In this article, you will learn three principle methods of magnetizing a steel bar.
If a piece of iron or steel is brought near either of the poles of a magnet, it is attracted. If a north pole of a magnet is brought near the south pole of another freely suspended magnet, there is again an attraction between them.
But if two south poles are brought near each other, they repel. The same happens in the case of two north poles. This means that (i) like poles repel each other and (ii) unlike poles attract each other.
From the above, it is clear that a magnet attracts pieces of iron or steel but repels only magnets. Therefore repulsion is a sure test of magnetism.
Now let’s understand how a can we magnetize a steel bar.
Methods of Magnetization
There are three principal methods of magnetizing a steel bar as given below:
- Touch method
- by means of electric current
- Induction method.
1. Touch Method
This method can be further divided as
- Single touch method
- double touch method
- divided touch method.
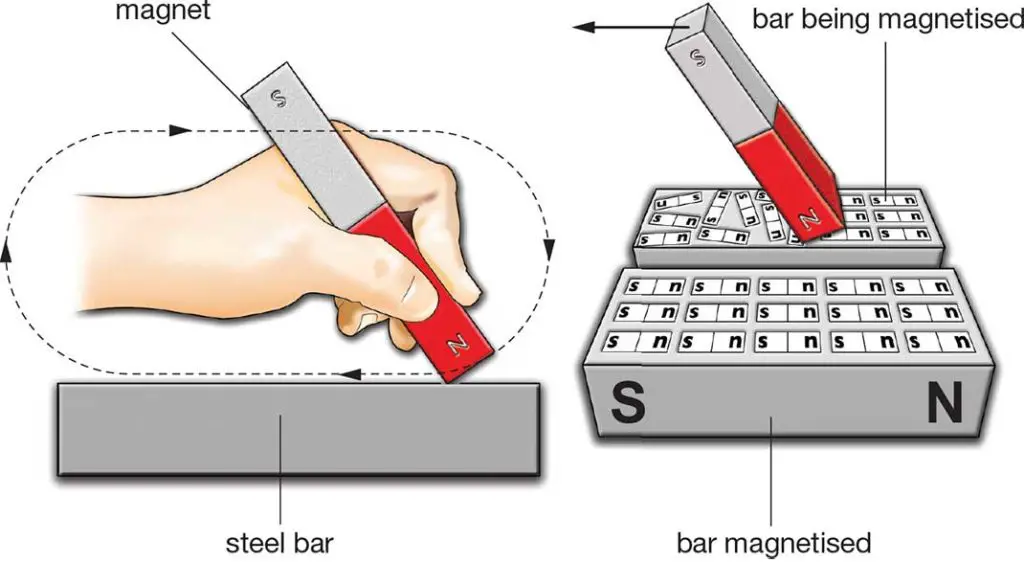
(a) Single Touch Method
In the single touch method, the steel bar to be magnetized is rubbed with either of the poles of a magnet, keeping the other pole away from it.
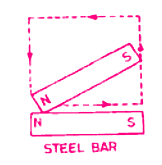
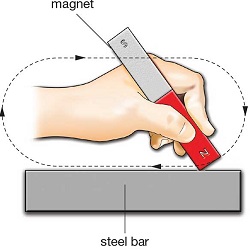
Rubbing is only done in one direction as shown. The process should be repeated many times for the magnetization of the bar.
(b) Double Touch Method
In this method, the steel bar to he magnetized is placed over the two opposite pole ends of a magnet and the rubbing magnets are placed together over the center of the bar with a small wooden piece in between, as shown.
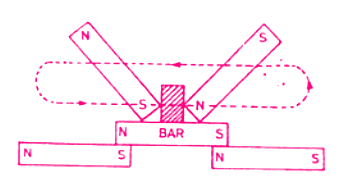
They are never lifted off the surface of the steel bar, but rubbed again and again from end to end, and finally ending at the center where the rubbing was started.
(c) Divided Touch Method
Here the two different poles of rubbing magnets are placed as in the previous case. They are then separated along the surface of the steel bar to the opposite ends.
The rubbing magnets are then lifted off the surface of the steel bar and placed back in the center of the bar. This whole process is repeated again and again as shown.
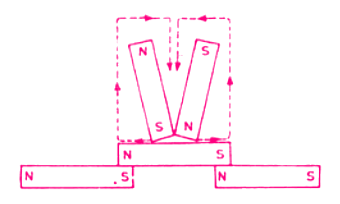
The steel bar thus magnetized becomes a permanent magnet but the degree of magnetization is very low.
2. By Electric Current
The bar to be magnetized is wound with insulated copper wire and then a strong electric current (dc) from a battery is passed through the wire for some time. The steel bar then becomes highly magnetized.
If the bar is of soft iron, the magnetism remains as long as the current continues but almost completely disappears as soon as the current ceases. The magnet made by such an arrangement is called an electromagnet and is generally used in laboratories.
3. Induction Method
This is a commercial method of making permanent magnets. In this method, a pole charger is used which has a coil of many turns and an iron core inside it as shown below. The direct current supply is fed to the coil through a push-button switch.
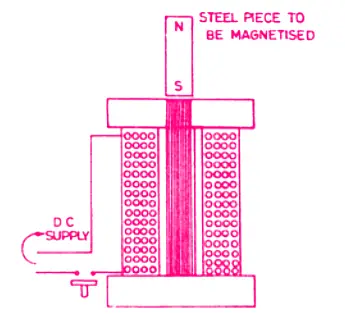
The steel piece to be magnetized is placed on the iron core kept inside the coil and the direct current is passed through the coil. The iron core now becomes a powerful magnet and thus the steel piece placed on it also becomes a magnet by induction. The magnetized piece of steel is then lifted up after switching off the current.
Advantages
The following are the advantages of the induction method of magnetization.
- In this method, small pieces of steel can easily be magnetized.
- It takes very little time to make a magnet.
- Steel pieces of any shape can be magnetized easily.
Uses
The induction method is a commercial process for making permanent magnets for speakers, telephones, microphones, earphones, electrical instruments, magnetos, etc.