In this article, we will explain the concept of electric charge and electric current as simply as we can.
Concept of Electric Charge
The electric charge is the fundamental principle explaining all electrical phenomena. In addition, it is the most important quantity in an electric circuit.
It’s common for us to experience electric charge when we attempt to remove our wool sweater but it sticks to our body or when we walk across the carpet and receive a shock.
Definition:
Charge is an electrical property of the atomic particles of which matter consists, measured in coulombs (C).
From elementary physics, we know that all matter is made up of fundamental building blocks called atoms. The electronic structure of an atom consists of electrons, protons, and neutrons.
In addition, we know that the electron carries a charge of 1.6×10-19 C negative, while the proton carries a charge of 1.6×10-19 C positive. Equal numbers of protons and electrons leave an atom neutrally charged.
Important Points on Electric Charge
Here are some points to remember regarding electric charges:
- Coulombs are large units for measuring charges. 1 C of charge contains 1/(1.602 x 10-19) = 6.24 x 1018 electrons. Therefore, realistic or laboratory values of charges are on the order of pC, nC, or µC.
- In contrast, large power supply capacitors can store up to 0.5 C of charge.
- Experimental observations have revealed that the only charges found in nature are integral multiples of the electronic charge 1.602 x 10-19
- According to the law of conservation of charge, charges cannot be created nor destroyed; they can only be transferred. As a result, the algebraic sum of the electric charges does not change in a system.
Concept of Electric Current
Now let’s consider the flow of electric charges. The one unique feature of electric charge or electricity is that it is mobile, meaning it can be transported from one place to another, where it can be converted into another form of energy.
Direction of Electric Current
An electric current flows through a conducting wire (consisting of several atoms) when it is connected to a voltage source or battery (which generates an electrical charge). Positive charges flow in one direction, while negative charges flow in the other direction. This movement of charges creates an electric current.
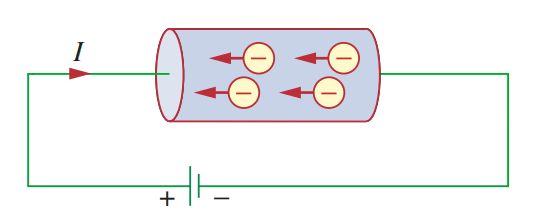
In conventional thinking, the flow of current is taken as the movement of positive charges. That is, it is the opposite of the flow of negative charges, as the figure illustrates. The convention was introduced by Benjamin Franklin (1706-1790), an American scientist and inventor.
Conventions are a way of conveying information in a common manner so other professionals in the field will understand what we mean. We will be using IEEE conventions throughout this article.
Though we now know that current in metallic conductors is caused by negatively charged electrons, we will continue to follow the universally accepted convention that current is the net flow of positive charges.
What is Electric Current?
Definition:
Electric current is the time rate of change of charge, measured in amperes (A).
The relationship between current i, charge q, and time t is mathematically defined as follows:
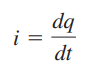
where current is measured in amperes (A), and
1 ampere = 1 coulomb/second
The charge transferred between time and t is obtained by integrating both sides of the current equation. Then we obtain
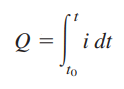
It is clear from the equation 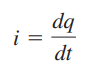
Direct Current and Alternating Current
Direct current and Alternating current are the two most common types of current.
Currents that do not varies with time, but remain constant, are called direct currents (dc).
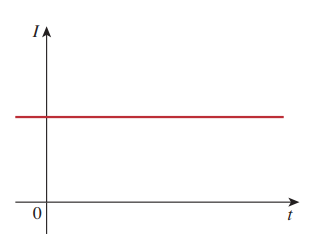
The symbol I is traditionally used to represent a constant current.
An alternating current (ac) is a current that varies sinusoidally with time.
Time-varying currents are represented by the symbol i or i(t). The sinusoidal current and alternating current (ac) are common forms of time-varying current.
Air conditioners, refrigerators, washing machines, and other appliances in your home use alternating current.
Positive and Negative Current
As we define current as the movement of charge, we expect that current will also have an associated direction. As previously mentioned, the direction of current flow is considered the direction of positive charge movement.
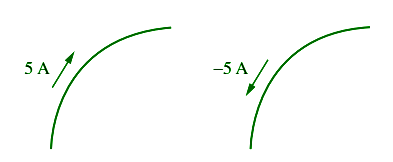
Using this convention, a current of 5 A may be represented positively or negatively as shown in figure.
In other words, a negative current of -5A flowing in one direction is the same as a current of +5A flowing in the opposite direction.
Also Read: EMF and Potential Difference