We all learn Ohms law from our elementary school. This a magical formula that solves most of the problems in electrical engineering.
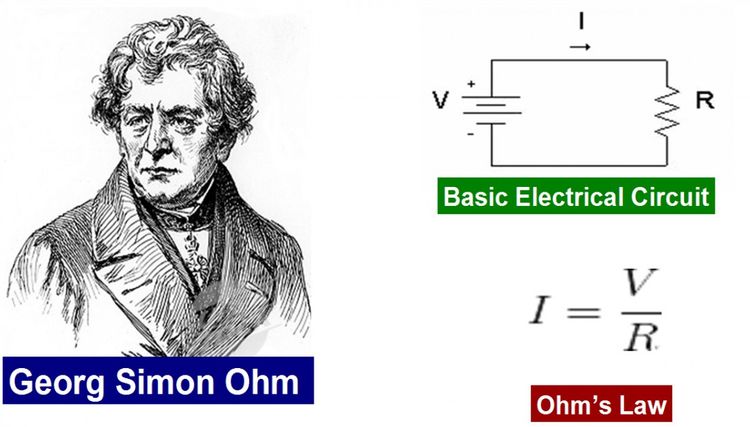
Did you know who is George Simon Ohm and how he created this amazing formula? We will explain it today.
Ohms Law Statement
We all know Ohm’s Law deals with the relationship between voltage and current in an ideal conductor.
This relationship states that: The potential difference (voltage) across an ideal conductor is proportional to the current through it. The constant of proportionality is called the “resistance”, R.
Read the difference between potential difference and Emf.
Ohm’s law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points. Introducing the constant of proportionality, the resistance, one arrives at the usual mathematical equation that describes this relationship:
V is the voltage measured across the conductor in units of volts,
R is the resistance of the conductor in units of ohms.
More specifically, Ohm’s law states that the R in this relation is constant, independent of the current.
Who is Georg Simon Ohm?
Georg Simon Ohm a German physicist investigated the relationship between current and voltage in a resistor and published his experimental results in 1827.
Georg Simon Ohm (16 March 1789 – 6 July 1854) was a German physicist and mathematician. As a school teacher, Ohm began his research with the new electrochemical cell, invented by Italian scientist Alessandro Volta.
Using equipment of his own creation, Ohm found that there is a direct proportionality between the potential difference (voltage) applied across a conductor and the resultant electric current. This relationship is known as Ohm’s law.
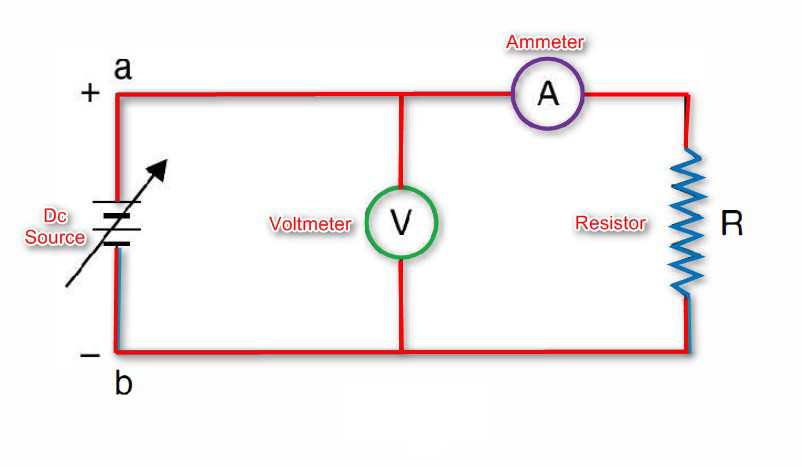
Ohms Experiment
As voltage is increased, the current recorded by the ammeter increases.
For every voltage value, the current is recorded and the corresponding point is plotted on the rectangular graph.
With this, a straight line graph passing through origin is obtained in the first quadrant.
Next the terminals of the variable dc supply are interchanged i.e. a is connected to -ve polarity of DC supply and b is connected to the +ve polarity of DC supply.
Since both the voltmeter and ammeter are moving coil, their individual connection should also be interchanged so that meters can read upscale.
Experiment Results
The experimental results indicate that there is a linear relationship between the current and voltage both in the first and third quadrant.
The slope of the straight line is also the same in both the quadrants which shows that the potential difference across the terminals of the conductor is proportional to the current passing through it i.e. V α I.
Also, it is found that for a constant current in the conductor resistance should be changed proportionally to the potential difference i.e. V α R.
Combining the two proportionalities, we have
V α IR
or V= kIR
where k is a constant of proportionality.
However, the units of voltage, current and resistance are defined so that the value of k = 1. When the current is 1 amp, voltage 1 volt, the resistance is 1 Ω.
1 = k . 1 . 1
Thus the equation becomes
V= IR
The equation explains ohm’s law which is stated as follows :
- The resistances which Ohm considered are linear.
- i.e. the resistances which have linear V-I characteristic.
- Also, these are bilateral
- i.e. irrespective of the direction of flow of current the resistance does not charge.
- Physical condition (Temperature, Pressure etc.) of the conductor remaining constant, the voltage across the terminals of a conductor is proportional to the current flowing through it.





Comments are closed.