What is Arduino?
Arduino is an open-source platform used for building electronics projects. Arduino consists of both a physical programmable circuit board (often referred to as a microcontroller) and a piece of software, or IDE (Integrated Development Environment) that runs on your computer, used to write and upload computer code to the physical board.
Arduino is a flexible programmable hardware platform designed for artists, designers, tinkerers, and the makers of things. Arduino’s little, blue circuit board, mythically taking its name from a local pub in Italy, has in a very short time motivated a new generation of DIYers of all ages to make all manner of wild projects found anywhere from the hallowed grounds of our universities to the scorching desert sands of a particularly infamous yearly arts festival and just about everywhere in between.
Usually these Arduino based projects require little to no programming skills or knowledge of electronics theory, and more often than not, this handiness is simply picked up along the way.
For programming the microcontrollers, the Arduino project provides an integrated development environment (IDE) based on a programming language named Processing, which also supports the languages C and C++.
Read Structuring Arduino program for more details
What Does it Do?
The Arduino hardware and software was designed for artists, designers, hobbyists, hackers, newbies, and anyone interested in creating interactive objects or environments. Arduino can interact with buttons, LEDs, motors, speakers, GPS units, cameras, the internet, and even your smart-phone or your TV! This flexibility combined with the fact that the Arduino software is free, the hardware boards are pretty cheap, and both the software and hardware are easy to learn has led to a large community of users who have contributed code and released instructions for a huge variety of Arduino-based projects.
For everything from robots and a heating pad hand-warming blanket to honest fortune-telling machines, and even a Dungeons and Dragons dice-throwing gauntlet, the Arduino can be used as the brains behind almost any electronics project.
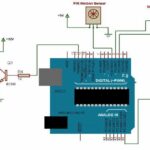
What’s on the board?
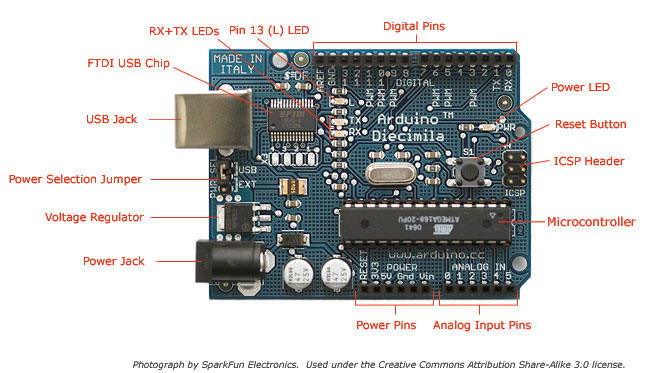
There are many varieties of Arduino boards that can be used for different purposes. Some boards look a bit different from the one below, but most Arduinos have the majority of these components in common:
Power (USB / Barrel Jack)
Every Arduino board needs a way to be connected to a power source. The Arduino UNO can be powered from a USB cable coming from your computer or a wall power supply (like this) that is terminated in a barrel jack. In the picture above the USB connection is labeled (1) and the barrel jack is labeled (2).
The USB connection is also how you will load code onto your Arduino board. More on how to program with Arduino can be found in our Installing and Programming Arduino tutorial.
Pins (5V, 3.3V, GND, Analog, Digital, PWM, AREF)
The pins on your Arduino are the places where you connect wires to construct a circuit (probably in conjuction with a breadboard and some wire. They usually have black plastic ‘headers’ that allow you to just plug a wire right into the board. The Arduino has several different kinds of pins, each of which is labeled on the board and used for different functions.
GND (3): Short for ‘Ground’. There are several GND pins on the Arduino, any of which can be used to ground your circuit.
5V (4) & 3.3V (5): As you might guess, the 5V pin supplies 5 volts of power, and the 3.3V pin supplies 3.3 volts of power. Most of the simple components used with the Arduino run happily off of 5 or 3.3 volts.
Analog (6): The area of pins under the ‘Analog In’ label (A0 through A5 on the UNO) are Analog In pins. These pins can read the signal from an analog sensor (like a temperature sensor) and convert it into a digital value that we can read.
Digital (7): Across from the analog pins are the digital pins (0 through 13 on the UNO). These pins can be used for both digital input (like telling if a button is pushed) and digital output (like powering an LED).
PWM (8): You may have noticed the tilde (~) next to some of the digital pins (3, 5, 6, 9, 10, and 11 on the UNO). These pins act as normal digital pins, but can also be used for something called Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM). We have a tutorial on PWM, but for now, think of these pins as being able to simulate analog output (like fading an LED in and out).
AREF (9): Stands for Analog Reference. Most of the time you can leave this pin alone. It is sometimes used to set an external reference voltage (between 0 and 5 Volts) as the upper limit for the analog input pins.
Reset Button
Just like the original Nintendo, the Arduino has a reset button (10). Pushing it will temporarily connect the reset pin to ground and restart any code that is loaded on the Arduino. This can be very useful if your code doesn’t repeat, but you want to test it multiple times. Unlike the original Nintendo however, blowing on the Arduino doesn’t usually fix any problems.
Power LED Indicator
Just beneath and to the right of the word “UNO” on your circuit board, there’s a tiny LED next to the word ‘ON’ (11). This LED should light up whenever you plug your Arduino into a power source. If this light doesn’t turn on, there’s a good chance something is wrong. Time to re-check your circuit!
TX RX LEDs
TX is short for transmit, RX is short for receive. These markings appear quite a bit in electronics to indicate the pins responsible for serial communication. In our case, there are two places on the Arduino UNO where TX and RX appear – once by digital pins 0 and 1, and a second time next to the TX and RX indicator LEDs (12). These LEDs will give us some nice visual indications whenever our Arduino is receiving or transmitting data (like when we’re loading a new program onto the board).
Main IC
The black thing with all the metal legs is an IC, or Integrated Circuit (13). Think of it as the brains of our Arduino. The main IC on the Arduino is slightly different from board type to board type, but is usually from the ATmega line of IC’s from the ATMEL company. This can be important, as you may need to know the IC type (along with your board type) before loading up a new program from the Arduino software. This information can usually be found in writing on the top side of the IC. If you want to know more about the difference between various IC’s, reading the datasheets is often a good idea.
Voltage Regulator
The voltage regulator (14) is not actually something you can (or should) interact with on the Arduino. But it is potentially useful to know that it is there and what it’s for. The voltage regulator does exactly what it says – it controls the amount of voltage that is let into the Arduino board. Think of it as a kind of gatekeeper; it will turn away an extra voltage that might harm the circuit. Of course, it has its limits, so don’t hook up your Arduino to anything greater than 20 volts.
Comments are closed.