Signals play an important role in our daily lives. We work with a wide variety of signals every day, whether we realize it or not.
Signals in Radio Broadcast
In a radio broadcast studio, when a commentator speaks into a microphone, the sound waves create changes in the air pressure around the microphone. When we are in the same studio, our ear membranes detect changes in air pressure and perceive them as sound.
The changes in pressure also cause vibrations to occur on the membrane inside the microphone. As a result, the microphone produces a time-varying electrical voltage in a way that mimics changes in air pressure in the studio. So, the microphone acts as a transducer in order to convert an acoustical signal into an electrical signal, generally speaking. This is just one step in the radio broadcasting process.
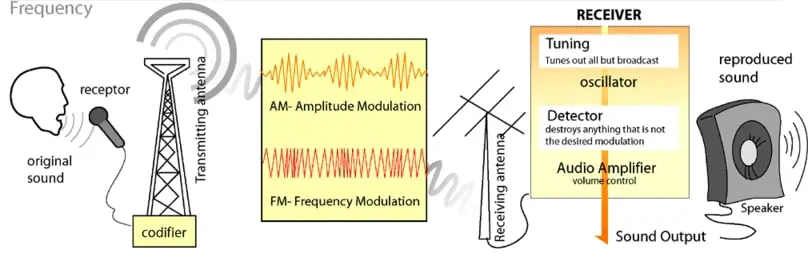
Various modifications and enhancements are made to the electrical signal produced by a microphone, and its strength is increased. Afterwards, it is converted into an electromagnetic signal that can be transmitted over long distances over air using a transmitting antenna. Throughout our lives, we are surrounded by electromagnetic waves. A radio receiver converts electromagnetic signals picked up by its antenna into electrical voltage signals, which are further processed within the receiver and sent to a loudspeaker. This electrical voltage signal is converted into vibrations by the loudspeaker, which simulate air pressure variations similar to those in the broadcast studio that began the whole process.
There are three types of signals included in the broadcast example discussed above: acoustic, electrical, and electromagnetic.
We can also find examples of different physical signals around us. The time variation of quantities such as force, torque, speed, and acceleration can be considered mechanical signals. As an example, a tachometer measures the speed of a vehicle as a signal and produces an electrical voltage proportional to the speed at any given moment in time. In addition, the electrical signal produced by the tachometer can be used as part of a speed control system to control the vehicle’s speed.
Photograph as Signal
Consider a grayscale photograph taken with an old film camera using a film negative. There are shades of gray ranging from pure black to pure white in the photograph. When shades of gray can be represented numerically, for example with values ranging from 0.0 to 1.0, then we can interpret the photograph as a signal. In this case, the strength of each point is not a function of time, but rather a function of horizontal and vertical distances from a reference point such as the bottom left corner of the photograph.
When a digital camera is used to capture an image, the resulting signal is slightly different. Sensors in digital cameras are made up of photo-sensitive cells arranged in rectangles. Light intensity is measured by each cell, and a voltage is produced in proportion to it. Therefore, the signal that represents a digital image also consists of light intensity values as a function of horizontal and vertical distances. Due to the finite number of cells on the sensor, only distance values that are multiples of the cell width and cell height are meaningful. Light intensity information only exists for certain values of the distance, and is undefined between them.
Signals in Non Engineering Disciplines
There are also examples of signals outside of engineering disciplines. For example, financial markets rely on certain economic indicators when making investments. The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) is one such indicator that is widely used. This index is based on the stock prices of 30 large public companies. The DJIA can be used by investors to determine the health of the economy and to decide whether to buy or sell.
