All electrical installations and equipment comply with insulation resistance specifications so they can operate safely.
Whether it involves the connection cables, the sectioning and protection equipment, or the motors and generators, the electrical conductors are insulated using materials with high electrical resistance in order to limit, as much as possible, the flow of current outside the conductors.
The quality of these insulating materials changes over time due to the stresses affecting the equipment.
These changes reduce the electrical resistivity (volume resistivity) of the insulating materials, thus increasing leakage currents that lead to incidents which may be serious in terms of both safety (people and property) and the costs of production stoppages.
In addition to the measurements carried out on new and reconditioned equipment during commissioning, regular insulation testing on installations and equipment helps to avoid such incidents through preventive maintenance.
These tests detect aging and premature deterioration of the insulating properties before they reach a level likely to cause the incidents described above.
Dielectric Testing and Insulation Resistance Measurement
At this stage, it is a good idea to clarify the difference between two types of measurements which are often confused:
- Dielectric Withstand Testing
- Insulation Resistance Measurement
Dielectric Testing (Breakdown Testing)
Dielectric strength testing also called “breakdown testing”, measures an insulation’s ability to withstand a medium duration voltage surge without spark over occurring.
In reality, this voltage surge may be due to lightning or the induction caused by a fault on a power transmission line.
The main purpose of this test is to ensure that the construction rules concerning leakage paths and clearances have been followed.
This test is often performed by applying an AC voltage but can also be done with a DC voltage. This type of measurement requires a hipot tester.
The result obtained is a voltage value usually expressed in kilovolts (kV).
Dielectric testing may be destructive in the event of a fault, depending on the test levels and the available energy in the instrument.
For this reason, it is reserved for type tests on new or reconditioned equipment.
Insulation Resistance Measurement
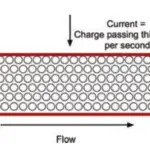
Insulation resistance measurement, however, is non destructive under normal test conditions.
Carried out by applying a DC voltage with a smaller amplitude than for dielectric testing, it yields a result expressed in kW, MW, GW or TW.
This resistance indicates the quality of the insulation between two conductors.
Because it is non-destructive, it is particularly useful for monitoring insulation aging during the operating life of electrical equipment or installations.
This measurement is performed using an insulation tester, also called a megohmmeter.



Comments are closed.