In order that protective relay system may perform this function satisfactorily, it should have the following qualities :
- Selectivity
- Speed
- Sensitivity
- Reliability
- Simplicity
- Economy
Selectivity
It is the ability of the protective system to select correctly that part of the system in trouble and disconnect the faulty part without disturbing the rest of the system.
- A well designed and efficient relay system should be selective i.e. it should be able to detect the point at which the fault occurs and cause the opening of the circuit breakers closest to the fault with minimum or no damage to the system.
If a fault occurs at bus-bars on the last zone, then only breakers nearest to the fault viz. 10, 11, 12 and 13 should open. In fact, the opening of any other breaker to clear the fault will lead to a greater part of the system being disconnected.
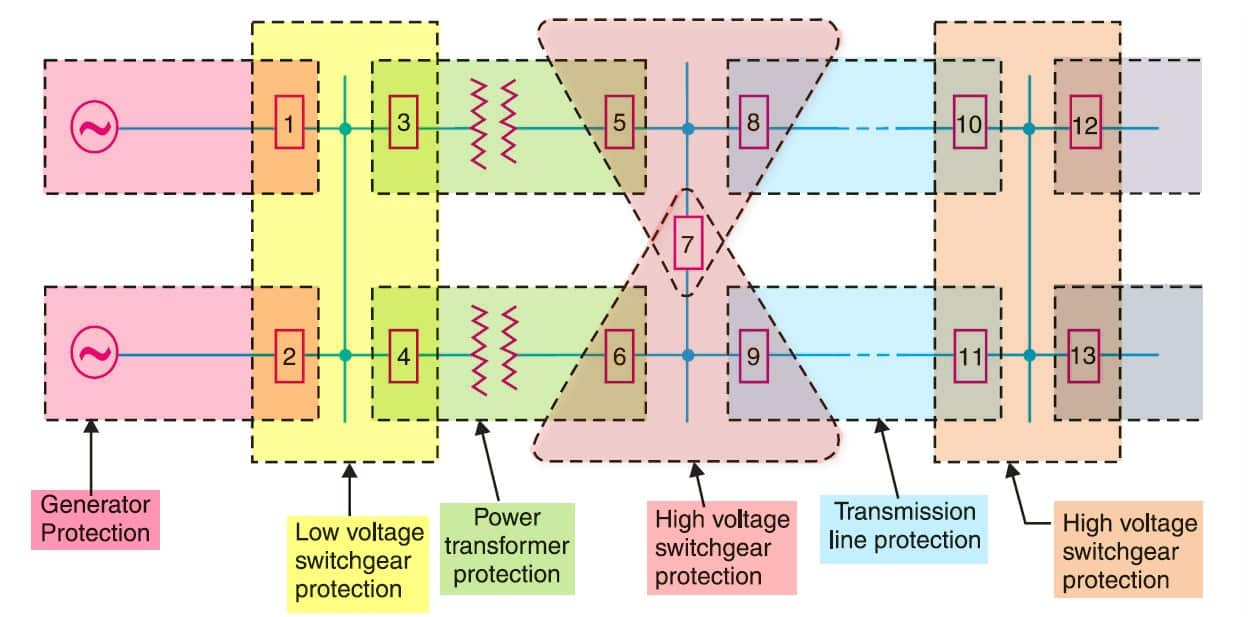 |
| Single Line Diagram of a portion of Power System |
In order to provide selectivity to the system, it is a usual practice to divide the entire system into several protection zones. When a fault occurs in a given zone, then only the circuit breakers within that zone will be opened. This will isolate only the faulty circuit or apparatus, leaving the healthy circuits intact.
The system can be divided into the following protection zones :
- (a) generators
- (b) low-tension switchgear
- (c) transformers
- (d) high-tension switchgear
- (e) transmission lines
It may be seen in the above figure that there is a certain amount of overlap between the adjacent protection zones. For a failure within the region where two adjacent zones overlap, more breakers will be opened than the minimum necessary to disconnect the faulty section.
But if there were no overlap, a failure in the region between zones would not lie in either region and, therefore, no breaker would be opened. For this reason, a certain amount of overlap is provided between the adjacent zones.
Speed
- Electrical apparatus may be damaged if they are made to carry the fault currents for a long time.
- A failure on the system leads to a great reduction in the system voltage. If the faulty section is not disconnected quickly, then the low voltage created by the fault may shut down consumers motors and the generators on the system may become unstable.
- The high-speed relay system decreases the possibility of development of one type of fault into the other more severe type.
Sensitivity
The sensitivity of a relay is a function of the volt-amperes input to the coil of the relay necessary to cause its operation.
- The smaller the volt-ampere input required to cause relay operation, the more sensitive is the relay.
Thus, a 1 VA relay is more sensitive than a 3 VA relay. It is desirable that the relay system should be sensitive so that it operates with low values of volt-ampere input.
Reliability
It is the ability of the relay system to operate under pre-determined conditions. Without reliability, the protection would be rendered largely ineffective and could even become a liability.
That protective-relaying equipment must be reliable is a basic requirement. When protective relaying fails to function properly, the allied mitigation features are largely ineffective.
Therefore, it is essential that protective-relaying equipment be inherently reliable, and that its application, installation, and maintenance be such as to assure that its maximum capabilities will be realized.
Simplicity
The relaying system should be simple so that it can be easily maintained. Reliability is closely related to simplicity. The simpler the protection scheme, the greater will be its reliability.
Economy
The most important factor in the choice of a particular protection scheme is the economic aspect. Sometimes it is economically unjustified to use an ideal scheme of protection and a compromise method has to be adopted.
- As a rule, the protective gear should not cost more than 5% of the total cost.