The gas turbine power plant obtains its power by utilizing the energy of burnt gases and air, which is at high temperature and pressure by expanding through several rings of fixed and moving blades. It thus resembles a steam turbine.
To get a high pressure (of the order of 4 to 10 bar) of the working fluid, which is essential for expansion a compressor, is required.

The quantity of the working fluid and speed required are more, so, generally, a centrifugal or an axial compressor is employed. The turbine drives the compressor and so it is coupled to the turbine shaft.
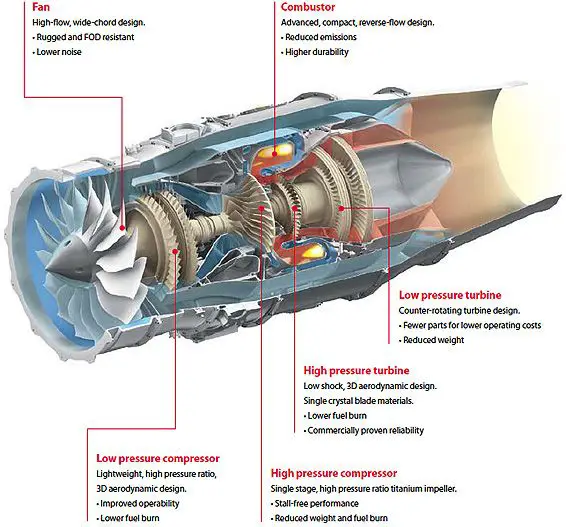
If after compression the working fluid were to be expanded in a turbine, then assuming that there were no losses in either component the power developed by the turbine would be just equal to that absorbed by the compressor and the work done would be zero.
To get a higher temperature of the working fluid a combustion chamber is required where the combustion of air and fuel takes place giving temperature rise to the working fluid.
- a compressor,
- a combustion chamber and
- a turbine.
Since the compressor is coupled with the turbine shaft, it absorbs some of the power produced by the turbine and hence lowers the efficiency. The network is, therefore, the difference between the turbine work and work required by the compressor to drive it.
Gas turbines have been constructed to work on the following: oil, natural gas, coal gas, producer gas, blast furnace, and pulverized coal.
Classification of Gas Power Plant
The gas turbine power plants which are used in the electric power industry are classified into two groups as per the cycle of operation.
- Open cycle gas turbine.
- Closed cycle gas turbine.
A simple open cycle gas turbine consists of a compressor, combustion chamber, and a turbine. The compressor takes in ambient air and raises its pressure. Heat is added to the air in the combustion chamber by burning the fuel and raises its temperature.
In a closed-cycle gas turbine plant, the working fluid (air or any other suitable gas) coming out from the compressor is heated in a heater by an external source at constant pressure.