
In this article, you will study the concept of electric potential, potential difference (PD) and electromotive force (EMF) and the difference between them.
Just as a body raised above the ground has gravitational potential energy, similarly, a charged body has electric potential energy.
When a body is charged, work is done in charging the body. This work done is stored in the body in the form of electric potential energy. The charged body has the capacity to do work by moving other charges either by attraction or repulsion.
Electric Potential
Quantitatively the electric potential is defined as under :
The electric potential at a point is the electric potential energy per unit charge.
Electric Potential, V = (Electric potential energy) / Charge = W/Q
The SI unit of energy or work is 1 J and that of charge is 1 C so that the SI unit of electric potential is 1 J/C which is also called 1 volt.
Thus when we say that electric potential at a point is 10 V, it means that if we place a charge of 1 C at that point, the charge will have electric potential energy of 10 J.
Similarly. if we place a charge of 2 C at that point, the charge will have the electric potential energy of 20 J.
Note that potential energy per unit charge (i.e electric potential) is 10 V.
Related: Voltage, Current and Resistance
Potential Difference
Consider two bodies A and B having potentials of +5 V and +3 V.
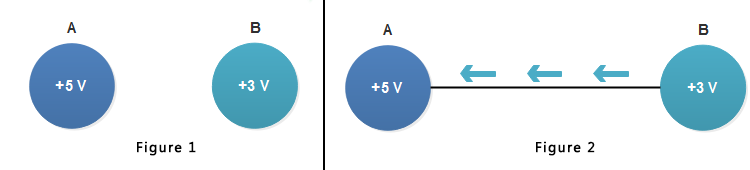 Each coulomb of charge on body A has an energy of 5 Joules and body B has an energy of 3 Joules. Clearly, the body A is at a higher potential than body B.
Each coulomb of charge on body A has an energy of 5 Joules and body B has an energy of 3 Joules. Clearly, the body A is at a higher potential than body B.
If the two bodies are joined through a conductor [right figure], then electrons will flow from body B to body A ( The conventional electric current will be in opposite direction i.e. from A to B).
When the two bodies attain the same potential, the flow of current stops.
Therefore, we arrive at a very important conclusion that current will flow in a circuit if the potential difference exists. No potential difference, no current flow.
It may be noted that the potential difference is sometimes called voltage.
Unit of Potential Difference
It is defined as :
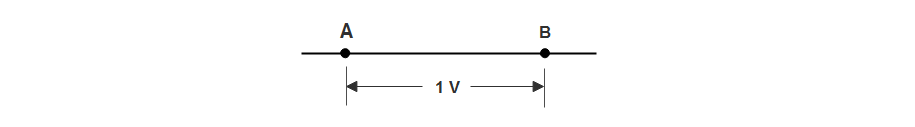
Consider points A and B in an electrical circuit as shown in the figure above. Suppose VA = VB = 1 Volt. It means that 1 J of work will be done in transferring 1C of charge from point B to point A.
Alternatively, 1 J of work (or energy) will be released (as heat) if 1 C of charge moves from point A to point B.
Note that volt is the unit of energy.
EMF and Potential Difference
There is a distinct difference between EMF and the potential difference.
Thus if a battery supplies 4 joules of energy per coulomb, we say that it has an e.m.f. of 4 volts. The energy given to each coulomb in a battery is due to the chemical action.
The potential difference between two points says A and B, is a measure of the energy used by one coulomb in moving from A to B.
Thus if the potential difference between points A and B is 2 volts, it means that each coulomb will give up the energy of 2 joules in moving from A to B.
Difference between EMF and Potential Difference
The name EMF, at first sight, implies that it is a force that causes current to flow. But this is not correct because it is not a force but energy supplied to charge by some active device such as a battery.
EMF maintains potential difference while potential difference causes current to flow.
When we say that EMF of a device (e.g., a cell) is 2 V, it means that the device supplies the energy of 2 joules to each coulomb of charge. When we say that potential difference between points A and B of a circuit (suppose point A is at higher potential) is 2 V, it means that each coulomb of charge will give up the energy of 2 joules in moving from A to B.
| EMF | Potential Difference |
| EMF maintains a potential difference | The potential difference causes current to flow |
| EMF of a device is 2 V means the device supplies the energy of 2 joules to each coulomb of charge. | Potential difference is 2 V means each coulomb of charge will give up the energy of 2 joules in moving from A to B. |




Comments are closed.