Two types of noises occur in an electric motor, one is electrical noise and the other is mechanical noise.
The causes of remedial treatments for both are discussed in this article.
Electrical Noise in Motor
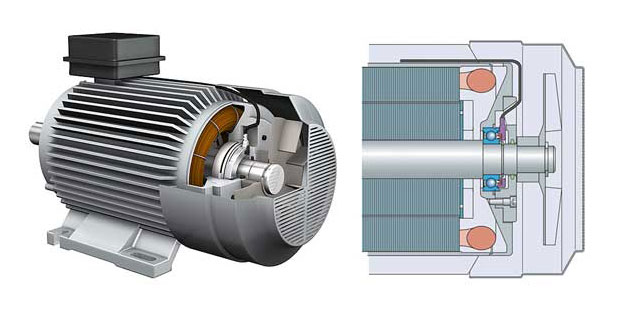
 When a motor runs, the commutator switches the direction of the electricity that flows in the windings. Though the system keeps the motor running, the occasional spark occurs between brushes and commutator at the timing of the commutation. The spark is one of the causes of electrical noise.
When a motor runs, the commutator switches the direction of the electricity that flows in the windings. Though the system keeps the motor running, the occasional spark occurs between brushes and commutator at the timing of the commutation. The spark is one of the causes of electrical noise.
Especially when the motor starts from its stalled position, comparably higher current, or a stall current, flows into the windings. Higher current usually causes higher noise.
Also, a similar noise happens when
- brushes stay unstable on the surface of the commutator,
- the input to the motor is much higher than expected and so on.
Other factors may be insulation created on the commutator surface, which results in the unstable flow of the electricity.
How to Reduce Electrical Noise
An electrical noise could be reduced by fitting a capacitor or a choke coil to a motor terminal part.
However, in order to reduce spark or voltage generated by a spark, these parts are to be fixed to the armature, which enables to eliminate the noise more effectively; fixing parts closer to the armature sometimes contributes to the lower cost policy.
- A disk varistor (D/V), a disk capacitor, a rubber ring resistor (RRR), and/or a chip capacitor to the inside of the motor ⇒Effective for the higher frequency band.
- Electrolytic or ceramic capacitors and/or the choke coil to the outside of the motor ⇒Effective for the lower frequency band.
Types of Electrical Noise
- Line Noise (Conductive Noise)
- Radiation Noise (Radiation Noise)
|
Type
|
Unit
|
Definition
|
Frequency*
|
|
Line Noise
(conductive noise) |
dBμV
|
Noise that travels through
power cables and connection cables. |
0.15 – 30MHz
|
|
Radiation Noise
(radio wave) |
dBμV/m
|
Noise that is radiated from the source to the air
and causes interference in TV and a radio. |
30 – 1000MHz
|
Types of Mechanical Noise
- Brush Noise
- Shaft Sound
- Clearance Sound
- Resonance
- Thrust Sound
- Wind
|
Type
|
Definition
|
|
|
1
|
Brush Noise
|
Frictional sound caused by brushes and commutator.
|
|
2
|
Shaft Sound
|
Frictional sound caused by shaft and bearings.
|
|
3
|
Clearance Sound
|
Specifically grating sound out of 2.
|
|
4
|
Resonance
|
Resonance that occurs at the specific speed range only.
|
|
5
|
Thrust Sound
|
Tapping noise caused by the thrust move of the rotor.
|
|
6
|
Wind
|
Wind that occurs in a motor especially with a built-in cooling fan.
|
Usually, the noise comes from multiple sources. To identify the root cause and specify the frequency, FFT analyzer is commonly used.
Measurement of Mechanical Noise
The calculation will be made to convert to JIS-A characteristics ( dB with RMS ).
- Voltage to be applied to the test motor.
- Speed (r/min) of the test motor.
- Mechanical load onto the test motor shaft.
- Radial load onto the test motor shaft.
- The positioning of the test motor.
- The positioning of the microphone
- Background noise.



Comments are closed.