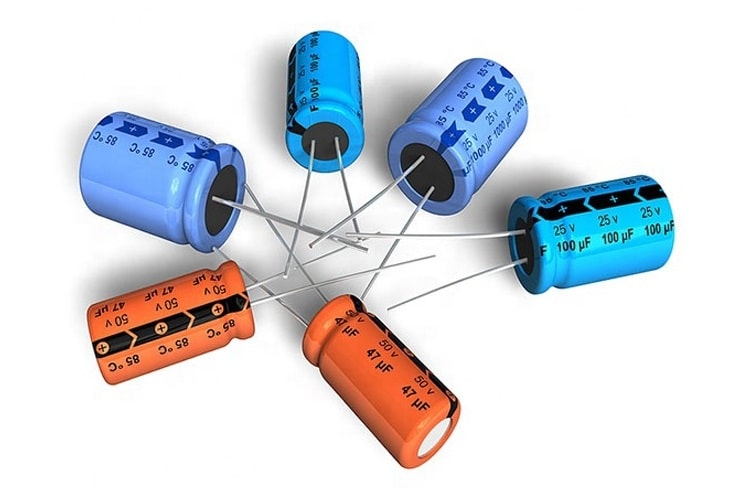
Electrolytic capacitors are one of the most commonly used types of capacitor. Their capacitance values range from about 1 μF to 6800 μF. Electrolytic capacitors are more popular because the electrolytes used in it provide the most capacitance in the smallest space with the least cost.
Construction of Electrolytic Capacitor
In this section, you will learn the construction of an aluminium-foil type electrolytic capacitor.
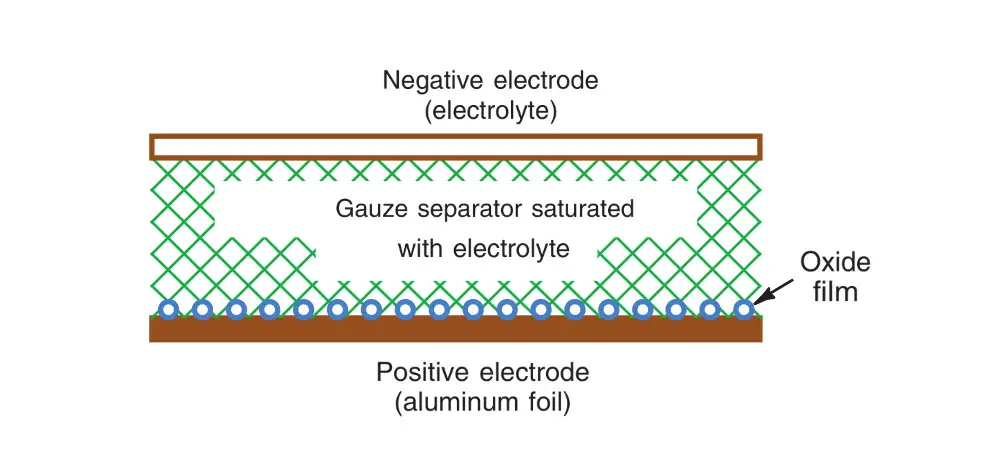
The two aluminium electrodes are in an electrolyte of borax, phosphate, or carbonate. Between the two aluminium strips, absorbent gauze soaks up the electrolyte to provide the required electrolysis that produces an oxide film. This type is considered a wet electrolytic, but it can be mounted in any position.
When dc voltage is applied to form the capacitance in the manufacture, the electrolytic action accumulates a molecular-thin layer of aluminium oxide at the junction between the positive aluminium foil and the electrolyte. The oxide film is an insulator. As a result, capacitance is formed between the positive aluminium electrode and the electrolyte in the gauze separator. The negative aluminium electrode simply provides a connection to the electrolyte. Usually, the metal can itself is the negative terminal of the capacitor, as shown in the figure.
Because of the extremely thin dielectric film, very large C values can be obtained. The area is increased by using long strips of aluminium foil and gauze, which are rolled into a compact cylinder with very high capacitance.
For example, an electrolytic capacitor the same size as a 0.1 μF paper capacitor, but rated at 10 V breakdown, may have 1000 μF of capacitance or more. Higher voltage ratings, up to 450 V, are available, with typical C values up to about 6800 μF. The very high C values usually have lower voltage ratings.
Electrolytic Capacitor Polarity
Electrolytic capacitors are used in circuits that have a combination of dc voltage and ac voltage.
The dc voltage maintains the required polarity across the electrolytic capacitor to form the oxide film.
A common application is for electrolytic filter capacitors to eliminate the 60- or 120-Hz ac ripple in a dc power supply. Another use is for audio coupling capacitors in transistor amplifiers.
In both applications, for filtering or coupling, electrolytes are needed for large C with a low-frequency ac component, whereas the circuit has a dc component for the required voltage polarity.
Incidentally, the difference between filtering out an ac component or coupling it into a circuit is only a question of parallel or series connections. The filter capacitors for a power supply are typically 100 to 1000 μF. Audio capacitors are usually 10 to 47μF.
If the electrolytic capacitor is connected in opposite polarity, the reversed electrolysis forms gas in the capacitor. It becomes hot and may explode. This is a possibility only with electrolytic capacitors.
Leakage Current
The disadvantage of electrolytes, in addition to the required polarization, is their relatively high leakage current compared with other capacitors, since the oxide film is not a perfect insulator.
The problem with leakage current in a capacitor is that it allows part of the dc component to be coupled into the next circuit along with the ac component. In newer electrolytic capacitors, the leakage current is quite small.
Section 16–10 takes a closer look at leakage current in capacitors.
Nonpolarized Electrolytic Capacitor
This type is available for applications in circuits without any dc polarizing voltage, as in a 60-Hz ac power line. One application is the starting capacitor for ac motors.
A nonpolarized electrolytic actually contains two capacitors, connected internally in series-opposing polarity.

Comments are closed.