Voltage, current, and resistance are three properties that are fundamental to almost everything you will do in electrical and electronics engineering. They are intimately related.
In this article, we used water in a river analogy to explain what is current, resistance and voltage. This method will help the beginners to imagine and understand these fundamentals much easily.
Current
The problem with electrons is that you cannot see them, so you just have to imagine how they do things. I like to think of electrons as little balls flowing through pipes.
Any physicists reading this will probably be clutching their heads in disgust now. But it works for me.
Each electron has a charge and it’s always the same — lots of electrons, lots of charge, a few electrons, and a little bit of charge.
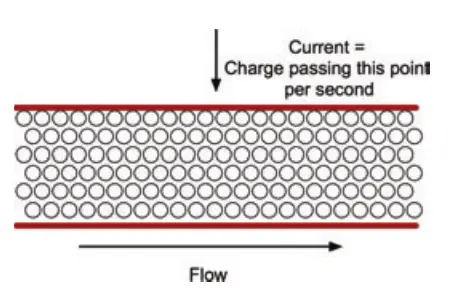
Current, rather like the current in a river, is measured by counting how much charge passes you per second.
Resistance
The resistor has reduced the amount of charge that can pass by a point. And it doesn’t matter which point you measure at (A, B, or C) because, if you look upstream of the resistor, the charge is hanging around waiting to move through the resistor. Therefore, less is moving past A per second. In the resistor (B), it’s restricted.
The “speed” analogy does not really hold true for electrons, but one important point is that the current will be the same wherever you measure it.
Imagine what happens when a resistor stops too much current from flowing through an LED.
Voltage
Read: Potential Difference and EMF
As everyone knows, a river that loses height quickly flows fast and furious, whereas a relatively gently sloped river will have a correspondingly gentle current.
This analogy helps with the concept of voltage being relative. That is, it does not matter if the river is falling from 10,000 ft to 5,000 ft or from 5,000 ft to 0 ft. The drop is the same and so will be the rate of flow.
Read: What is Voltage Source?




Comments are closed.