Definition: Any device that produces voltage output continuously is known as a voltage source.
There are two types of voltage sources,
- Direct voltage source
- Alternating voltage source
Direct voltage source
As the name implies, a direct voltage source continuously produces direct voltage output. Typical examples are batteries and DC generators.
An important characteristic of a direct voltage source is that it maintains the same polarity of the output voltage i.e. positive and negative terminals remain the same.
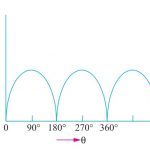
When load resistance RL, is connected across such a source, current flows from positive terminal to negative terminal via the load. This current is the conventional current however the flow of electrons are in the opposite direction.
This is called direct current because it has just one direction. The current has one direction as the source maintains the same polarity of output voltage. The opposition to load current inside the DC source is known as internal resistance Ri.
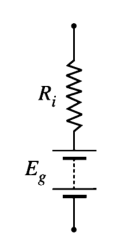
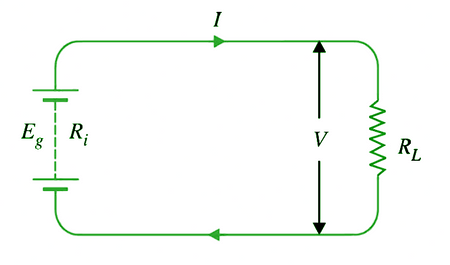
The equivalent circuit of a DC source is the generated emf Eg, in series with internal resistance Ri , of the source as shown in the figure.
Load Current I = Eg / ( RL + Ri )
Terminal Voltage V = Eg – I Ri or I RL
Alternating Voltage Source
A device which produces alternating voltage output continuously is known as alternating voltage source. Example of ac voltage source is an Alternator.
An important characteristic of alternating voltage source is that it periodically reverses the polarity of the output voltage. When load impedance ZL is connected across such a source, current flows through the circuit that periodically reverses in direction. This is called alternating current.
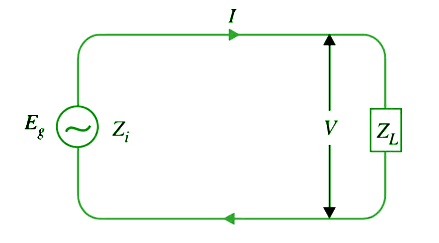
The opposition to load current inside the AC source called its internal impedance Zi . The equivalent circuit of an AC source is the generated e.m.f. Eg (rms) in series with internal impedance Zi of the source as shown in the figure above.
The equivalent circuit of an AC source can be drawn as below.
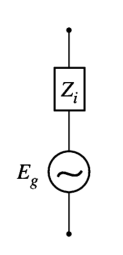
From the images, it is clear that,
Load Current I (rms) = Eg / ( ZL + Zi )
Terminal Voltage V = (Eg – I Zi ) or I ZL
(Vector difference since AC quantities are vector quantities)
Constant Voltage Source
The term constant voltage source refers to a voltage source whose internal impedance is very low in comparison to the load impedance.
In such a case, the output voltage nearly remains the same when load current changes.