This involves a bank of many components like transformers, rectifiers, inverters, capacitors, thyristors, compressors and other such paraphernalia, housed within the locomotive body or the “shell”, and there is no central “Engine” or prime mover.
All this has to be done for optimum performance of the traction motors under different conditions and loads. Bi-Current locomotives work according to the same principles, only they have more equipment packed inside them to enable them to work under both type of currents.
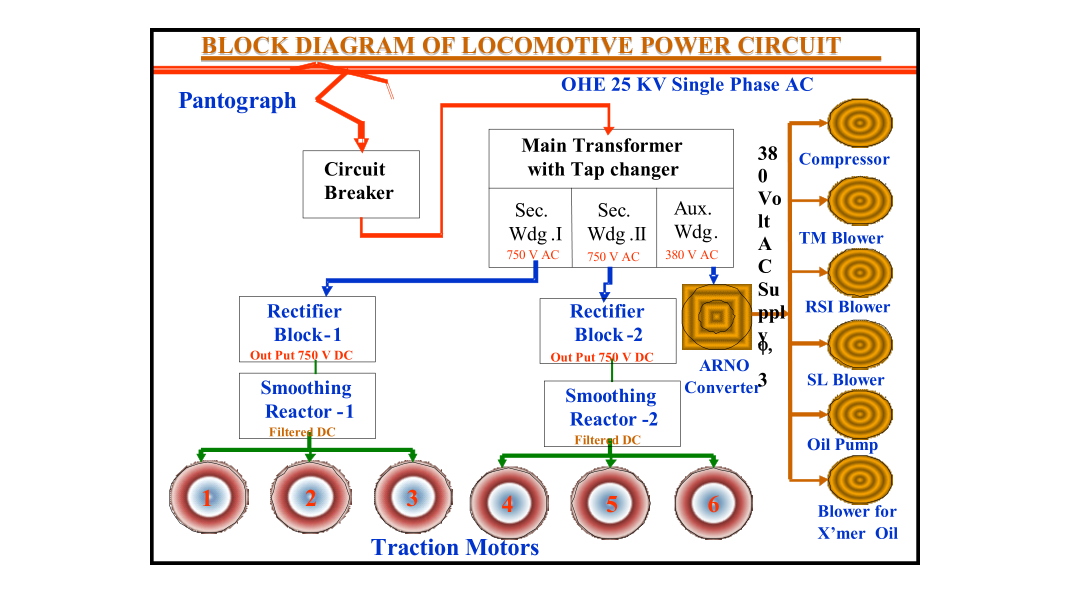
Power Circuit in AC Electric Locomotive
The electric locomotive draws power from the over head equipment (OHE) with the help of Pantograph and converts this electrical energy to mechanical energy, in controlled manner, through Traction Motors which drive the axles.
To enable the locomotive to perform this task, it is equipped with suitable equipment, which enable loco pilot to control the speed of the train as per requirement by controlling the applied voltage to traction motors.
In conventional locomotives, 25KV, Single phase, AC supply is collected by a roof-mounted pantograph from the OHE and is stepped down by a transformer inside the locomotive.
This supply is then converted to DC supply by a full wave silicon rectifier and associated smoothing filter before being fed to the traction motors.
Torque / speed control is achieved by variation of the AC input voltage to the rectifier through an on-load tap changing arrangement on the primary winding of the loco transformer.
The equipment on electric locomotive, depending up on where it is located, can be classified in three different categories viz.
- Roof equipment,
- Inside equipment and
- Under Frame equipment
Both the roof and the under frame equipment are subjected to lot of dust and atmospheric pollution and are therefore designed to withstand these severe working conditions.
1. Roof Equipment:
Pantograph
The High Tension current (25 kV) for feeding locomotive is taken from contact wire by means of current collecting device called pantograph. Each loco is provided with two similar pantographs on the roof. As a practice, the rear pantograph is generally used.
Circuit Breaker (Air blast circuit breaker, Vacuum circuit breaker)
When the
Circuit breaker closed manually through remote control, OHE supply collected by pantograph is made available to the main transformer in side the locomotive.
It opens automatically in case of over current or earth fault in the loco under the action of protective devices.
Now,
air blast circuit breakers are being replaced by vacuum circuit breaker (VCB) due to its superior qualities and less maintenance.
2. Inside Equipment:
Voltage regulating equipment:
The high OHE voltage is stepped down to low voltage by the main transformer comprising of an Autotransformer with 32 taps and a stepped down transformer with two separate secondary windings.
The low voltage can be controlled from Zero to Maximum through on load tap changer which can be compared with a fan regulator used to control the fan speed.
Silicon Rectifiers
Since the traction motors are
DC motors, alternating current supplied by secondary windings of main transformer is converted in to direct current by means of two silicon rectifiers (RSI), one each feeding to set of three traction motors.
ARNO converter :
ARNO converter converts the single-phase 380 Volt input from transformer auxiliary winding to 3 phase 380 Volt output.
The three-phase output of ARNO converter is supplied to various auxiliary motors provided for supplying compressed air, creating a vacuum in train and cooling of electrical equipment such as Traction motors, smoothing reactor, rectifier block, main transformer etc.
3. Under frame equipment
Traction Motors
In general, the locomotive is provided with six DC series type traction motors(TMs).
These TMs are mounted in two under frame bogies coupled with wheels through pinion-gear arrangement.
Smoothing reactor
As output of rectifier is of undulating (Pulsating) nature, it is passed through an inductive choke called smoothing reactor (SL) to reduce the undulation of the current and to make current smoother.
4. Brakes
Loco is provided with following brakes:
- Air brake system
- Independent brake
- Proportionate brake
- Dynamic (Rheostatic) brake
- Regenerating brake
Working of DC Electric Locomotive
In DC locomotives, the speed of DC traction motors is controlled by connecting all the traction motors in series during starting period and introducing starting resistances.
These starting resistances are gradually cut out from the circuit and the voltage across the traction motors gradually increased.
This is further followed by changing motor combinations from series to series parallel and finally all the motors are connected in parallel so that loco can haul the train at its maximum permissible speed.
Advantages of Three Phase Induction Motors over DC Motors
Nowadays DC motors are largely replaced by Three Phase Induction Motors due to their advantages over DC motors. Some of them are pointed below.
- Three Phase Induction Motors are robust & require little maintenance.
- Due to the absence of a commutator, its peripheral speed puts no limit on the speed of the motor. AC traction motors can easily operate at 4000 RPM in contrast to DC motors which normally operate at speeds of 2400 RPM.
- The limit imposed due to bar to bar voltage for DC commutator is eliminated in induction motors. This means that the whole power flow from the transformer to the motor is chosen at higher operating voltages.
- Against a nominal system of 750 volts, 1000 ampere with DC motor, the three-phase motor works at around 2800 volts, 300 amperes. With the heavy reduction in operating current, power cables & switch gears are much lighter thereby losses are reduced.
- The power to weight ratio of three-phase traction motor is much higher than the DC motor -1500 kW per axle can be packed with these motors.
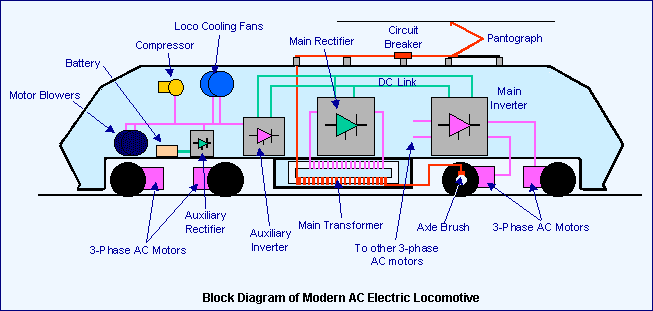
Working Of Three-Phase Locomotive

25 kV overhead AC supply is stepped down with the main transformer in the locomotive and fed to a front end (line) twin 4-quadrant line converter where AC is converted to DC through Pulse Width Modulation( PWM) thus achieve unity power factor.
This supply is linked with an input side converter through DC link which is a reservoir of energy.
Drive converter (VVVF Converter) converts DC supply into 3 phase which is then fed to 3 phase traction motors.
Gate turn off (GTO) thyristors are used in converter/inverter.
The output of Drive converter (inverter) is Variable Voltage Variable Frequency (VVVF) supply which helps in controlling the starting and running torques of three-phase traction motors to suite traffic requirements.
Drawback of Electric Locomotive
Electric locomotives have this major drawback of being totally dependent on the power which has to be supplied for it to run.
Any power outage,
short circuit or breaking of Overhead Equipment (OHE) will cause trains to come to a standstill. Hence, even on fully electrified routes,
diesel locomotives are kept on standby always. And on partly electrified routes, trains are run on diesel under the wire because it is more efficient than switching locomotives.






Comments are closed.