Circuit vs Overload
People usually get confused with overload and short circuit as both of them cause trouble to the system in a similar way. It is worthwhile to make a distinction between a short-circuit and an overload.
When a short-circuit occurs, the voltage at fault point is reduced to zero and current of abnormally high magnitude flows through the network to the point of fault.
On the other hand, an overload means that loads greater than the designed values have been imposed on the system. Under such conditions, the voltage at the overload point may be low, but not zero. The under voltage conditions may extend for some distance beyond the overload point into the remainder of the system.
The currents in the overloaded equipment are high but are substantially lower than that in the case of a short-circuit.
What causes a Short Circuit?
- Internal effects are caused by the breakdown of equipment or transmission lines from the deterioration of insulation in a generator, transformer etc. Such troubles may be due to the aging of insulation. inadequate design or improper installation.
- External effects causing short circuit include insulation failure due to lightning surges. overloading of equipment causing excessive heating: mechanical damage by public etc.
Effects of Short-Circuit
When a short-circuit occurs, the current in the system increases to an abnormally high value while the system voltage decreases to a low value.
The heavy current due to short-circuit causes excessive heating which may result in fire or explosion. Sometimes short-circuit takes the form of an arc and causes considerable damage to the system.
For example, an arc on a transmission line not cleared quickly will burn the conductor severely causing it to break, resulting in a long time interruption of the line.
The low voltage created by the fault has a very harmful effect on the service rendered by the power system. If the voltage remains low for even a few seconds, the consumer’s motors may be shut down and generators on the power system may become unstable.
Short circuits can produce very high temperatures due to the high power dissipation in the circuit. This high temperature can be utilized in the application. Arc welding is a common example of the practical application of the heating due to a short circuit.
The power supply for an arc welder can supply very high currents that flow through the welding rod and the metal pieces being welded. The point of contact between the rod and the metal surfaces get heated to the melting point, fusing a part of the rod and both surfaces into a single piece.






Comments are closed.