
Protective relaying is necessary with almost every electrical plant, and no part of the power system is left unprotected. The choice of protection depends upon several aspects such as type and rating of the protected equipment, its importance, location, probable abnormal conditions, cost, etc.
Between generators and the final load points, there are several electrical equipment and machines of various ratings. Each needs certain adequate protection.
The protective relaying senses the abnormal conditions in a part of the power system and gives an alarm or isolates that part from the health system.
How Protective Relaying Works?
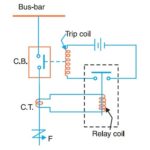
The relays are compact, self-contained devices that respond to an abnormal condition. The relays distinguish between normal and abnormal conditions. Whenever an abnormal condition develops, the relays close its contacts. Thereby the trip circuit of the circuit breaker is closed. Current from the battery supply flows in the trip-coil of the circuit-breaker and the circuit breaker opens and the faulty part is disconnected from the supply.
The entire process, ‘occurrence of a fault, operation of the relay, the opening of the circuit breaker, removal of the faulty part from the system’, is automatic and fast. Circuit breakers are switching devices that can interrupt normal currents and fault currents.
Besides relays and circuit-breakers, there are several other important components in the protective, relaying scheme, these include protective current transformers and voltage transformers, protective relays, time-delay relays, auxiliary relays, secondary circuits, trip circuits, auxiliaries, and accessories, etc. Each component is important. Protective relaying is teamwork of those components.
Function of Protective Relaying
The functions of protective relaying include the following :
- To sound an alarm or to close the trip circuit of circuit-breaker so as to disconnect a component during an abnormal condition in the component, which includes overload, under-voltage, temperature rise, unbalanced load, reverse power, under-frequency, short circuits, etc.
- To disconnect the abnormally operating part so as to prevent the subsequent faults, e.g.over-load protection of a machine protects the machine and prevents insulation failure.
- To disconnect the faulty part quickly so as to minimize the damage to the faulty part, e.g. If a machine is disconnected immediately after a winding fault, only a few coils may need replacement. If the fault is sustained, the entire winding may get damaged and the machine may be beyond repairs.
- To localize the effect of fault by disconnecting the faulty part, from the healthy part, causing the least disturbance to the health system.
- To disconnect the faulty part quickly so as to improve system stability, service continuity, and system performance. Transient stability can be improved by means of improved protective relaying.
Faults cannot be avoided completely. They can be minimized. Protective relaying plays an important role in minimizing the faults, and also in minimizing the damage in the event of faults.





Comments are closed.