The losses in a DC machine (generator or motor) may be divided into three classes viz
- Copper losses
- Iron or core losses and
- Mechanical losses.
All these losses in dc machine appear as heat and thus raise the temperature of the machine. They also lower the efficiency of the machine.
Read: Construction of DC machines
Copper losses
Copper losses is one of the losses in dc machine that occurs due to currents in the various windings of the machine.
- Armature copper loss = Ia2Ra
- Shunt field copper loss = Ish2Rsh
- Series field copper loss = Ise2Rse
Note. There is also brush contact loss due to brush contact resistance (i.e., the resistance between the surface of brush and surface of commutator). This loss is generally included in armature copper loss.
Iron or Core losses
Iron losses are another type of losses in DC machine that occur in the armature of a DC machine and are due to the rotation of armature in the magnetic field of the poles. They are of two types viz.,
- hysteresis loss
- eddy current loss.
(i) Hysteresis loss
Magnetic hysteresis loss occurs in the armature of the DC machine since any given part of the armature is subjected to magnetic field reversals as it passes under successive poles.
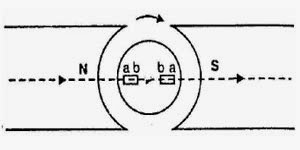
Figure shows an armature rotating in a two-pole machine. Consider a small piece ab of the armature. When the piece ab is under N-pole, the magnetic lines pass from a to b.
Half a revolution later, the same piece of iron is under S-pole and magnetic lines pass from b to a so that magnetism in the iron is reversed.
Bmax = Maximum flux density in armature
f = Frequency of magnetic reversals = NP/120 (where N is in r.p.m.)
V = Volume of armature in m3
h = Steinmetz hysteresis co-efficient
In order to reduce this loss in a DC machine, armature core is made of such materials which have a low value of Steinmetz hysteresis co-efficient e.g., silicon steel.
(ii) Eddy current loss
In addition to the voltages induced in the armature conductors, there are also voltages induced in the armature core. These voltages produce circulating currents in the armature core as shown in figure. These are called eddy currents and power loss due to their flow is called eddy current loss.
The eddy current loss appears as heat which raises the temperature of the machine and lowers its efficiency.
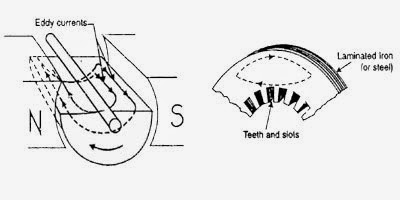
If a continuous solid iron core is used, the resistance to eddy current path will be small due to large cross-sectional area of the core. Consequently, the magnitude of eddy current and hence eddy current loss will be large.
The magnitude of eddy current can be reduced by making core resistance as high as practical.
The core resistance can be greatly increased by constructing the core of thin, round iron sheets called laminations. The laminations are insulated from each other with a coating of varnish. The insulating coating has a high resistance, so very little current flows from one lamination to the other.
Also, because each lamination is very thin, the resistance to current flowing through the width of a lamination is also quite large. Thus laminating a core increases the core resistance which decreases the eddy current and hence the eddy current loss.
where,
Ke = Constant depending upon the electrical resistance of core and system of units used
Bmax = Maximum flux density in Wb/m2
f = Frequency of magnetic reversals in Hz
t = Thickness of lamination in m
V = Volume of core in m³
It may be noted that eddy current loss depends upon the square of lamination thickness. For this reason, lamination thickness should be kept as small as possible.
Mechanical losses
Mechanical losses are another type of losses in dc machine. These losses are due to friction and windage.
- friction loss – e.g., bearing friction, brush friction etc.
- windage loss – i.e., air friction of rotating armature.
These losses depend upon the speed of the machine. But for a given speed, they are practically constant.
Note. Iron losses and mechanical losses together are called stray losses

Comments are closed.