What is Back EMF?
When the armature of a DC motor rotates under the influence of the driving torque, the armature conductors move through the magnetic field and hence emf is induced in them as in a generator.
The induced emf acts in opposite direction to the applied voltage V (Lenz’s law) and is known as Back EMF or Counter EMF (Eb).
The equation to find out back emf in a DC motor is given below,
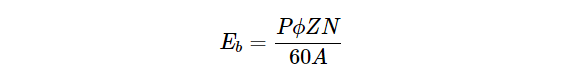 The back emf Eb(= PΦZN/60 A) is always less than the applied voltage V, although this difference is small when the motor is running under normal conditions.
The back emf Eb(= PΦZN/60 A) is always less than the applied voltage V, although this difference is small when the motor is running under normal conditions.
Voltage and Power Equations of DC Motor
Working Principle of DC Motor
How Back EMF Occur in DC Motor
In this section, we will understand how back emf occur in DC motor. For better understanding please read Working of DC Motor before continuing.
Consider a shunt wound dc motor as shown in the figure below.
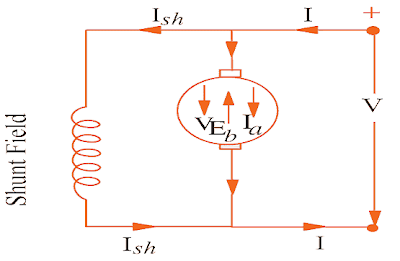
When dc voltage V is applied across the motor terminals, the field magnets are excited and armature conductors are supplied with current.
Therefore, driving torque acts on the armature which begins to rotate. As the armature rotates, back emf Eb is induced which opposes the applied voltage V.
The applied voltage V has to force current through the armature against the back emf Eb.
The electric work done in overcoming and causing the current to flow against Eb is converted into mechanical energy developed in the armature.
It follows, therefore, that energy conversion in a dc motor is only possible due to the production of back emf Eb.
Net voltage across armature circuit = V – Eb
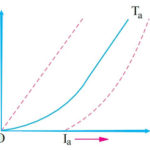
Since V and Ra are usually fixed, the value of Eb will determine the current drawn by the motor.
If the speed of the motor is high, then back e.m.f. Eb (= PφZN/60 A) is large and hence the motor will draw less armature current and vice-versa.
The significance of Back EMF
Back emf is very significant in the working of a dc motor.
The presence of back emf makes the d.c. motor a self-regulating machine i.e., it makes the motor to draw as much armature current as is just sufficient to develop the torque required by the load.
Armature current (Ia),
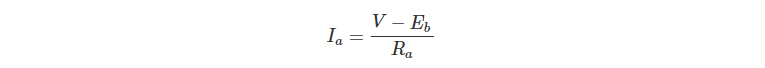
When the motor is running on no load, small torque is required to overcome the friction and windage losses. Therefore, the armature current Ia is small and the back emf is nearly equal to the applied voltage.
If the motor is suddenly loaded, the first effect is to cause the armature to slow down. Therefore, the speed at which the armature conductors move through the field is reduced and hence the back emf Eb falls.
The decreased back emf allows a larger current to flow through the armature and larger current means increased driving torque.
Thus, the driving torque increases as the motor slows down. The motor will stop slowing down when the armature current is just sufficient to produce the increased torque required by the load.
If the load on the motor is decreased, the driving torque is momentarily in excess of the requirement so that armature is accelerated.
As the armature speed increases, the back emf Eb also increases and causes the armature current Ia to decrease. The motor will stop accelerating when the armature current is just sufficient to produce the reduced torque required by the load.
Therefore, the back emf in a DC motor regulates the flow of armature current i.e., it automatically changes the armature current to meet the load requirement.
Find more articles related to DC Motor





Comments are closed.