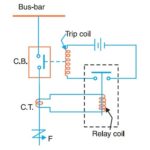
 The IEEE defines protective relays as: “relays whose function is to detect defective lines or apparatus or other power system conditions of an abnormal or dangerous nature and to initiate appropriate control circuit action ”.
The IEEE defines protective relays as: “relays whose function is to detect defective lines or apparatus or other power system conditions of an abnormal or dangerous nature and to initiate appropriate control circuit action ”. Relays detect and locate faults by measuring electrical quantities in the power system which are different during normal and intolerable conditions. The most important role of protective relays is to first protect individuals, and second to protect equipment
All the relays consist of one or more elements which get energized and actuated by the electrical quantities of the circuit. Most of the relays used are electromechanical type which work on the principles of electromagnetic attraction and electromagnetic induction.
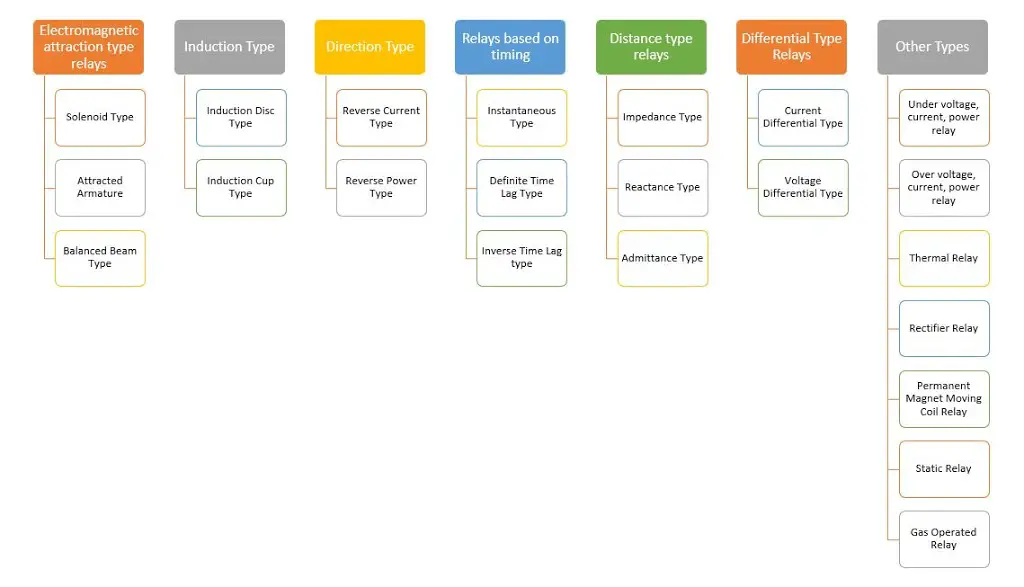
There are different types of protective relays available now. They can be broadly classified in to the following types. Each of them will be explained in detail in coming articles.
- Electromagnetic attraction type Relays
-
- Solenoid Type
- Attracted Armature
- Balanced Beam Type
- Induction Type Relays
- Induction Disc Type
- Induction Cup Type
- Direction Type Relays
- Reverse Current Type
- Reverse Power Type
- Relays based on Timing
- Instantaneous Type
- Definite Time Lag Type
- Inverse Time Lag type
- Distance type Relays
- Impedance Type
- Reactance Type
- Admittance Type
- Differential Type Relays
- Current Differential Type
- Voltage Differential Type
- Other Types of Relays
- Under voltage, current, power relay
- Over voltage, current, power relay
- Thermal Relay
- Rectifier Relay
- Permanent Magnet Moving Coil Relay
- Static Relay
- Gas Operated Relay
Protection relays can also be classified in accordance with their construction, actuating signal, application and function.
Classification based on Construction
Depending upon the principle of construction, the following four broad categories are found.
- Electromechanical Relay
- Solid State Relay
- Microprocessor Relay
- Numerical Relay
Classification based on Actuating Signals
The actuating signal may be any of the following signals including a numbers of different combinations of these signals depending upon whether the designed relay require a single or multiple inputs for its realization.
• Current
• Voltage
• Power
• Frequency
• Temperature
• Pressure
• Speed
• Others
Classification based on Function
The functions for which the protection system is designed classify the relays in the following few categories.
• Directional Over current Relay
• Distance Relay
• Over voltage Relay
• Differential Relay
• Reverse Power Relay
• Others
It is important to notice that the same set of input actuating signals may be utilized to design to relays having different function or application.
For example, the voltage and current input relays can be designed both as a Distance and/ or a Reverse Power relay.
Electromagnetic Attraction Type Relays
The electromagnetic attraction type relays operate on the principle of attraction of an armature by the magnetic force produced by undesirable current or movement of plunger in a solenoid. These relays can be actuated by AC or DC quantities. The various types of these relays are.
- Solenoid Type
- Attracted Armature Type
- Balanced Beam Type

1. Solenoid Type
In this relay, the plunger or iron core moves into a solenoid and the operation of the relay depends on the movement of the plunger.
2. Attracted Armature Type :
This relay operate on the current setting. When currant in the circuit exceeds beyond the limit, the armature gets attracted by the magnetic force produced by the undesirable current. The current rating of the circuit in which relay is connected plays an important role in the operation of the relay.
3. Balanced Beam Type :
In this relay, the armature is fastened to a balanced beam. For normal current, the beam remains horizontal but when current exceeds, the armature gets attracted and beam gets tilted causing the required operation
Induction Type Relays
These relays work on the principle of an electromagnetic induction. The use of these relays is limited to AC quantities. The various types of these relays are,
- Induction Disc Type
- Induction Cup Type
1. Induction Disc Type
In this relay. a metal disc is allowed to rotate between the two electromagnets. The electromagnets are energised by alternating currents. The two types of constructions used for this type are shaded pole type and watthour meter type.
2. Induction Cup Type :
In this relay, electromagnets act as a stator and energised by relay coils. The rotor is metallic cylindrical cup type.
Directional Type Relays
These relays work on the direction of current or power flow in the circuit. The various types of these relays are
- Reverse Current Type
- Reverse Power Type

1. Reverse Current Type :
The relay is actuated when the direction of the current is reversed ur the phase of the current becomes more than the predetermined calve
2. Reverse Power Type :
The relay is actuated when the phase displacement between applied voltage and current attains a specified value.
Relays Based on Timing
In relays the time between instant of relay operation and instant at which tripping of contacts takes place can be controlled. The time is called operation time. Based om this, the time relays are classified as,
- Instantaneous Type
- Definite Time Lag Type
- Inverse Time Lag type
1. Instantaneous Type :
In this type no time is lust between operation of relay and tripping of contacts. No intentional time delay is provided.
2. Definite Time Lag Type :
In this type intentionally a definite time lag is provided between operation of relay and tripping of contact.
3. Inverse Time Lag type :
In this type, the operating time Is approximately Inversely proportional to the magnitude of the actuating quantity.
Distance Type Relays
These relays work on the principle of measurement of voltage to current ratio. In this type, there are two coils. One coil is energized by current while other by voltage.
The torque produced is proportional to the ratio of the two quantities. When the ratio reduces below a set value, the relay operates.
The various types of these relays are,
- Impedance Type
- Reactance Type
- Admittance Type
1. Impedance Type :
In this type, the ratio of voltage to current is nothing but an impedance which is proportional to the distance ol the relay form the fault point.
2. Reactance Type :
The operating time is proportional to the reactance which is proportional to the distance of the relay from the fault point.
3. Admittance Type :
This is also called mho type. In this type, the operating time is proportional to the admittance.
Differential Type Relays
A differential relay operates when the vector difference of two or more electrical quantities in the circuit in which relay is connected. exceeds a set value. These are classified as,
- Current Differential Type
- Voltage Differential Type

1. Current Differential Type :
In this type, the relay compares the current entering a section of the system and the current leaving the section. Under fault condition, these currents are different.
2. Voltage Differential Type :
In this type, two transformers are used. The secondaries of the transformers are connected in series with the relay in such a way that the induced e.m.fs are in opposition under normal conditions.
Under fault condition, primaries carry different currents due to which induced e.m.f.s no longer remain in opposition and the relay operates.
Other Types of Relays
Various other types of relays which are used in practice are,
1. Under voltage, current, power relay :
Under voltage, current, power relay operates when the voltage, current or power in a circuit falls below a set value
2. Over voltage, current, power relay :
Over voltage, current, power relay actuates when the voltage, current or power In a circuit rises above a set value.
3. Thermal Relay :
Thermal Relay actuates due to the heat produced by the current in the relay coil.
4. Rectifier Relay :
In this relay, the quantities to be sensed are rectified and then given to the moving coil unit of the relay.
5. Permanent Magnet Moving Coil Relay :
In Permanent Magnet Moving Coil Relay, the coil carrying current is free to rotate in the magnetic field of a permanent magnet. This is used for DC only.
6. Static Relay :
Static Relay uses some electronic method for sensing the actuating quantity. It uses a stationary circuit.
7. Gas Operated Relay :
The gas pressure is adjusted according to the variations in the actuating quantity. This gas pressure is used to actuate the relay. Buchholz relay is an example of such type of relay.





Comments are closed.