Did you ever think about what will happen to a transformer on dc supply? In this article, you will learn why the transformer does not work on the DC supply.
You already know that dc supply cannot be used for the transformers. The transformer does not work on the DC supply. The reason why the transformer does not work on dc supply is explained below.
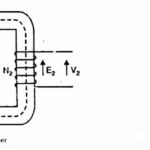
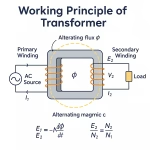
The transformer works on the principle of mutual induction, for which current in one coil must change uniformly. If dc supply is given, the current will not change due to constant supply and the transformer will not work.
Practically winding resistance is very small (Read Practical Transformer). For dc, the inductive reactance XL is zero as dc has no frequency. So the total impedance of the winding is very low for dc.

Thus winding will draw very high current if dc supply is given to it. This may cause the burning of windings due to extra heat generated and may cause permanent damage to the transformer.
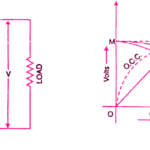
There can be a saturation of the core due to which transformer draws very large current from the supply when connected to dc.
If the primary of a transformer is connected to dc supply, the primary will draw steady current and hence produce constant flux. Consequently, no back e.m.f will be produced. The primary winding will draw excessive current due to the low resistance of the primary.
The result is that the primary will overheat and burn out or the fuses will blow. Care must be taken not to connect the primary of a transformer across the d.c. supply.
Thus dc supply should not be connected to the transformers.