Moulded Case Circuit Breaker is an electromechanical device which protects a circuit from overcurrent and short circuit. It provides overcurrent and short circuit protection for circuits ranging from 63 Amps up to 3000 Amps.
The primary function of an MCCB is to provide a means to manually open a circuit and automatically open a circuit under overload or short circuit conditions. The overcurrent, in an electrical circuit, may result from short circuit, overload or faulty design.
It is generally installed on the secondary side of transformer stations (main switch or for protecting individual branches). In industry, we can use it in switchgear or for protecting the motors as well we have big requirements in shipbuilding. For building applications, you can find it as the main protection switch.
Definition
The Molded Case Circuit Breaker is a specific type of circuit breaker.
NEMA defines Molded Case Circuit Breaker as devices designed to open or close a circuit by nonautomatic means and to open the circuit automatically on a predetermined overcurrent without damage to itself when properly applied within its rating.
The term “molded case” simply refers to the construction of the circuit breaker and refers to the fact that the circuit breaker is an assembled unit in a supporting housing of insulating material.
Read: Miniature Circuit Breaker
MCCB vs Fuse
MCCB is an alternative to a fuse since it does not require replacement once an overload is detected.
Unlike a fuse, an MCCB can be easily reset after a fault and offers improved operational safety and convenience without incurring the operating cost.
Difference between MCCB and ELCB
ELCB ( Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker ) is a type of Moulded Case Circuit Breaker.
ELCB is a molded case circuit breaker used in a low-voltage AC electrical circuit to provide electric shock protection and prevent fires from current leakages.
ELCB is called a “Circuit-breaker incorporating residual current protection” (IEC60947-2) or a “Residual current operated circuit breaker” (IEC61009-1). It is also referred to as a “Ground-fault circuit-interrupter”.
There are two types of ELCB, a current-operated type, and a voltage-operated type. In many countries, only the more beneficial current operating-type is manufactured
Construction of MCCB
A Moulded case circuit breaker generally have
- A thermal element for overcurrent and
- A magnetic element for short circuit release which has to operate faster.
MCCBs are manufactured such that end user will not have access to internal workings of the over-current protection device.
Generally constructed of two pieces of heavy-duty electrically insulated plastic, these two halves are riveted together to form the whole. Inside the plastic shell is a series of thermal elements and a spring-loaded trigger.
When the thermal element gets too warm, from an overcurrent situation, the spring trips, which in turn will shut off the electrical circuit.
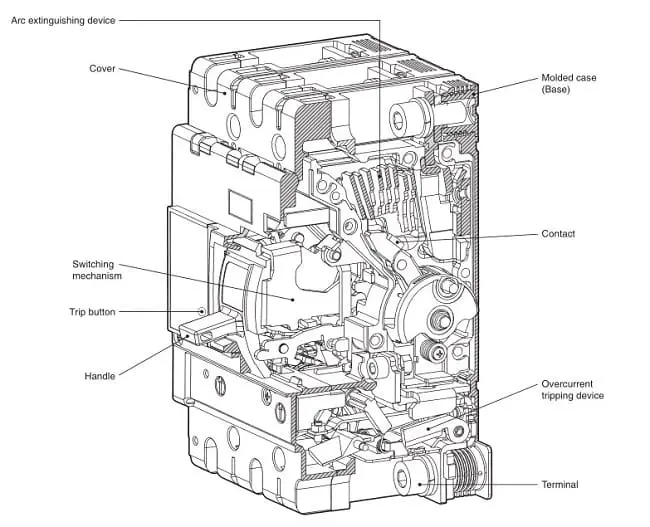
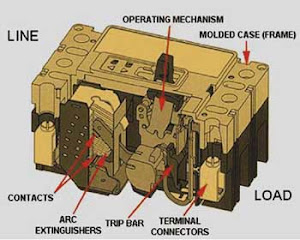
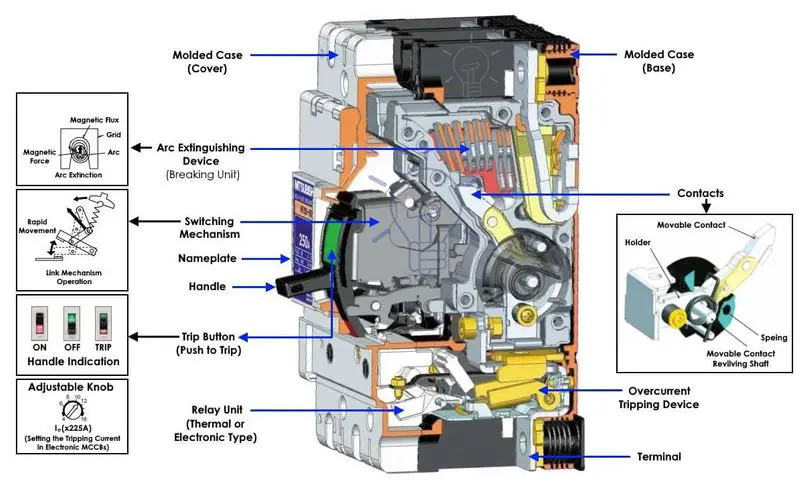
The major components of MCCB include
- a mechanism which makes and breaks a contact through a toggle link mechanism having a spring which can store tripping force,
- an overcurrent trip device which reacts with overcurrent and short circuit current and trips MCCB,
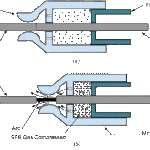
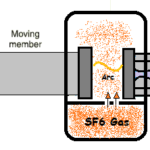
- an Arc extinguishing device which extinguishes the arc generated upon current interruption,
- terminals for connecting wires and conductors,
- contacts which open and close the circuit and
- a moulded case in which these components are integrated and compactly contained.
Types of MCCB
The larger moulded case circuit breaker has an adjustable range setting on the face of the device. Moulded case circuit breakers can range in size from 32amperes up to 3000 amperes.
Moulded Case Circuit Breakers have the following Specifications
Current Rating – Amperes
Current Setting Range – Amperes
Short Circuit Rating – Kilo Amperes (KA)
operating Characteristics – Normal / Current Limiting Type
MCCBs are now available with a variety of Releases or Operating Mechanisms these are given below
- Thermal Magnetic Release
- Electronic Release
- Microprocessor Release
1. Thermal Magnetic Release MCCB
Thermal-magnetic circuit breakers use bimetals and electromagnetic assemblies to provide overcurrent protection.
Their characteristic inverse time-tripping under overload conditions is ideally suited for many applications varying from residential to heavy industrial loads.

For higher level (short circuit) over-currents, instantaneous trip characteristics allow moulded case circuit breaker to interrupt with no intentional delay.
The adjustable overload protection is from 70% to 100% of the nominal current and short circuit setting from 5 to 10 times the rated current is possible.
The minor disadvantage of the release is that operating characteristics of the breaker may vary depending on the ambient temperature.
2. Electronic Release MCCB
Electronic or Static Release Moulded Case circuit breakers use power electronic circuitry to provide overcurrent protection.

The Continuous adjustable overload protection from 60% to 100% of the nominal current and short circuit setting from 2 to 10 times the rated current is possible.
The advantage Of the release is that operating characteristics of the breaker is independent of the ambient temperature.
This wide flexibility takes care of future increases in load capacity of installation and ensures better planning at an optimum cost.
3. Microprocessor release MCCB
Microprocessor release Moulded Case circuit breaker use microprocessors to provide overcurrent protection.

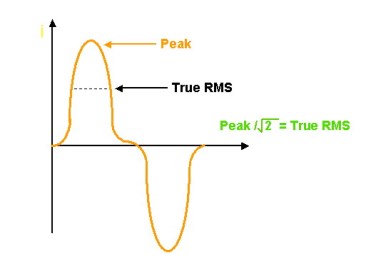
The Microprocessor release works on monitoring of current True R.M.S value. It is simulated and calculated from peak values, which installed microprocessor, can detect.
There is high Flexibility through multiple adjustments of protection settings, High repeat accuracy, and High reliability.
Time delays can be provided for Short Circuit Release better discrimination and co-ordination using LCD display. System Diagnosis is possible as it stores the Trip history within the internal memory. Trip current indication is also available for the understanding of the type of fault and set-up programming at the site.
Reference: Siemens USA





Comments are closed.