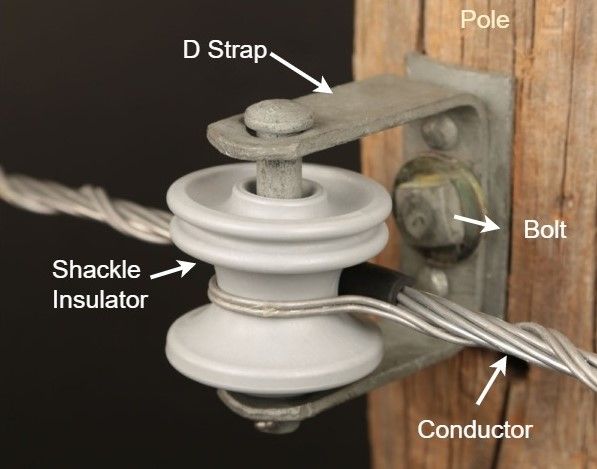
Shackle insulators are one type of overhead insulator used to provide insulation to conductors on low voltage power lines. It is also known as a spool insulator or a butterfly insulator.
They are typically installed horizontally or vertically on low voltage transmission lines. A typical shackle insulator has a hole at the center which provides a platform for mounting. The groove at the outside makes it easy for you to mount the wire.
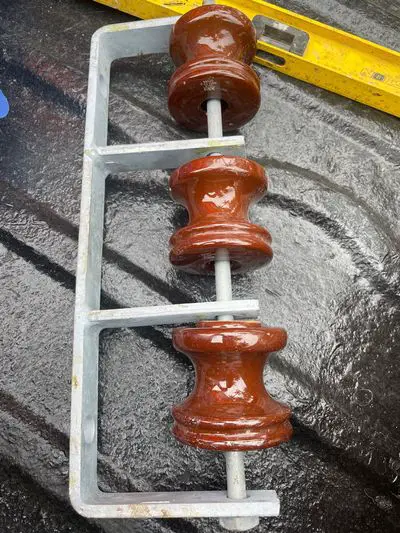

Most of them are made of porcelain, but some are made of polymer.
Shackle insulators are used at low voltages of below 11 kV. They provide insulation on both the primary and secondary conductors of a distribution line. All major wind power generation companies use porcelain shackle insulators.
Types of Shackle Insulators
According to the material used for the construction, spool insulators are of two types:
- Porcelain shackle insulator
- Ceramic shackle insulator

Porcelain shackle insulator is suitable for overhead transmission and distribution line terminal, and fixed on tension rod or angle pole to supporting conductors and playing a role in insulating.
As one part of electrical fitting strings, porcelain shackle insulator is used in order to simplify the fitting structure. It is normally used in 400V lines.
Ceramic insulator is widely used in the line with the ceramic suspension insulator.
Construction and Working
Unlike other insulators, the shackle/spool insulator has a hole in the middle that is used for bolting. On both sides of the insulator, a 25mm wide galvanized plate is available. The other side of the plates is arranged in the region of the pole. Conductors are fixed within channels with wires that are secured with soft bindings. When the distribution line’s angle changes, these insulators are more effective than strain insulators.
It is essential that the porcelain used in making the shackle insulator be sound, thoroughly vitrified. The insulator’s glaze does not contain any cracks. The porcelain type is smoothly glazed.
The insulator body does not suffer from fractures that extend through the manufacturing process, or a glaze that forms due to a strain setting up. The entropy of mixing is achieved in order to ensure all the constant materials making the body are properly mixed. Any outside stresses in any part of the insulator do not lead to deterioration.
A hole is included in the middle of the porcelain wire insulator to guarantee the stud pin goes through. The porcelain shackle insulators can roll on the secondary clevis. Guy wires or other conductors pass through the insulator wrap on the grooves of the shackle insulator.

Spool insulators are available in three different sizes: (50 mm x 65 mm), (75 mm x 90 mm) & (100 mm x 115 mm). As a rule, 75 mm x 90 mm & 100 mm x 115 mm insulators are used for main lines, while 50 mm x 65 mm insulators are used for low voltage connections in houses.
Tapered holes in this insulator balance load distribution and significantly reduce the chances of fracture. You can position the conductor within the groove of this insulator by using a soft binding wire.
Materials Used
Ceramic and porcelain are the two main materials used in the manufacture of these insulators.
They are used because of their distinct physical, mechanical and electrical properties. The two materials are unique, although some of their properties are different.
- Ceramic and porcelain shackle insulators both have high thermal strength and resistance. They are not easily affected by large temperature changes. They can, for instance, handle temperatures up to 1000C.
- These materials can only be deformed when subjected to extreme physical force. Porcelain and ceramic insulators are strong and durable
- Another reason why ceramic and porcelain are preferred for making shackle insulators is their resistance to surface degradation.
- Surfaces of these two materials are unlikely to corrode unless you employ extreme measures to damage them.
The surface of ceramics and porcelain insulators is glazed to shield them from the vagaries of nature.
How to Install Shackle Insulator
Here is a video explaining how to install a spool tie on spool insulator installed on transmission line.
Applications
Shackle insulator is used in the following applications.
- It is used in a distribution system by arranging in between tower & conductors to support & insulate.
- These insulators are used in overhead lines with low & medium voltage.
- This insulator is used with a bolt by placing on the pole otherwise telegraph to avoid outflow current from conductors
- It can be used in both horizontal & vertical positions.