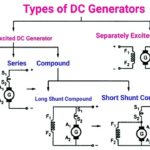
Like DC generators, there are different types of DC motors characterized by the connections of the field winding in relation to the armature. They are
- Shunt Wound DC Motor
- Series Wound DC Motor
- Compound Wound DC Motor
- Short Shunt Connection
- Long Shunt Connection
- Permanent Magnet DC Motor
- Separately Excited DC Motor
Shunt Wound DC Motor
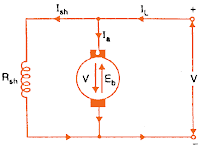
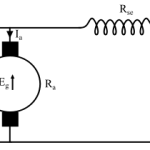
A shunt-wound motor is a type of dc motor in which the field winding is connected in parallel with the armature.
Like DC generators, there are different types of DC motors characterized by the connections of the field winding in relation to the armature. They are
- Shunt Wound DC Motor
- Series Wound DC Motor
- Compound Wound DC Motor
- Short Shunt Connection
- Long Shunt Connection
- Permanent Magnet DC Motor
- Separately Excited DC Motor
The current through the shunt field winding is not the same as the armature current. Shunt field windings are designed to produce the necessary m.m.f. by means of a relatively large number of turns of wire having high resistance. Therefore, the shunt field current is relatively small compared with the armature current.
Series Wound DC Motor
A series-wound DC motor is one type of dc motor in which the field winding is connected in series with the armature.
Therefore, the series field winding carries the armature current. Since the current passing through a series field winding is the same as the armature current, series field windings must be designed with much fewer turns than shunt field windings for the same MMF. Therefore, a series field winding has a relatively small number of turns of thick wire and, therefore, will possess a low resistance.
Compound Wound DC Motor
The compound motor is the basis of a shunt motor with series windings, in which the source current is passed in the short compound motor or the current of the armature in the long compound motor. In a certain direction so that the effect of the magnetic field given by these coils is in the magnetic field of shunt windings. Thus, the motor acquires certain properties for speed and torque.
The compound motor can be used to obtain high torque and constant speed, which are not significantly affected by the change in load as in moving locomotives, electric buses, and printing machines
The compound-wound DC motor which has two field windings:
- One winding is connected in parallel with the armature
- The other winding is connected in series with it.
There are two types of compound motor connections (like generators).
- Short Shunt Connection
- Long Shunt Connection
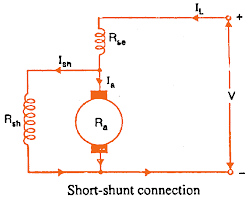
1. Short Shunt Compound DC Motor
When the shunt field winding is directly connected across the armature terminals, it is called a short-shunt connection.
2. Long Shunt Compound DC Motor
When the shunt winding is so connected that it shunts the series combination of armature and series field, it is called a long-shunt connection.
The compound machines (generators or motors) are always designed so that the flux produced by shunt field winding is considerably larger than the flux produced by the series field winding. Therefore, the shunt field in compound machines is the basic dominant factor in the production of the magnetic field in the machine.
Permanent Magnet (PMDC) motors
The stator is a permanent magnet, so the motor is smaller in size. They are commonly used as a starter motor in automobiles, windshield wipers, washers, blowers used in heaters and air conditioners, to raise and lower windows – and they are extensively used in toys.
In a PMDC motor, the field is produced by a permanent magnet, there is no need for drawing field coils in the equivalent circuit of a permanent magnet DC motor.
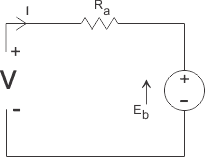
A disadvantage is these motors are only used for low torque applications.
Separately Excited motor
A separately excited dc motor is a motor whose field circuit is supplied from a separate constant-voltage power supply, while a shunt dc motor is a motor whose field circuit gets its power directly across the armature terminals of the motor. When the supply voltage to a motor is assumed constant, there is no practical difference in behavior between these two machines.
This gives another degree of freedom for controlling the motor over the shunt.