
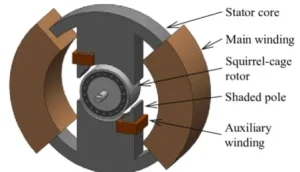
Shaded pole motor is a split-phase type single phase induction motor. The shaded pole induction motors are very popular for ratings below 0.05 HP (~ 40 W) because of its extremely simple construction.
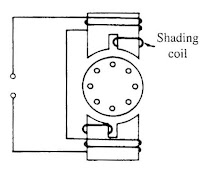
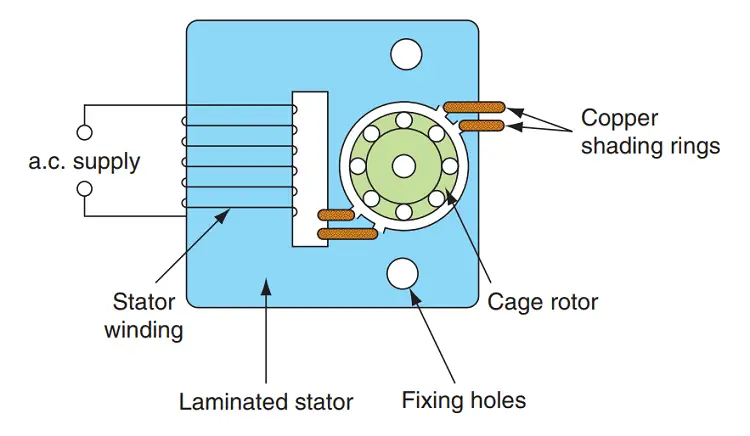
It has salient poles on the stator excited by a single-phase supply and a squirrel cage rotor. A portion of each pole is surrounded by a short-circuited turn of a copper strip called shading coil.
A shaded pole motor and its schematic diagram are shown in the figures above.
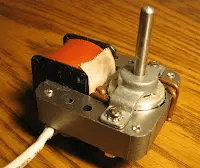
Construction of Shaded Pole Induction Motor
A shaded pole induction motor may be of 2 poles or 4 poles. Here we are considering a 2 pole shaded pole motor. The figures in this article also show a 2 pole motor.
Stator
 The stator has salient poles. Usually, 2 to 4 poles are used. Each of the poles has its own exciting coil.
The stator has salient poles. Usually, 2 to 4 poles are used. Each of the poles has its own exciting coil.
A part of each pole is wrapped by a copper coil. The copper coil forms a closed-loop across each pole. This loop is known as the shading coil.
The poles are laminated. A slot is cut across the lamination of the pole. The slot is approximately one-third distance from the edge of the pole. The short-circuited copper coil described above is placed in this slot. So we can call this part as the shaded part and other parts of the pole as unshaded part.
Selecting a 2 poled stator gives a synchronous speed of 3000 rpm while a 4 poled stator speed will be 1500rpm for 50Hz supply.
Rotor
The rotor of shaded pole induction motors is the Squirrel Cage type rotor. The rotor bars are provided with a 60-degree skew. This is to obtain an optimum starting torque and for limiting the torque dip during the run-up.
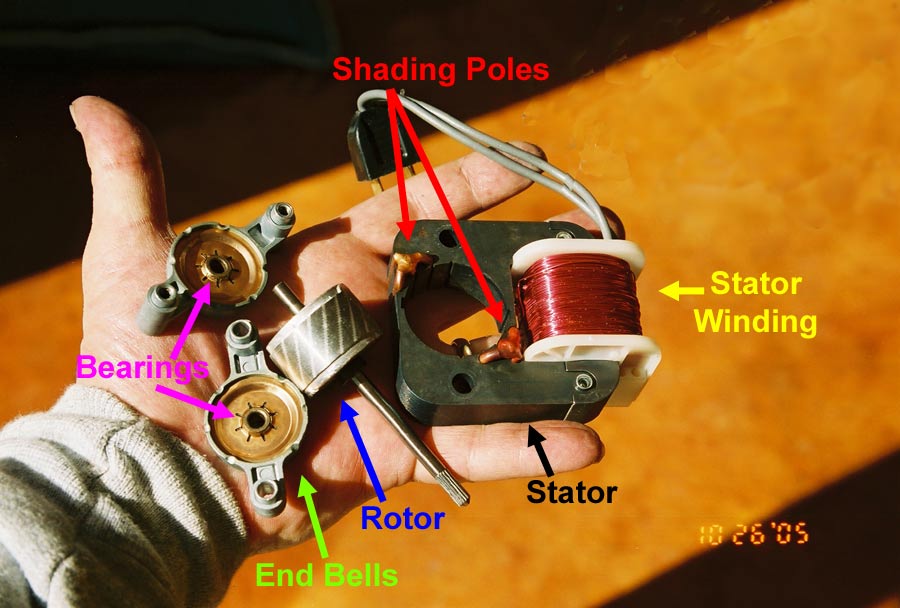 |
| Parts of a Shaded Pole Induction Motor |
Airgap length between stator and rotor is of the order 0.25 to 0.5 mm. Too short air-gap may result in starting-torque variations due to rotor slotting.
The shaded pole induction motors has no commutator, brushes, collector rings, contactors, capacitors or moving switch parts, so it is relatively cheaper, simpler and extremely rugged in construction and reliable. The absence of a centrifugal switch eliminates the possibility of motor failure due to faulty centrifugal switch mechanisms.
Working of Shaded Pole Induction Motors
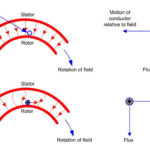
The operation of the motor can be understood by referring to the figure which shows one pole of the motor with a shading coil.
Considering a cycle of alternating current (fig 1) applied to the stator winding we will explain the working of shaded pole induction motors.

During the portion OA
During the portion OA of the alternating-current cycle [Fig 1], the flux begins to increase and an e.m.f. is induced in the shading coil. The resulting current in the shading coil will be in such a direction (Lenz’s law) so as to oppose the change in flux.
Thus the flux in the shaded portion of the pole is weakened while that in the unshaded portion is strengthened as shown in figure 2.
During the portion AB
During the portion AB of the alternating-current cycle, the flux has reached the almost maximum value and is not changing. Consequently, the flux distribution across the pole is uniform [See Fig 3] since no current is flowing in the shading coil.
During the portion BC
As the flux decreases (portion BC of the alternating current cycle), the current is induced in the shading coil so as to oppose the decrease in current. Thus the flux in the shaded portion of the pole is strengthened while that in the unshaded portion is weakened as shown in Fig 4.
The effect of the shading coil is to cause the field flux to shift across the pole face from the unshaded to the shaded portion. This shifting flux is like a rotating weak field moving in the direction from the unshaded portion to the shaded portion of the pole.
The rotor is of the squirrel-cage type and is under the influence of this moving field. Consequently, a small starting torque is developed. As soon as this torque starts to revolve the rotor, additional torque is produced by single-phase induction-motor action. The motor accelerates to a speed slightly below the synchronous speed and runs as a single-phase induction motor.
Characteristics of Shaded Pole Motors
Some of the important characteristics of shaded pole induction motors are given below. The details of the characteristics of the shaded pole motor will be discussed later.
- The salient features of this motor are extremely simple construction and absence of centrifugal switch.
- Since starting torque, efficiency and power factor are very low, these motors are only suitable for low power applications e.g., to drive: (a) small fans (b) toys (c) hair driers (d) desk fans, etc.


Comments are closed.