Before reading Split Phase and Capacitor Start Induction Motors, please read the previous article, Why a Single Phase Induction Motor is not Self Starting?
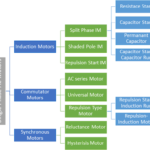
Making a Single Phase Induction Motor Self Starting
As discussed in the previous article single-phase induction motors are not self-starting. It is because a single-phase supply cannot produce a rotating magnetic field. But we can create a rotating magnetic field by a two-phase construction.
So simply we can say in order to make a single-phase induction motor self-starting, we have to temporarily convert it into a two-phase motor during its starting period.
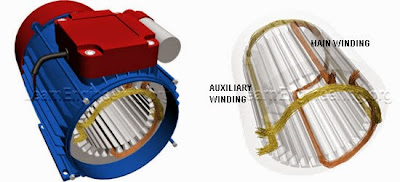
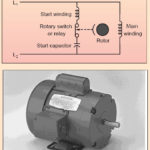
For this purpose, the stator of the single-phase induction motor is provided with an extra winding known as Starting or Auxillary Winding in addition to the Main or Running Winding. The two winding are 90 degrees electrically displaced and are connected in parallel across the single-phase supply.
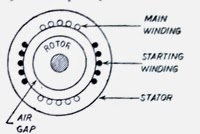
The phase difference between the currents in the main winding and running winding can be obtained through different methods. The phase shift can be achieved by connecting a resistance, inductance or capacitance in series with the starting winding.
Crating Phase difference between two windings
Split Phase Induction Motor
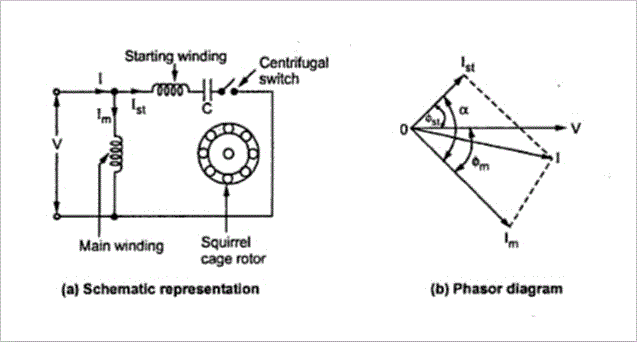
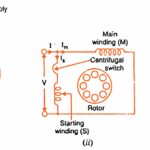
In a split-phase machine, the main-winding has low resistance but high reactance whereas the starting winding has a high resistance but low reactance.

The resistance of the starting winding may be increased either by connecting a high resistance R in series with it or by choosing a high-resistance fine copper wire for winding purposes.
Hence, as shown in Fig (b), the current Is drawn by the starting winding lags behind the applied voltage by a small angle whereas current Im taken by the main winding lags behind V by a very large angle. The phase angle between Is and Im is made as large as possible because the starting torque of a split-phase motor is proportional to sin α.
A centrifugal switch S is connected in series with the starting winding and is located inside the motor. Its function is to automatically disconnect the starting winding from the supply when the motor has reached 70 to 80 percent of its full load speed.
The centrifugal switch is necessary because the auxiliary winding cannot support high currents for more than a few seconds without being damaged because it is made of fine wire. In case of a capacitor start motor its is necessary because most motors use a cheap electrolytic capacitor that can only carry a.c current for a short period of time.
In the case of split-phase motors that are hermetically sealed in refrigeration units, instead of an internally mounted centrifugal switch, an electromagnetic type of relay is used.
As shown in figure, the relay coil is connected in series with main winding and the pair of contacts which are normally open, is included in the starting winding. During the starting period when Im is large, relay contacts close thereby allowing Is to flow and the motor starts as usual. After motor speeds up to 75 percent of full-load speed, Im drops to value that is low enough to cause the contacts to open.
These motors are often used in preference to the costlier capacitor-start motors.
Typical applications of split-phase motors are fans and blowers, centrifugal pumps and separators, washing machines, small machine tools, duplicating machines, domestic refrigerators, and oil burners, etc. Commonly available sizes range from 1/20 to 1/3 h.p. (40 to 250 W) with speeds ranging from 3,450 to 865 r.p.m.
The speed regulation of standard split-phase motors is nearly the same as of the 3-phase motors. Their speed varies about 2 to 5% between no load and full- load’ For this reason such motors are usually regarded as practically constant-speed motors.
Read: Shaded Pole Induction Motor
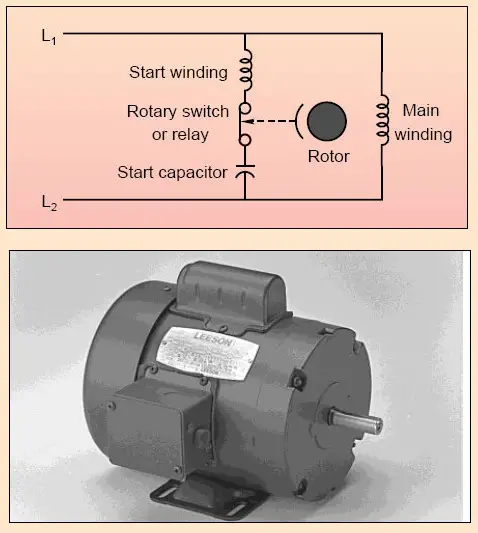
Capacitor Start Induction run motors
The capacitor is designed for extremely short-duty service and is guaranteed for not more than 20 periods of operation per hour, each period not to exceed 3 seconds. When the motor reaches about 75 percent of fulls speed, the centrifugal switch S opens and cuts out both the starting winding and the capacitor from the supply, thus leaving only the running winding across the lines.
As shown in Fig, current Im drawn by the main winding lags the supply voltage V by a large angle whereas Is leads V by a certain angle. The two currents are out of phase with each other by about 80° (for a 200-W 50-Hz motor) as compared to nearly 30 degrees for a split phase motor. Their resultant current I is small and is almost in phase with V as shown in figure.


Comments are closed.