What is an ACB?
A circuit breaker in which the contacts open and close in the air at atmospheric pressure is defined as an Air Circuit Breaker. The working of air circuit breakers is similar to miniature circuit breakers.
Air Circuit Breaker is a switchgear device used to provide Overcurrent and Short Circuit Protection for circuits ranging from 800 Amps to 10000 Amps.
One should not be confused between Air Circuit Breaker and Air Blast Circuit Breaker.
Air Circuit Breakers are usually used in low voltage applications below 450 volts. You can today find these in Distribution Panels (below 450 volts).
Air Blast Circuit Breakers are high capacity breakers and can be seen in old substations mainly above 132 kV. The working principle of these two circuit breakers is quite different. Here we will only discuss the working of Air Circuit Breaker (ACB).
Working of Air Circuit breaker
We have already discussed the working of the circuit breaker in another article. In this section, we will discuss the working of the air circuit breaker.
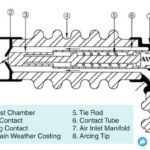
Air Circuit breakers normally have two pairs of contacts. The main pair of contacts carry the current at normal load and these contacts are made of copper. The additional pair is the arcing contact and is made of carbon.
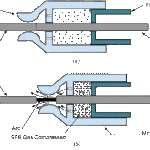
When the circuit breaker is being opened, the main contacts open first and during the opening of main contacts the arcing contacts are still in touch with each other.
As the current gets. a parallel low resistive path through the arcing contact during the opening of main contacts. there will not be any arcing in the main contact.
The arcing is only initiated when finally the arcing contacts are separated. Each of the arc contacts is fitted with an arc runner which helps the arc discharge to move upward due to both thermal and electromagnetic effects as shown in the figure.
As the arc is driven upward it enters in the arc chute, consisting of splatters. The arc in chute will become colder, lengthen and split hence arc voltage becomes much larger than system voltage at the time of operation of the air circuit breaker, and therefore the arc is quenched finally during the current zero.
Types of Air circuit Breaker
The Electrically operated motor is used to operate the spring charging mechanism for closing and opening the Circuit Breaker.
The power supply could be single-phase 230V AC Supply or low voltage 24V-110V DC supply for operation during no availability of power.
Air Circuit breakers (ACBs) are also available as Fixed Type and Withdrawable (Drawout) Type formats.





Comments are closed.