The Stroboscopic Effect in Fluorescent lamp is a phenomenon which causes running or moving equipment to appear stationary or appear to be operating slower than they actually are.

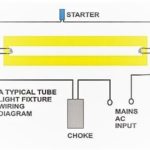
Fluorescent materials when subjected to electromagnetic radiations of a particular wavelength, get excited and in turn, gives out radiations at some other wavelength. This is the working principle behind fluorescent lamps.
These lamps are widely used in homes as they have higher efficiency and lifetime is almost 3 times of those of filament lamps.
What is Stroboscopic Effect?
Fluorescent lamps are provided with 50Hz or 60Hz ac current supply.
When operating under these frequencies the lamp becomes zero (crosses zero wave) double the supply frequency. That is 100 times for 50Hz frequency and 120 times for 60Hz frequency per second. Due to the persistence of vision our eyes do not notice those flickering.
However, if the light falls on the moving parts due to illusion, they may appear to be either running slow or in reverse direction or even may appear stationary. This effect is called the “Stroboscopic effect“.
What is the Danger?
The danger of the stroboscopic effect is explained below using some examples.
Imagine a worker in a factory observes a running machine. Say a flywheel under the illumination of fluorescent light, the flywheel may appear to be stationary or to be operating at reduced speed. This can result in accidents and is highly dangerous.
These are some examples where the stroboscopic effect in the Fluorescent lamps can prove to be dangerous.
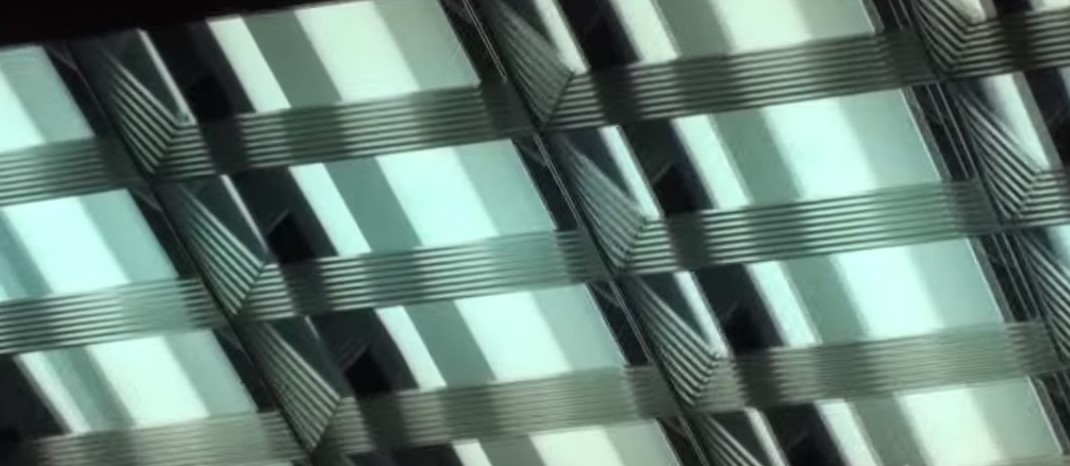
Fluorescent lamps had this effect (flicker) when mostly line frequency magnetic ballasts were used.
Studies involving these kinds of ballasts showed a
- doubling incidence of headaches with office workers,
- triggering migraines in people sensitive to it (about 10% of the people),
- and impairment of performance.
Even worse, with the aging of the lamps, AC polarity dependent fluctuation could start to occur in the 20-70 Hz frequency ranges, which can induce epileptic seizures!
With the introduction of electronic ballasts for fluorescent lights, most of the flicker problems were almost eliminated.
Methods to Avoid Stroboscopic Effect
However, this effect occurs in three-phase as well as single-phase supply. It can be avoided by some simple techniques.
Method to Avoid Stroboscopic Effect in Three-Phase Supply
If the industry is supplied with a three-phase supply, adjacent lamps should be fed with a different phase so that the zero instants of the two lamps will not be the same.
Fluorescent lamps around rotating or moving machinery, two lamps powered by two different phases should be used. This ensures that both the lamps do not flicker due to the zero-crossing at the same time.
Method to Avoid Stroboscopic Effect in Single-Phase Supply
If single-phase supply is only available, then the connection of two adjacent lamps is made such that the two lamps are connected in parallel with the supply.
In one lamp connection, a capacitor or condenser is kept in series with the choke. This makes a phase shift thereby eliminating the stroboscopic effect