What is the Rectifier Transformer?
Rectifier transformers are different from normal power and distribution transformers because they are special transformers made for industrial application. A Rectifier transformer is a special application transformer which includes diodes and thyristors in the same tank.
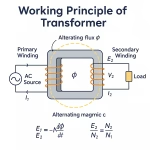
Power electronic circuits that convert alternating current (ac) to direct current (dc) is called rectifier circuits. Similarly, the circuits which can convert direct current to alternating current are called inverter circuits. Both of these circuits are considered to be converters.
A transformer that has one of its windings connected to one of these converter circuits, as a dedicated transformer, is a rectifier transformer or converter transformer.

The figure shown is a Siemens made rectifier transformer used in an aluminium plant.
Some other special industrial purpose transformers are Electric arc furnace transformers (EAF), DC electric arc furnace transformers (DC EAF), Converter Transformers, Line Feeders.
Read: Substation Equipment and their working
Where Rectifier Transformers are Used?
Today, there are numerous applications that require transformers to supply rectifiers with ever-increasing levels of power.
The classic example is provided by those industries that use electrolysis processes for the production of aluminum, and the high secondary currents, together with the harmonic currents generated by the rectification systems, must be taken into account fully when designing transformers to power such loads.
Another typical use of rectifiers is in electric traction systems in railways and subways.
They are also used in variable-speed-drive motor controls, transit traction applications, mining applications, electric furnace applications, higher-voltage laboratory-type experiments, high-voltage direct-current power transmission (HVDC), static precipitators, and others.
Operation of Rectifier Transformers
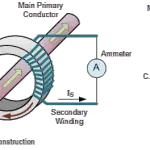
Two types of rectifiers are available: thyristor rectifiers and diode rectifiers.
In both cases, the transformers that power them must supply a gradually adjustable secondary voltage, which is normally produced via on-load tap changers (OLTC).
In cases in which the range of secondary voltages is high, the variation is produced through a regulation transformer, which can be located in a separate tank or in the same tank as the main transformer.
Dry type transformers were primarily used in distribution-voltage classes.
Dry type and cast coil — are limited by voltage and kVA size. However, liquid-immersed transformers can be built to all voltage levels and current levels. High-fire-point fluids can be used for fire-protection considerations.
Voltage regulation is achieved with no-load or on-load tap changers on the high voltage side. Fine levels of voltage regulation can be achieved using saturable reactors on the secondary side. Regulation units may be built in or separate.