What is the Power Plant?
A power plant is an assembly of systems or subsystems to generate electricity, i.e., power with economy and requirements. The power plant itself must be useful economically and environmentally friendly to society.
 Power or energy is generated in a power plant which is the place where power is generated from a given source.
Power or energy is generated in a power plant which is the place where power is generated from a given source.
Actually the term “generated” in the previous sentence is a misnomer since energy cannot be created or destroyed but merely changed from one form to the other.
Types of Power Plants
There are several different types of power plants used across the world today. Power plants are classified into different groups based on the criteria used for the classification.
The criteria used in this article is what source of energy is utilized to produce the electricity. Using the criteria of the source of energy for electricity production, we can broadly classify power plants to,
- Conventional Power Plants
- Non-Conventional Power Plants
Conventional power plants use conventional sources of energy while non-conventional power plants utilize non-conventional sources of energy.
Conventional Power Plants
They include the generation of electricity from conventional sources of energy. These resources are finite and exhaustible. Once consumed, these sources cannot be replaced by others. Examples include coal, timber, petroleum, lignite, natural gas, fossil fuels, nuclear fuels etc.
- Steam Engines Power Plants
- Steam Turbine Power Plants
- Diesel Power Plants
- Gas Turbine Power Plants
- Hydro Electric Power Plants
- Nuclear Power Plants
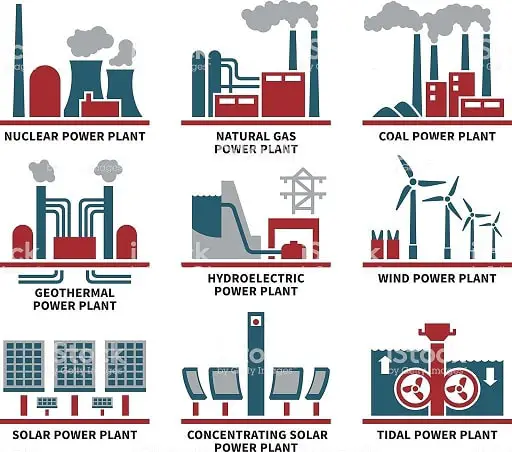
Non-Conventional Power Plants
The following are the power plants from non-conventional sources of energy.
- Thermoelectric Generator
- Thermionic generator
- Fuel-cells Power Plants
- Photovoltaic solar cells Power System
- MHD Power Plants
- Fusion Reactor NPP Power System
- Biogas, Biomass Energy Power system
- Geothermal Energy
- Wind Energy Power System
- Ocean Thermal energy conversion (OTEC)
- Wave and Tidal Wave
- Energy Plantation Scheme
A power plant may be defined as a machine or assembly of equipment that generates and delivers a flow of mechanical or electrical energy.
The main equipment for the generation of electric power is alternator. When coupling it to a prime mover runs the generator, the electricity is generated. The type of prime move determines, the type of power plants.
The major power plants are,
- Steam power plant
- Diesel power plant
- Gas turbine power plant
- Nuclear power plant
- Hydroelectric power plant
Let us have a look in these types of power stations in detail.
Steam Power Plant
As the name suggests, these power plants convert heat energy into electrical energy. The working fluid of these plants is mostly steam and they work on the Rankine cycle.
A steam power plant consists of a boiler which is used to generate the steam from water, a prime mover like a steam turbine to convert the enthalpy of the steam into rotary motion of the turbine which is linked to the alternator to produce electricity.
The steam is again condensed in the condenser and fed to the boiler again.
Hydro-Electric Power Station
Hydro-Electric Power plants use the kinetic energy of flowing water to rotate the turbine blades, hence converting kinetic energy into electrical energy. These types of power plants are very good for peak loads.
Their main disadvantage lies in the fact that their location depends on a number of factors which are beyond the control of human beings such as the hydrological cycle of the region and so forth.
If there is a shortage of water it could lead to shutting down of these plants. For this reason, alternative arrangements such as thermal power plants need to be made to ensure uninterrupted generation of power.