The term microprocessor and microcontroller have always been confused with each other. Both of them have been designed for real-time application. They share many common features and at the same time, they have significant differences.
Both the IC’s i.e., the microprocessor and microcontroller cannot be distinguished by looking at them. They are available in different version starting from 6 pins to as high as 80 to 100 pins or even higher depending on the features.
Definition
A microprocessor is an IC which has only the CPU inside them i.e. only the processing powers such as Intel’s Pentium 1,2,3,4, core 2 duo, i3, i5, etc. These microprocessors don’t have RAM, ROM, and other peripheral on the chip. A system designer has to add them externally to make them functional.
Application of microprocessor includes Desktop PC’s, Laptops, notepads etc.
The microcontroller incorporates all the features that are found in the microprocessor. The important thing is that microcontroller has built-in ROM, RAM, Input-Output ports, Serial Port, timers, interrupts and clock circuit. A microcontroller is an entire computer manufactured on a single chip.
For example, microcontrollers are used as engine controllers in automobiles and as exposure and focus controllers in cameras. Arduino is an example of a microcontroller.
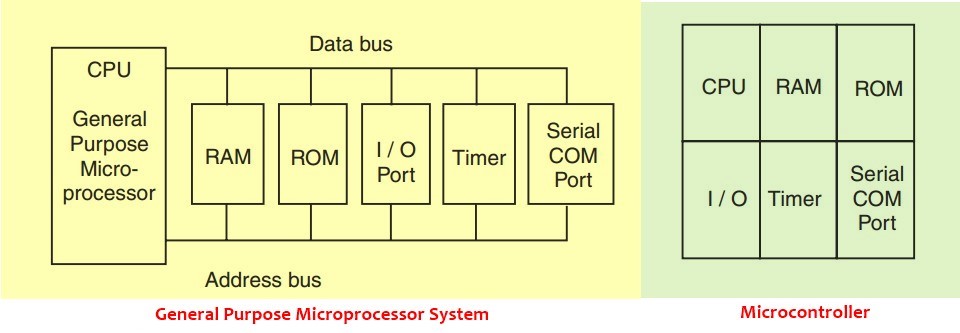
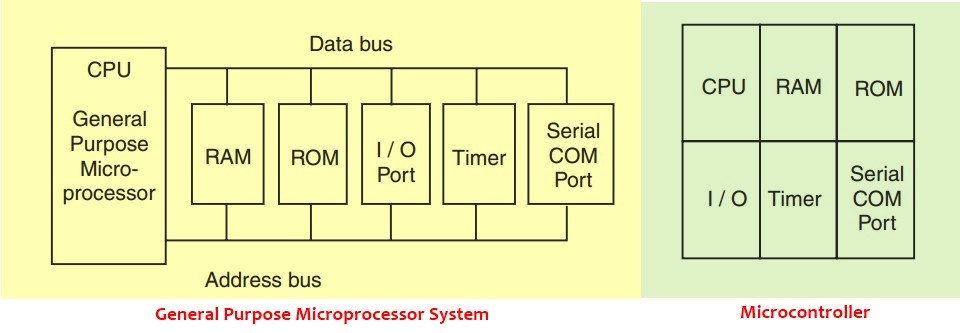
Microprocessor V/S Microcontroller
- It is very clear from the figure above that in microprocessor we have to interface additional circuitry for providing the function of memory and ports.
- For example, we have to interface external RAM for data storage, ROM for program storage, programmable peripheral interface (PPI) 8255 for the Input-Output ports, 8253 for timers, USART for the serial port.
- While in the microcontroller RAM, ROM, I/O ports, timers, and serial communication ports are inbuilt. Because of this, it is called a “system on a chip”.
- So in a microcontroller, there is no necessity of additional circuitry which is interfaced in the microprocessor because memory and input-output ports are inbuilt in the microcontroller.
- Microcontroller gives satisfactory performance for small applications. But for large applications, the memory requirement is limited because only 64 KB memory is available for program storage.
- So for large applications, we prefer microprocessor than microcontroller due to its high processing speed.
Criteria for Selection of a Microcontroller in Embedded System
Criteria for selection of microcontroller in any embedded system is as follows:
- Meeting the computing needs of the task at hand efficiently and cost-effectively
- Speed of operation
- Packing
- Power consumption
- Amount of RAM and ROM on-chip
- No. of I/O pins and timers on-chip
- Cost
- Availability of software development tools such as compiler, assembler, and debugger.