A DC motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. DC motor working is based on the principle that when a current carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a mechanical force.
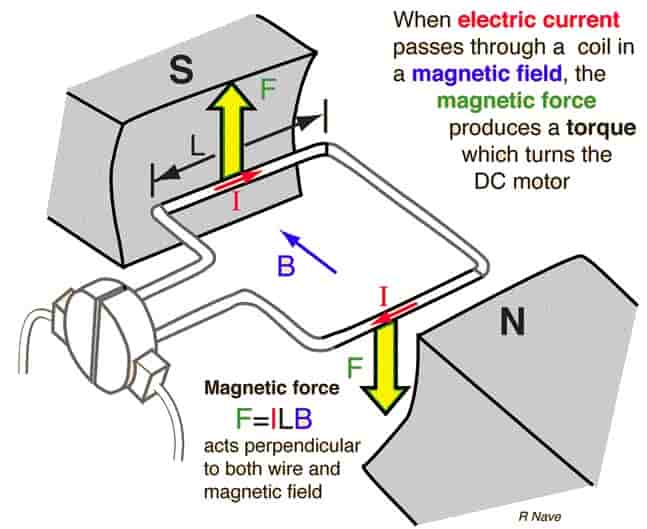
The direction of the mechanical force is given by Fleming’s Left-hand Rule and its magnitude is given by F = BIL Newton.
The working of the AC motor (Induction motor and Synchronous Motor) is different from the DC motor.

There is no basic difference in the construction of a DC generator and a DC motor. In fact, the same DC machine can be used interchangeably as a generator or as a motor.
Like generators, there are different types of DC motors which are also classified into shunt-wound, series-wound and compound-wound dc motors.
DC motors are seldom used in ordinary applications because all electric supply companies furnish alternating current.
However, for special applications such as in steel mills, mines, and electric trains, it is advantageous to convert alternating current into direct current in order to use dc motors. The reason is that the speed/torque characteristics of DC motors are much more superior to that of AC motors.
Therefore, it is not surprising to note that for industrial drives, DC motors are as popular as three-phase induction motors.
DC Motor Principle
A machine that converts DC electrical power into mechanical power is known as a Direct Current motor.
DC motor working is based on the principle that when a current carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field, the conductor experiences a mechanical force.
The direction of this force is given by Fleming’s left-hand rule and magnitude is given by;
F = BIL Newtons
According to Fleming’s left-hand rule when an electric current passes through a coil in a magnetic field, the magnetic force produces a torque that turns the DC motor.
The direction of this force is perpendicular to both the wire and the magnetic field.
Basically, there is no constructional difference between a DC motor and a DC generator. The same DC machine can be run as a generator or motor.
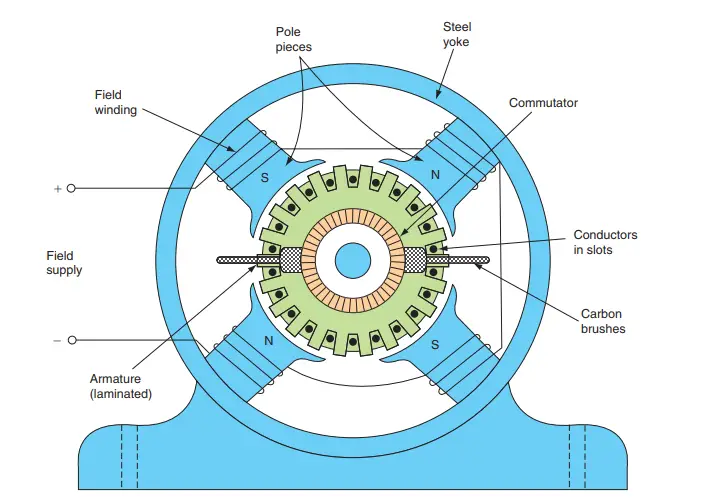
Working of DC Motor
Consider a part of a multipolar DC motor as shown in the figure below. When the terminals of the motor are connected to an external source of DC supply:
- the field magnets are excited developing alternate North and South poles
- the armature conductors carry currents.
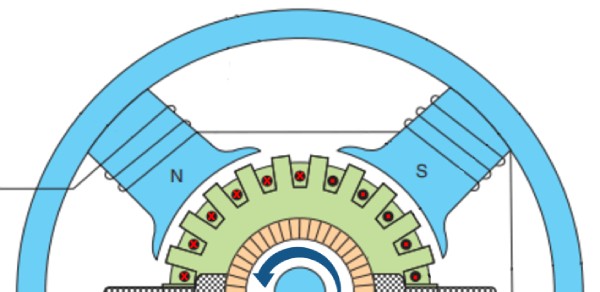
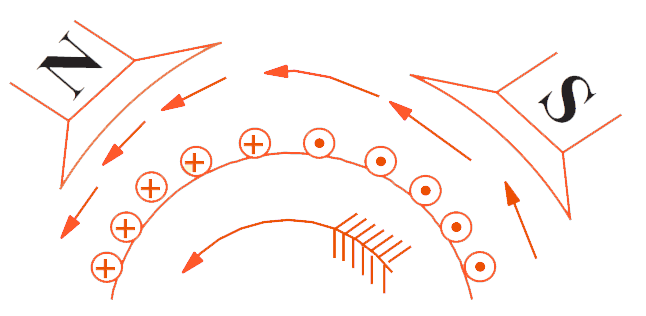
All conductors under North-pole carry currents in one direction while all the conductors under South-pole carry currents in the opposite direction.
The armature conductors under N-pole carry currents into the plane of the paper (denoted as ⊗ in the figure). And the conductors under S-pole carry currents out of the plane of the paper (denoted as ⨀ in the figure).
Since each armature conductor is carrying current and is placed in the magnetic field, a mechanical force acts on it.
On applying Fleming’s left-hand rule, it is clear that force on each conductor is tending to rotate the armature in the anticlockwise direction. All these forces add together to produce a driving torque which sets the armature rotates.
When the conductor moves from one side of a brush to the other, the current in that conductor is reversed. At the same time, it comes under the influence of the next pole which is of opposite polarity. Consequently, the direction of the force on the conductor remains the same.
It should be noted that the function of a commutator in the motor is the same as in a generator. By reversing current in each conductor as it passes from one pole to another, it helps to develop a continuous and unidirectional torque.
Working Animation of DC Motor
Watch the working of DC motor by learnengineering.org in this video.
Next: Back EMF in DC Motor






Comments are closed.