Neutral grounding, also known as neutral earthing, involves connecting the neutral point of the supply system, rotating machines, or transformers to the earth directly or through certain circuit elements. In electrical power systems, a three-phase system can be operated in two different ways: ungrounded or isolated neutral system and grounded or earthed neutral system.
- Ungrounded or Isolated Neutral System: In an ungrounded system, the neutral point of the power system is not connected to the earth. It is isolated from the ground. This configuration is typically used in some industrial and commercial applications where continuity of power supply is crucial, and any fault to ground should not disrupt the system. However, ungrounded systems have limited fault detection capabilities, and if a single line-to-ground fault occurs, it may go undetected until a second fault occurs, leading to a phase-to-phase fault.
- Grounded or Earthed Neutral System: In a grounded neutral system, the neutral point of the power system is intentionally connected to the earth, either directly or through some circuit elements such as resistors, grounding transformers, or neutral grounding devices. This configuration is commonly employed in most residential, commercial, and industrial power distribution systems. Grounding the neutral offers several advantages, including enhanced safety, improved fault detection, and better system stability.
Grounding the neutral provides a reference point for voltage levels and helps limit voltage rise during faults. It allows fault currents to flow, facilitating the detection of faults by protective devices like circuit breakers and protective relays. Additionally, neutral grounding helps prevent the occurrence of high voltages between phases and reduces the risk of electric shock to personnel.
Neutral grounding, also known as neutral earthing, is essential in electrical power systems for several reasons:
In the power system, grounding or earthing means connecting the frame of electrical equipment (non-current carrying part) or some electrical part of the system (e.g. neutral point in a star-connected system, one conductor of the secondary of a transformer, etc.) to earth i.e. soil. This connection to earth may be through a conductor or some other circuit element (e.g. a resistor, a circuit breaker, etc.) depending upon the situation.
Advantages of Grounding or Earthing
Grounding or earthing offers two principal advantages. First, it provides protection to the power system. For example, if the neutral point of a star-connected system is grounded through a circuit breaker and phase to earth fault occurs on any one line, a large fault current will flow through the circuit breaker. The circuit breaker will open to isolate the faulty line. This protects the power system from the harmful effects of the fault.
Secondly, earthing of electrical equipment (e.g. domestic appliances, hand-held tools, industrial motors, etc.) ensures the safety of the persons handling the equipment. For example, if insulation fails, there will be a direct contact of the live conductor with the metallic part (i.e.frame) of the equipment. Any person in contact with the metallic part of this equipment will be subjected to a dangerous electrical shock which can be fatal.
Importance of Neutral Grounding
Neutral grounding specifically is important for several reasons:
- Safety: Neutral grounding helps protect both equipment and personnel from dangerous voltage levels. When a fault occurs in an electrical system, such as a short circuit between a phase conductor and ground, the grounded neutral limits the voltage rise and prevents the development of high voltages that could pose a risk of electric shock or damage to equipment. By providing a low-impedance path to ground, it ensures that fault currents are quickly detected and interrupted by protective devices like circuit breakers.
- Fault Detection: Neutral grounding facilitates the detection of faults in electrical systems. When a fault occurs, such as a line-to-ground fault, the grounded neutral allows fault currents to flow, creating an unbalance in the system. Protective relays can detect this unbalance and initiate appropriate actions to isolate the faulted section, ensuring the continuity of power supply to the rest of the system.
- System Stability: Neutral grounding contributes to the stability of electrical power systems. By providing a reference point for voltage levels, it helps maintain balanced voltages between the phases. Unbalanced voltages can lead to various issues such as increased stress on equipment, inefficient operation of motors, and poor power quality. Neutral grounding helps mitigate these problems by limiting the voltage imbalances and allowing for proper voltage regulation.
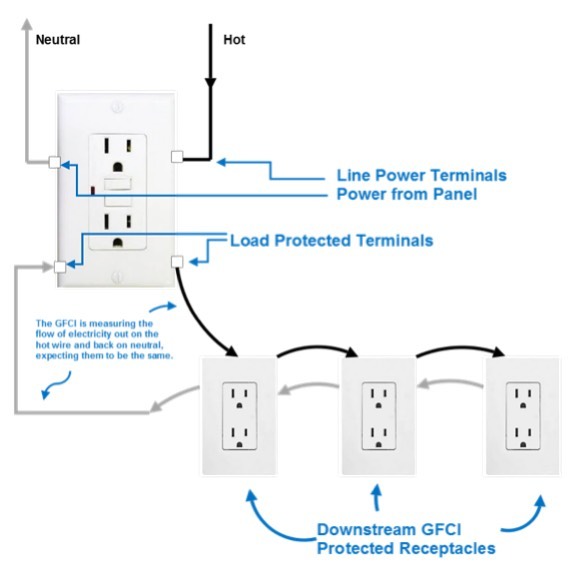
- Ground Fault Protection: In systems where sensitive equipment is connected, such as hospitals or data centers, neutral grounding is crucial for effective ground fault protection. Ground fault current detection devices, such as ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs), rely on the presence of a grounded neutral to sense and interrupt excessive current flow to ground. This protects against the risk of electric shock and fire hazards.
- Transient and Surge Protection: Neutral grounding helps mitigate transient overvoltages and voltage surges in electrical systems. Transients and surges can occur due to lightning strikes, switching operations, or other external factors. By providing a low-impedance path to ground, neutral grounding helps divert these high-energy disturbances away from sensitive equipment, reducing the risk of damage and ensuring the system’s reliability.
Conclusion
Overall, neutral grounding plays a critical role in electrical power systems by promoting safety, enabling fault detection, ensuring system stability, facilitating ground fault protection, and guarding against transient and surge events.




Comments are closed.