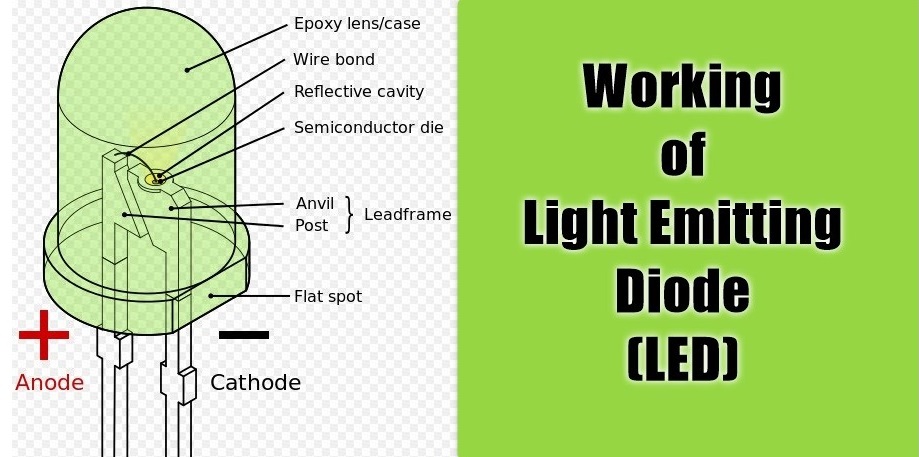
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a diode that gives off visible light when forward biased.
Light-emitting diodes are not made from silicon or germanium but are made by using elements like gallium, phosphorus and arsenic. By varying the quantities of these elements, it is possible to produce light of different wavelengths with colors that include red, green, yellow and blue.
For example, when a LED is manufactured using gallium arsenide, it will produce red light. If the LED is made with gallium phosphide, it will produce a green light.
Working Theory of LED
When light-emitting diode (LED) is forward biased as shown in figure below, the electrons from the n-type material cross the pn junction and recombine with holes in the p-type material.
We know that these free electrons are in the conduction band and at a higher energy level than the holes in the valence band.
When recombination takes place, the recombining electrons release energy in the form of heat and light. In germanium and silicon diodes, almost the entire energy is given up in the form of heat and emitted light is insignificant.
However, in materials like gallium arsenide, the number of photons of light energy is sufficient to produce quite intense visible light.
The schematic symbol for a LED is shown in the above figure. The arrows are shown as pointing away from the diode, indicating that light is being emitted by the device when forward biased.
Although LEDs are available in several colours (red, green, yellow and orange are the most common), the schematic symbol is the same for all LEDs. There is nothing in the symbol to indicate the colour of a particular LED.
This is a graph between radiated light and the forward current of the LED. It is clear from the graph that the intensity of radiated light is directly proportional to the forward current of LED.
LED Voltage and Current
The forward voltage ratings of most LEDs is from 1V to 3V and forward current ratings range from 20 mA to 100 mA.
In order that current through the LED does not exceed the safe value, a resistor Rs is connected in series with it. The input voltage is Vs and the voltage across LED is Vⅆ.




Comments are closed.