Definition
The connected load is the sum of the continuous ratings of all the equipment connected to the supply system.
In other words, the connected load is the sum of all the nameplate ratings of the equipment within the consumer installation.
Connected load represents the maximum possible energy consumption when all connected systems, circuits, components, devices, or equipment are simultaneously operating and drawing power. Think of it as the “worst-case scenario” when every electrical item is switched on and demanding electricity simultaneously.
For instance, in a household, the connected load would encompass the collective power requirements of all electrical appliances and devices, including lights, air conditioners, refrigerators, and more, assuming they are all running concurrently at their maximum capacity. In a manufacturing plant, it would include all machines and equipment running at full tilt.
Connected Load is essential for sizing electrical infrastructure, such as wiring, circuit breakers, transformers, and generators. It helps ensure that the electrical system can handle the peak power demands without overloading or causing safety issues.
Calculation of Connected Load
Here is an example to illustrate what is the connected load on a power station and how it is calculated. Consider a power station supplying loads to 1000 consumers. In every consumer’s home, there is certain equipment installed. “Connected load” of a consumer is the sum of the continuous ratings of all the equipment of the consumer’s premises.
For example, if each consumer of the power station has the following connections
- Five 100-watt lamps
- Two 60 watt fans
- Power socket point of 500 watts
Then the CL of one consumer is 5×100 + 2×60 + 500 = 1120 watts.
This is the Connected Load of one consumer. Similarly, every consumer has their own connected load depending on the electrical equipment used in their house.
When you add up the CL of all the consumers, you get the connected load for the power station.
Connected Load for the power station = 1120 × 1000 = 1120000 W = 1120 kW.
Connected Load vs Demand Load
Electrical load, in simple terms, refers to the total energy consumed by various components, devices, or equipment connected to a power source. It can be further divided into two: Connected Load and Operating Demand Load. These distinctions play a crucial role in efficient power management for both residential and industrial applications.
Connected Load is the energy consumed when all connected systems, circuits, components,
devices or equipment are operating and drawing power at the same time.
While Connected Load provides a critical perspective on the electrical infrastructure’s capacity requirements, it often paints an unrealistic picture of everyday energy consumption. In practice, not all electrical devices and equipment operate simultaneously at their maximum capacity. This is where Operating Demand Load comes into play.
Operating Demand Load represents a more practical and accurate estimation of energy consumption. It takes into account the likely simultaneous operation of electrical items based on real-world usage patterns. For example, in a home, it acknowledges that the furnace and air conditioning unit are unlikely to run simultaneously, as they serve opposing purposes in different seasons. Therefore, when calculating the Operating Demand Load, these two items are not added together.
In an industrial setting, Operating Demand Load considers the specific production processes, shifts, and operational schedules. It ensures that the electrical infrastructure is designed to meet the actual demands placed on it during regular operations, minimizing wasted energy and resources.
Maximum Demand
The maximum demand often referred to as peak demand can be found in the load curve is defined as the greatest of all the demands which have occurred in the power station during a given period.
The figure below shows the maximum demand in a daily load curve.
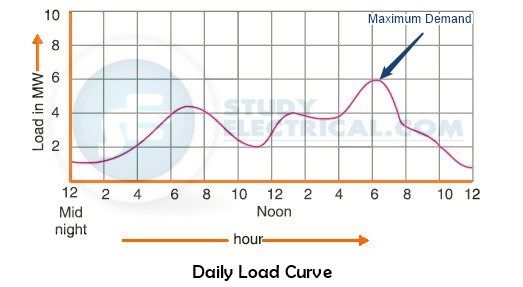
The power plant supplies power to all the loads connected to it. This does not necessarily mean that they will all receive power together. For example, you might switch off the lighting loads during the daytime. During the night, certain factory loads might be disconnected. Occasionally, some motors will turn on and off. When the long travel motor of the crane is running, the hoist motor is switched off. Therefore, in practice, the total load on at any one time is less than the total connected load.
Example:
Imagine you were an electric company serving 1000 homes with only a 3000 watt electric oven in each house. Your connected load would be 3,000,000 watts.
In reality, there may never be a time when all homes use heaters at the same time. Let’s say that only 500 homes use heaters all at the same time. The reason for this is what we call load diversity, or load factor. This would result in a demand load (maximum demand) of 1,500,000 watts. In that case, you only need to design your system for half the value of the connected load.
Many high-wattage appliances (such as toasters) have a very low load factor. Other appliances (electric heat) can have very large load factors at times (in very cold weather).
Ultimately, there are a great variety of appliance types, each with its own load factor, and the utility has to worry about only the aggregate of ALL connected loads.
Demand Factor
Demand Factor is the ratio of maximum demand on the power station to its connected load.
Demand factor = Maximum demand/Connected load
The value of the demand factor is usually less than 1. It is expected because the maximum demand (peak load) on the power station is generally less than the CL.
If the maximum demand on the power station is 80 MW and the connected load is 100 MW, then the demand factor = 80/100 = 0·8.
The knowledge of the demand factor is vital in determining the capacity of the plant equipment.
Comments are closed.