It may be noted that this method is applicable to those machines in which flux is practically constant at all loads e.g., shunt and compound machines.
Steps to find the Efficiency
- Determination of hot resistances of windings
- Determination of constant losses
Determination of hot resistances of windings
Since these resistances are measured when the machine is cold, they must be converted to values corresponding to the temperature at which the machine would work on full-load.
Determination of constant losses
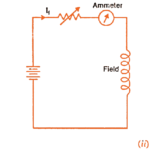
The machine is run as a motor on no-load with supply voltage adjusted to the rated voltage i.e. voltage stamped on the nameplate.
The speed of the motor is adjusted to the rated speed with the help of field regulator R as shown in figure (for more details please visit speed control of dc shunt motor).
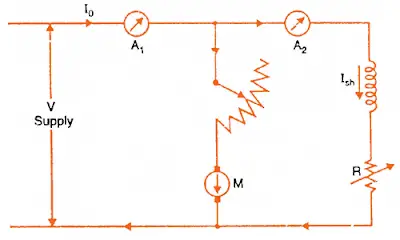
Since the output of the motor is zero, the no-load input power to the armature supplies
- iron losses in the core
- friction loss
- windage loss
- armature Cu loss [ Iao2Ra or (Io – Ish)2Ra .
Since constant losses are known, the efficiency of the machine at any other load can be determined. Suppose it is desired to determine the efficiency of the machine at load current I. Then,
Efficiency when running as a motor
Efficiency when running as a generator
Advantages of Swinburne’s test
- The power required to carry out the test is small because it is a no-load test. Therefore, this method is quite economical.
- The efficiency can be determined at any load because constant losses are known.
- This test is very convenient.
Disadvantages of Swinburne’s test
- It does not take into account the stray load losses that occur when the machine is loaded.
- This test does not enable us to check the performance of the machine on full-load. For example, it does not indicate whether commutation on full load is satisfactory and whether the temperature rise is within the specified limits.
- This test does not give quite accurate efficiency of the machine. It is because iron losses under actual load are greater than those measured. This is mainly due to the armature reaction distorting the field.


Comments are closed.