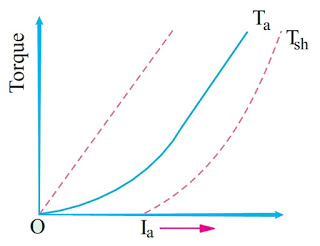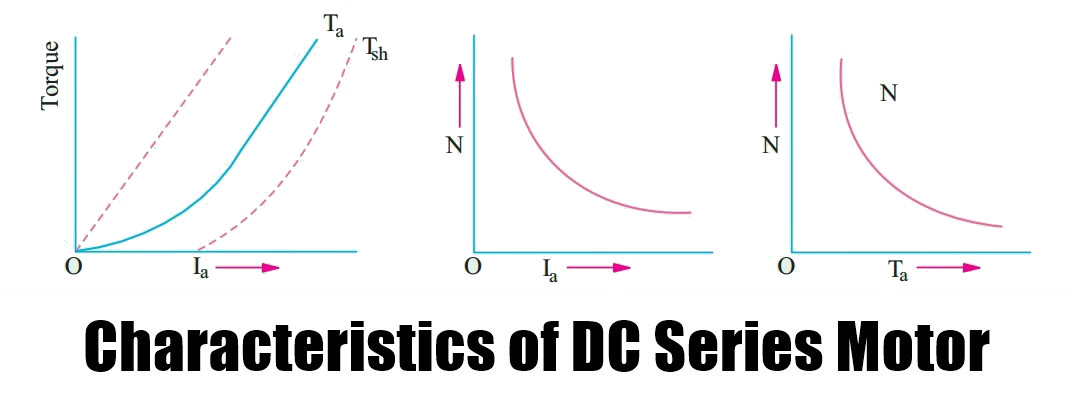
- Torque and armature current (Ta/Ia characteristic). It is known as an electrical characteristic.
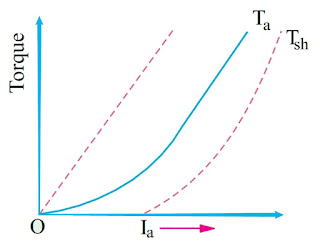
- Speed and armature current (N/Ia characteristic)
- Speed and torque (N/Ta characteristic) It is also known as mechanical characteristic. It can be found from (1) and (2) above.
While discussing dc motor characteristics, the following two relations should always be kept in mind :
Ta ∝ ΦIa and
N ∝ Eb/Φ
Ta/Ia Characteristic (Electrical)
We have seen that in series motor Ta ∝ ΦIa. In a series motor, as field windings also carry the armature current, Φ ∝ Ia up to the point of magnetic saturation. Hence, before saturation,
Ta ∝ ΦIa and ∴ Ta ∝ Ia2
At light loads, Ia and hence Φ is small. But as Ia increases, Ta increases as the square of
the current. Hence, Ta/Ia curve is a parabola as shown in the figure.
After saturation, Φ is almost independent of Ia hence Ta ∝ Ia only. So the characteristic becomes a straight line. The shaft torque Tsh is less than armature torque due to stray losses. It is shown dotted in the figure.
So we conclude that (prior to magnetic saturation) on heavy loads, a series motor exerts a torque proportional to the square of armature current.
Hence, in cases where huge starting torque is required for accelerating heavy masses quickly as in hoists and electric trains, etc., series motors are used.
N/Ia Characteristic
N ∝ Eb/Φ

When the load is heavy, Ia is large. Hence, speed is low (this decreases Eb and allows more armature current to flow).
But when load current and hence Ia falls to a small value, speed becomes dangerously high. Hence, a series motor should never be started without some mechanical (not belt-driven) load on it otherwise it may develop excessive speed and get damaged due to heavy centrifugal forces so produced.
It should be noted that the series motor is a variable speed motor.
N/Ta Characteristic (Mechanical)
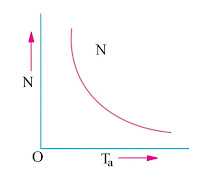
It is found from above that when speed is high, torque is low and vice-versa.
It is clear that series motor develops high torque at low speed and vice-versa.
It is because an increase in torque requires an increase in armature current, which is also the field current. The result is that flux is strengthened and hence the speed drops