A lightning arrester is connected to protect a piece of equipment from lightning and switching surges.
Overvoltages may cause the burning of insulation of substation equipment if not well protected. Lightning is one of the most serious causes of overvoltages.
There are various types of lightning arrester construction. They are
- Rod gap LA
- Expulsion type LA
- Valve type LA
- Horn gap LA
- Pellet type LA
- Thyrite type LA, etc.
- It must not take any current at normal system voltage
- Any transient wave with a voltage peak exceeding the spark over voltage must cause it to break down.
- After the breakdown, it must be capable of carrying the resulting discharge current without any damage to itself and without voltage across it exceeding the breakdown voltage.
- The power frequency current following the breakdown must be interrupted as soon as the transient voltage has fallen below the breakdown value.
Location of Lightning Arrester
-
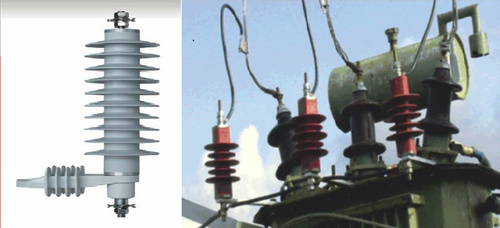
Lightning Arrester on a Transformer
In large substations, arrestors should be installed at take-off points of the lines and of the terminal apparatus.
Many factors like system voltages, basic impulse insulation level, arrestor rating, station layout, number and arrangement of lines, the position of isolators, the distance between equipment, etc. have to be taken into account in fixing the location of the arrestors.
The length of the arrester lead should be as low as possible and should not exceed 10M.
The Arresters are installed both on the High Voltage and Low Voltage side of the transformers. Junction of an OH line and the cable should be protected by LA. Separate earth should be provided for each LAs. LA ground leads should not be connected to the station earth bus.
Lightning Arrester Ratings
- Normal or rated voltage: It is designated by the maximum permissible value of power frequency voltage which it can support across its line and earth terminal while still carrying effectively and without the automatic extinction of the follow-up current. The voltage rating of the arresters should be greater than the maximum sound phase to ground voltage.
- Normal Discharge current: It is the surge current that flows through the LA after the spark over, expressed in crest value (peak value) for a specified wave shape. Example 10, 5, 2.5, 1.5, 1 kA rating.
- Power frequency spark over voltage: It is the RMS value of the power frequency voltage applied between the line and earth terminals of the arrester and earth which causes spark over of the series gap. As per IS 3070, the recommended spark overvoltage is 1.5 times the rated voltage.
Selection of LA
Here we are selecting an appropriate rating of lightning arresters for the substation.
For the protection of substation above 66kV, an arrester of 10kA rating is used.
Power frequency spark over voltage = 1.5 ×Voltage rating of LA
For 220KV side:
For 110KV side:
For 66kV Side
For 11 KV side:





Comments are closed.