What is Voltage Surge or Transient Voltage?
The sudden rise in voltage for a very short duration on power system is known as voltage surge or transient voltage.
Surges or transients can damage, degrade, or destroy electronic equipment within any home, commercial building, industrial, or manufacturing facility. Transients can reach amplitudes of tens of thousands of volts. Surges are generally measured in microseconds (μs).
How does Surges Occur?
Transients or surges are of temporary nature and exist for a very short duration (a few hundred microseconds) but they cause overvoltages on the power system.
They originate from switching and from other causes but by far the most important transients are those caused by lightning striking a transmission line. When lightning strikes a line, the surge rushes along the line, just as a flood of water rushes along a narrow valley when the retaining wall of a reservoir at its head suddenly gives way.
In most of the cases, such surges may cause the line insulators (near the point where lightning has struck) to flash over and may also damage the nearby transformers, generators or other equipment connected to the line if the equipment is not suitably protected.
Lightning Surge
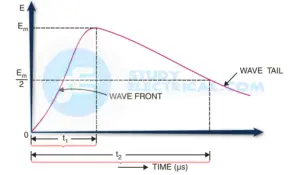
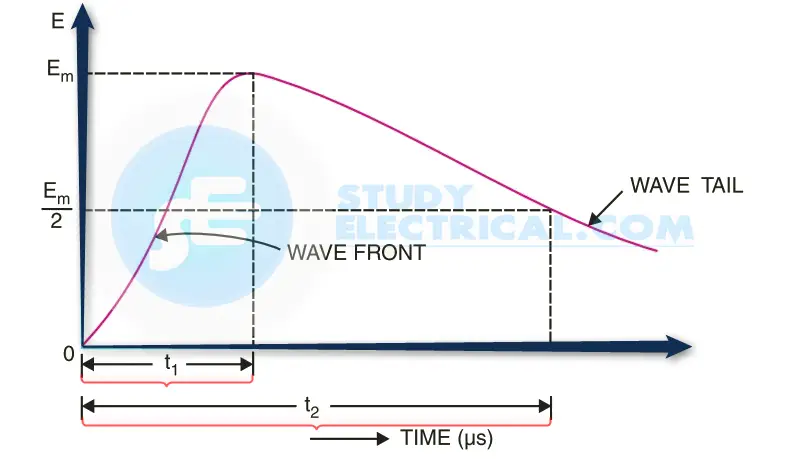
Waveform of a typical lightning Surge
The figure above shows the waveform of a typical lightning surge. The voltage build-up is taken along the y-axis and the time along the x-axis.
It may be seen that lightning introduces a steep-fronted wave. The steeper the wavefront, the more rapid is the build-up of voltage at any point in the network. In most of the cases, this build-up is comparatively rapid, being of the order of l-5 μs.
Voltage surges are generally specified in terms of the rise time t1 and the time t2 to decay to half of the peak value. For example, a 1/50μs surge is one which reaches its maximum value in 1μs and decays to half of its peak value is 50μs.
Causes of Surges
60-80% of surges are created within a facility. A common source for surges generated inside a building are devices that switch power on and off. This can be anything from a simple thermostat switch operating a heating element to a switch-mode power supply found on many devices. Surges that originate from outside the facility include those due to lightning and utility grid switching.