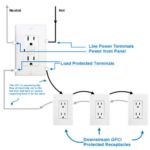
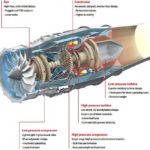
In this article, you will learn the importance of protection in the modern power system and why we need power system protection.
It is fair to say that without discriminative protection it would be impossible to operate a modern power system.
The protection is needed to remove as speedily as possible any element of the power system in which a fault has developed.
So long as the fault remains connected, the whole system may be in danger from three main effects of the fault, namely:
- it is likely to cause the individual generators in a power station or groups of generators in different stations, to lose synchronism and fall out of step with a consequent splitting of the system
- risk of damage to the affected plant
- risk of damage to the healthy plant.
It is the function of the protective equipment, in association with the circuit breakers, to avert these effects. This is wholly true of large HV networks, or transmission systems.
In the lower-voltage distribution systems, the primary function of protection is to maintain continuity of supply. This, in effect, is achieved incidentally in transmission systems if the protection operates correctly to avert the effects mentioned above; indeed it must be so because the ultimate aim is to provide 100 percent continuity of supply.
Obviously, this aim cannot be achieved by the protection alone. In addition, the power system and the distribution networks must be so designed that there are duplicate or multiple outlets from power sources to load centers (adequate generation may be taken for granted), and at least two sources of supply (feeders) to each distributing station.
There are certain conventional ways of ensuring alternative supplies, as we shall see, but if full advantage is to be taken of their provision (always a costly matter) the protection must be highly selective in its functioning.
For this, it must possess the quality known as discrimination, by virtue of which it is able to select and to disconnect only the faulty element in the power system, leaving all others in normal operation so far as that may be possible.
With a few exceptions, the detection and tripping of a faulty circuit is a very simple matter; the art and the skill lie in selecting the faulty one, bearing in mind that many circuits – generators, transformers, feeders – are usually affected, and in much the same way by a given fault. This accounts for the multiplicity of relay types and systems in use.