It is necessary to adjust the speed of a DC shunt motor to meet specific requirements. This deliberate adjustment is known as speed control of DC shunt motor.
Mainly there are three methods used to control the speed of DC shunt motors just like in the speed control of DC series motor.
- Flux Control Method
- Armature Control Method
- Voltage Control Method
- Multiple Voltage Control
- Ward Leonard System
Flux Control Method
The first method for speed control of DC shunt motor is flux control method.
We know that, speed is inversely proportional to flux. So by varying flux, we can change the speed of the motor.
N ∝ Eb/
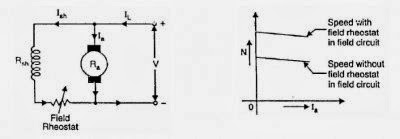
In this method, a variable resistance (known as shunt field rheostat) is placed in series with shunt field winding.
The field rheostat reduces the shunt field current Ish. So the flux also gets reduced. There the speed can be raised above normal speed as shown in the figure.
Generally, this method permits to increase the speed in the ratio 3:1. Wider speed ranges tend to produce instability and poor commutation.
Armature control method
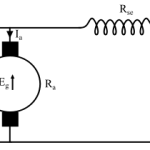
The concept behind this method is that the back emf and the speed of the motor can be changed by varying the voltage across armature V.

A variable resistance Rc ( controller resistance ) is placed in series with the armature as shown in the figure.
Since Rc is introduced, the voltage drop is increased and hence back emf [Eb = V – IaRa] decreases.
Also N ∝Eb, therefore speed decreases.
The highest speed is when Rc=0 i.e, normal speed. Hence, this method can only provide speeds below the normal speed.
Voltage control method
There are some disadvantages for flux control method and armature control method in the speed control of dc shunt motor such as poor speed regulation and poor efficiency. In order to overcome these problems Voltage control method is used.
In this method, the voltage source supplying the field current is different from that which supplies the armature. This method is used for large size motors since it is very expensive.
1. Multiple voltage control
In this method, the shunt field of the motor is connected permanently across a-fixed voltage source.
The armature can be connected across several different voltages through a suitable switchgear. In this way, voltage applied across the armature can be changed.
The speed will be approximately proportional to the voltage applied across the armature. Intermediate speeds can be obtained by means of a shunt field regulator.
2. Ward Leonard system
Ward Leonard drive system, was a widely used speed control system introduced by Harry Ward Leonard in 1891.
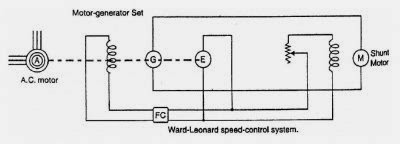
In this method of speed control of DC shunt motor, adjustable voltage is obtained from the system shown in below diagram.
The armature of the shunt motor M (whose speed is to be controlled) is connected directly to a DC generator G driven by a constant-speed AC motor A.
The field of the shunt motor is supplied from a constant-voltage exciter E. The field of the generator G is also supplied from the exciter E.
The voltage of the generator G can be varied by means of its field regulator. By reversing the field current of generator G by controller Fc, the voltage applied to the motor may be reversed.
Sometimes, a field regulator is included in the field circuit of shunt motor M for additional speed adjustment. With this method, the motor may be operated at any speed upto its maximum speed.
Summary
Here’s a table summarizing the methods of speed control of DC shunt motors:
| Method | Description | Key Points |
|---|---|---|
| Flux Control Method | Speed is inversely proportional to flux. A variable resistance (shunt field rheostat) is placed in series with the shunt field winding to vary the flux and thus the speed. | – Reduces shunt field current (Ish), thus reducing flux. – Can increase speed above normal (ratio 3:1). |
| Armature Control Method | The back EMF and speed of the motor can be changed by varying the voltage across the armature (V). A variable resistance (Rc) is placed in series with the armature to achieve this. | – Increases voltage drop, decreasing back EMF (Eb = V – IaRa). – Speed decreases as Rc increases. |
| Voltage Control Method | This method overcomes disadvantages of flux and armature control methods, such as poor speed regulation and efficiency. The voltage source for the field current is different from that of the armature. | – Used for large size motors due to expense. |
| Multiple Voltage Control | The shunt field is connected to a fixed voltage source, and the armature is connected across different voltages via switchgear to change the applied voltage. Speed is proportional to the armature voltage. | – Speed is approximately proportional to armature voltage. – Intermediate speeds obtained using a shunt field regulator. |
| Ward Leonard System | A DC generator, driven by a constant-speed AC motor, supplies the adjustable voltage. The shunt motor’s armature is connected to the generator, and its field is supplied by a constant-voltage exciter. Generator voltage is varied by a field regulator. | – Reversing the generator field current can reverse motor voltage. – Additional speed adjustment via shunt motor field regulator. |