Using a resistor to limit the current can be used for small LEDs. For such low power LEDs, where the supply current is not critical it works okay.
But for high-power Light Emitting Diodes, a better way is to use the Constant Current Driver.
As the name suggests, the constant current driver will supply the same current whatever voltage it is supplied with and whatever the forward voltage of the LED. You just set the current and that is how much current will flow through the high-power LED.
A very useful IC that is often used for this purpose is the LM317. This IC is primarily intended as an adjustable voltage regulator, but can easily be adapted for use in regulating current.
Design of Constant Current Driver
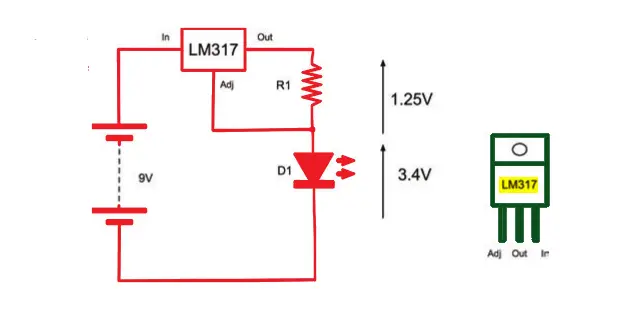
The figure below shows the schematic diagram for regulating the current to a high-power LED.
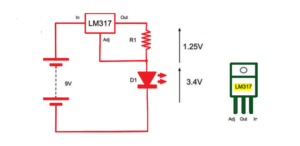
The LM317 is very easy to use in a constant current mode. It will always strive to keep its output voltage at exactly 1.25V above whatever voltage the Adj (adjust) pin is at.
The LED we are going to use is a 1W white light LED. It has an If (forward current) of 300mA and a Vf (forward voltage) of 3.4V.
The formula for calculating the right value for R for use with the LM317 is:
R = 1.25V / I so in this case, R = 1.25 / 0.3 = 4.2Ω If we used a standard resistor value of 4.7Ω, then this would reduce the current to: I = 1.25V / 4.7Ω = 266 mA Checking the power rating for the resistor, the LM317 will always have 1.25V between Out and Adj. So:P = V × I = 1.25V × 266mA = 0.33W
A half-watt resistor will, therefore, be fine.
The LM317 also needs its input to be about 3V higher than its output to guarantee 1.25V between Adj and the output.
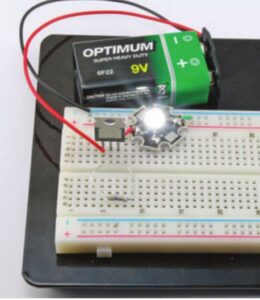 This means that a 6V battery would not be quite high enough because the forward voltage is 3.4V. However, we could drive the circuit using a 9V battery or even a 12V power supply without modification, since whatever the input voltage, the current will always be limited to about 260mA.
This means that a 6V battery would not be quite high enough because the forward voltage is 3.4V. However, we could drive the circuit using a 9V battery or even a 12V power supply without modification, since whatever the input voltage, the current will always be limited to about 260mA.
A quick calculation of the power consumed by the LM317 will reassure us that we are not going to come near exceeding its maximum power rating.
For a 9V battery, the voltage between In and Out will be
9 – (1.25 + 3.4) = 4.35V.
The current is 260mA, so the power is:
4.35 × 0.26 = 1.13W.
According to its datasheet, the maximum power handling capability of the LM317 is 20W, and it can cope with a current of up to 2.2A for a supply voltage of less than 15V. So we are fine.


Comments are closed.